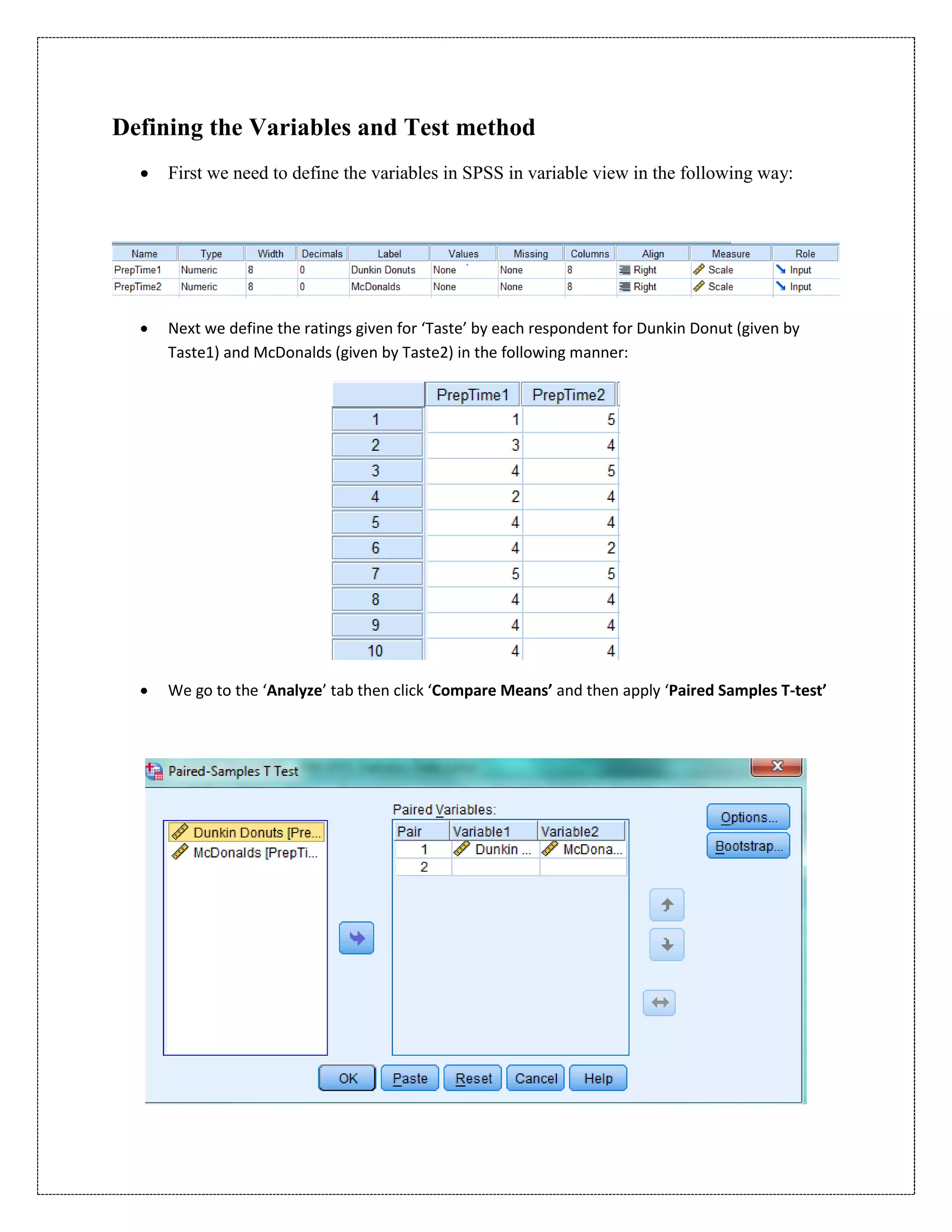
