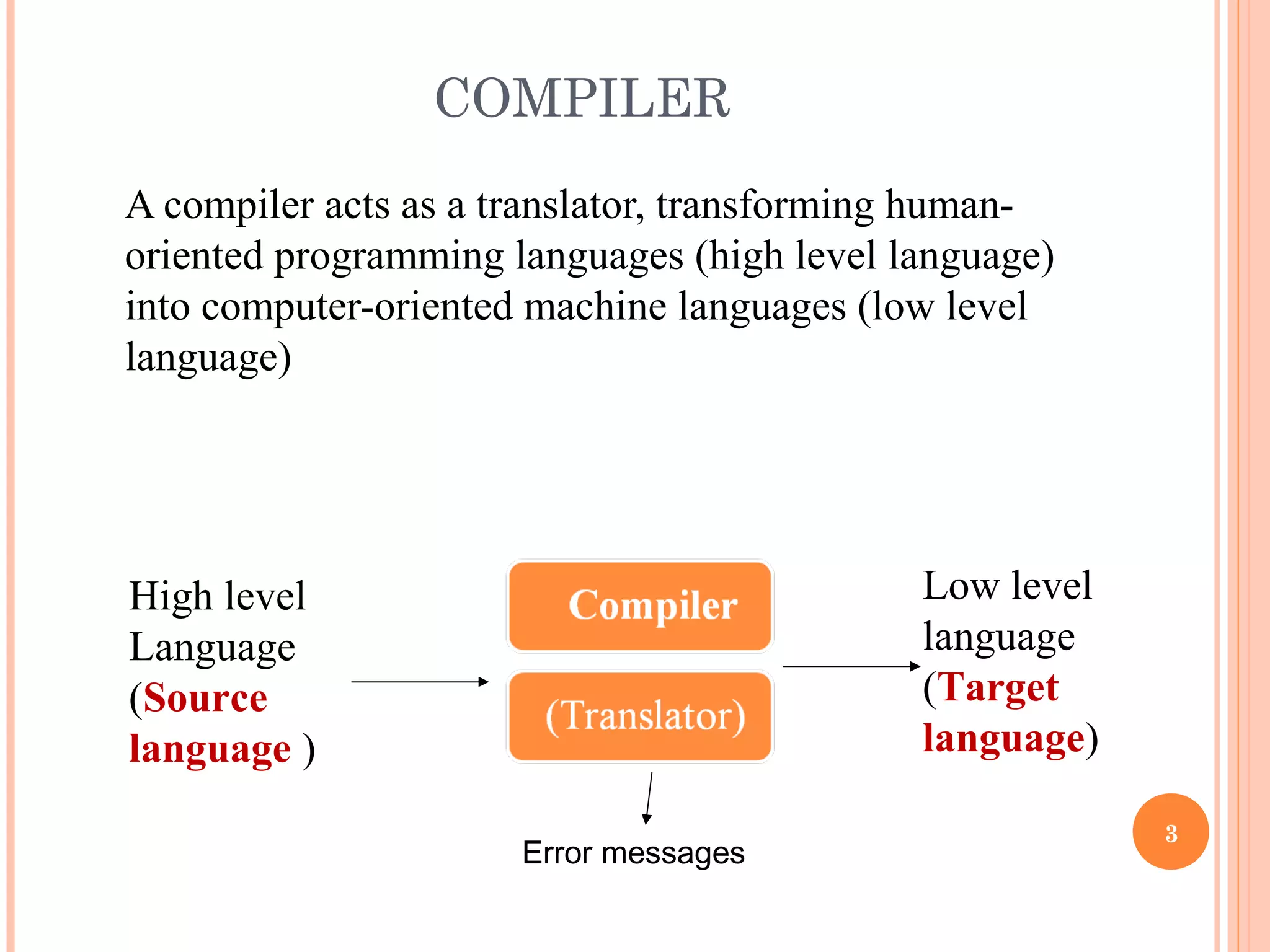
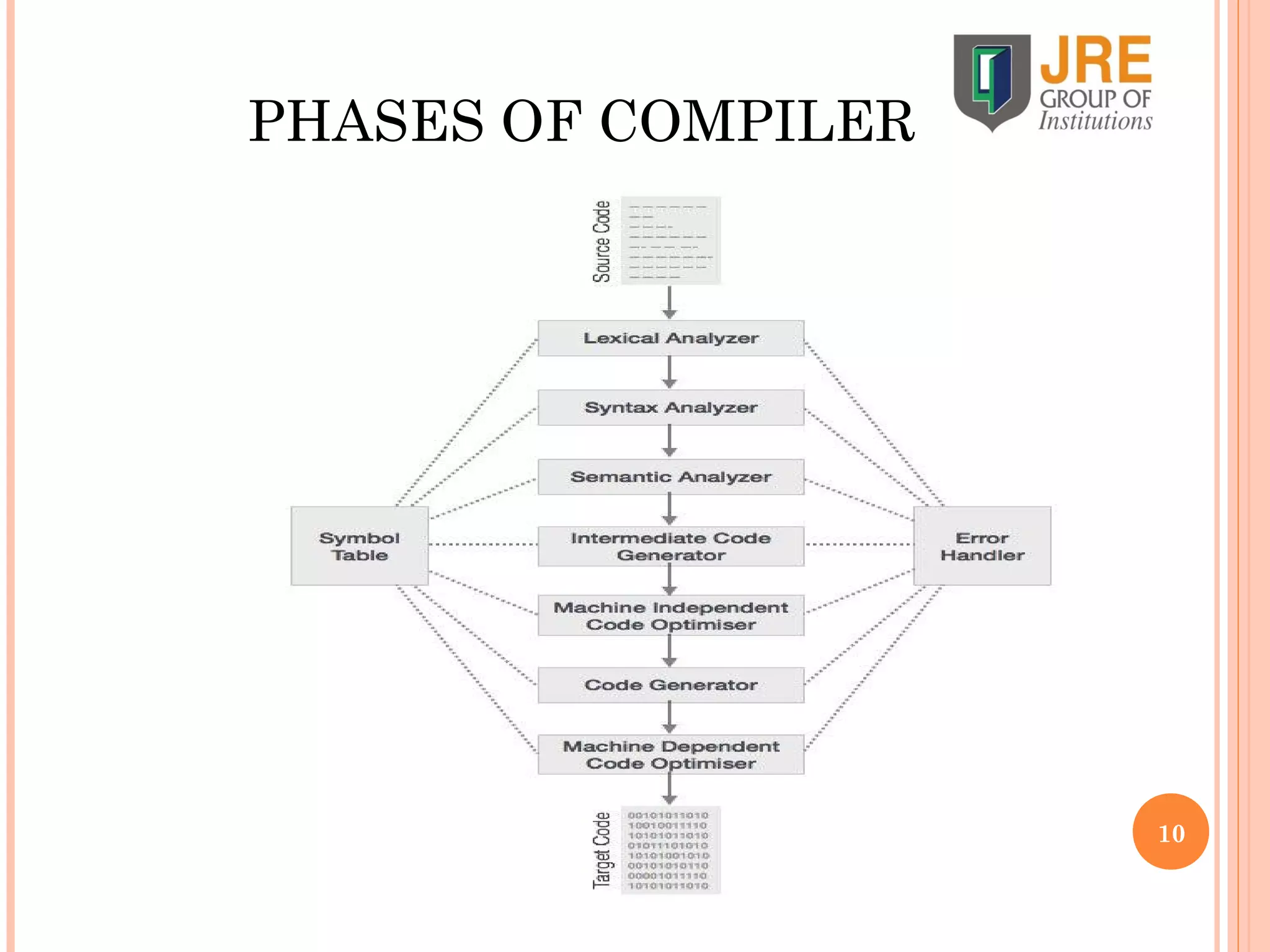
A compiler acts as a translator that converts programs written in high-level human-readable languages into machine-readable low-level languages. Compilers are needed because computers can only understand machine languages, not human languages. A compiler performs analysis and synthesis on a program, breaking the process into phases like scanning, parsing, code generation, and optimization to translate the high-level code into an executable form. The phases include lexical analysis, syntax analysis, semantic analysis, code generation, and optimization.






![THE STRUCTURE OF A
COMPILER
11
Scanner
[Lexical Analyzer]
Parser
[Syntax Analyzer]
Semantic Process
[Semantic analyzer]
Code Generator
[Intermediate Code Generator]
Code Optimizer
Tokens
Parse
tree
Abstract Syntax Tree w/
Attributes
Non-optimized Intermediate
Code
Optimized Intermediate Code
Code Optimizer
Target machine code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalcompilerppt1-180626131756/75/basics-of-compiler-design-11-2048.jpg)