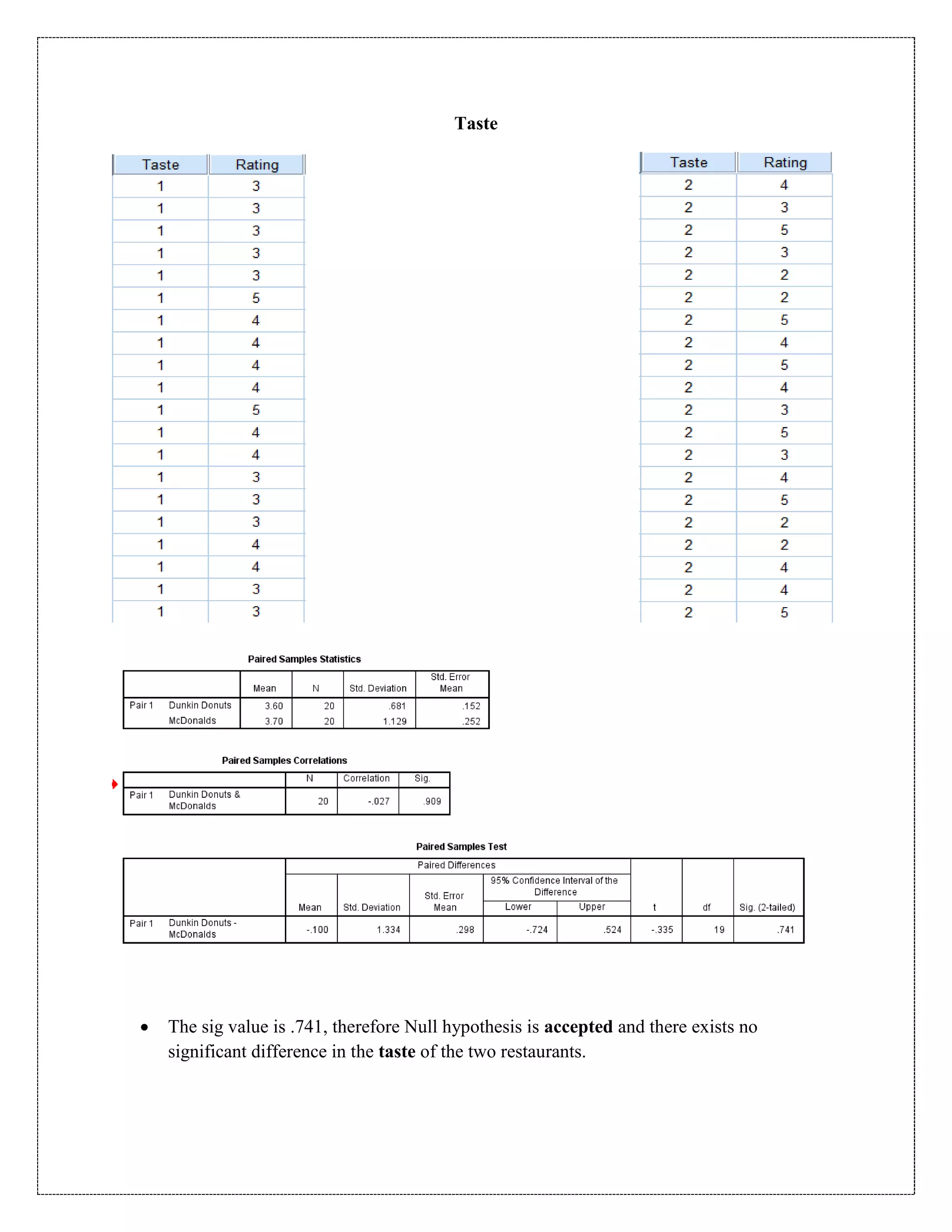
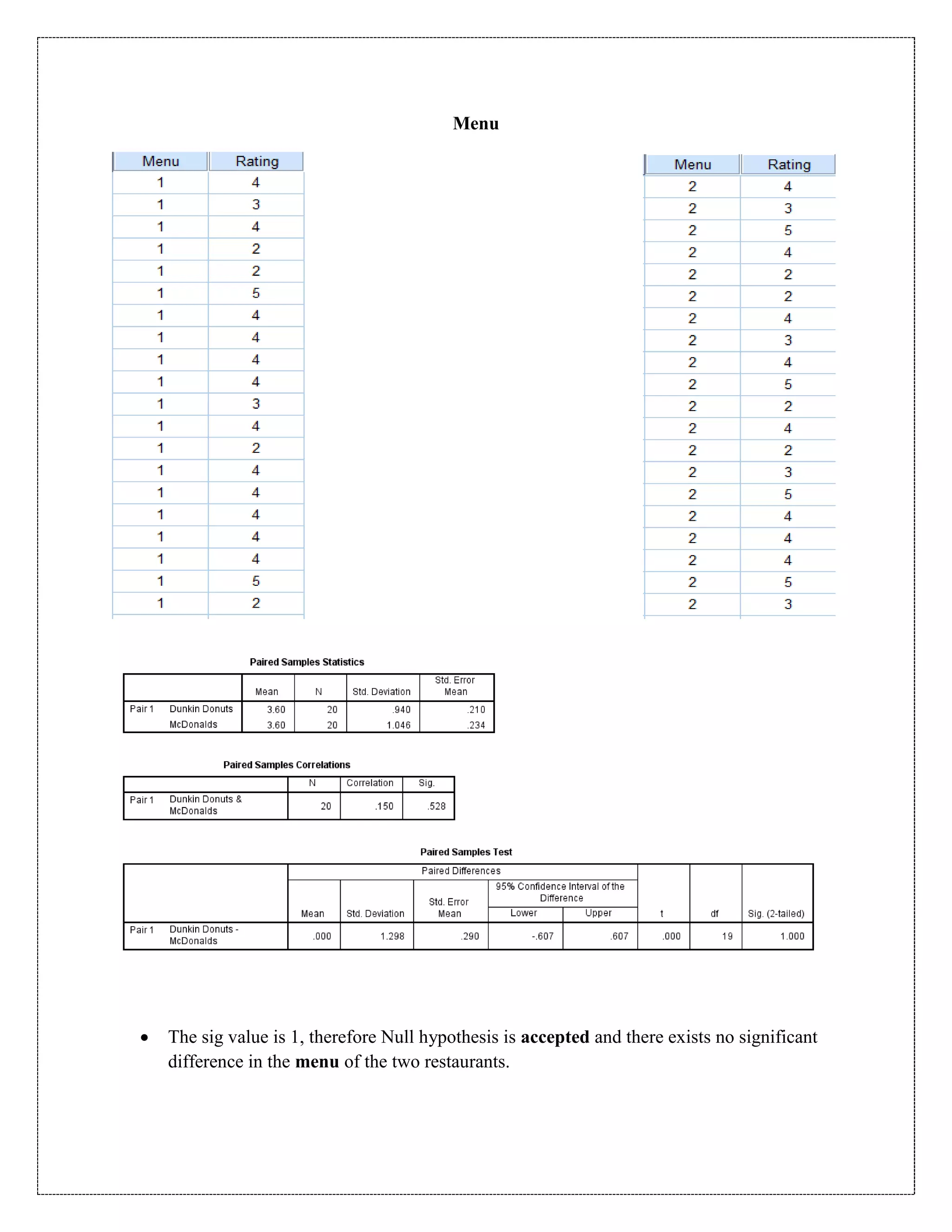
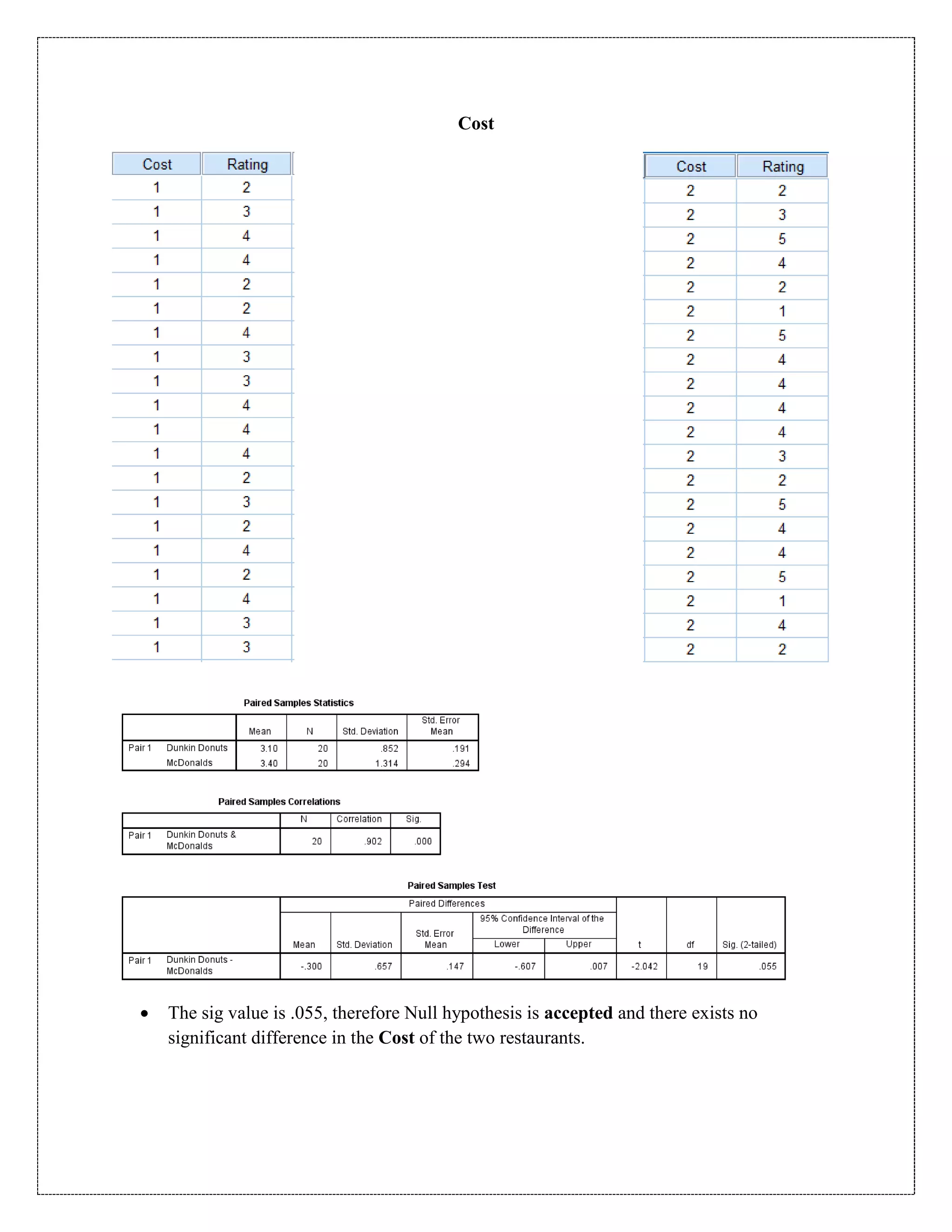
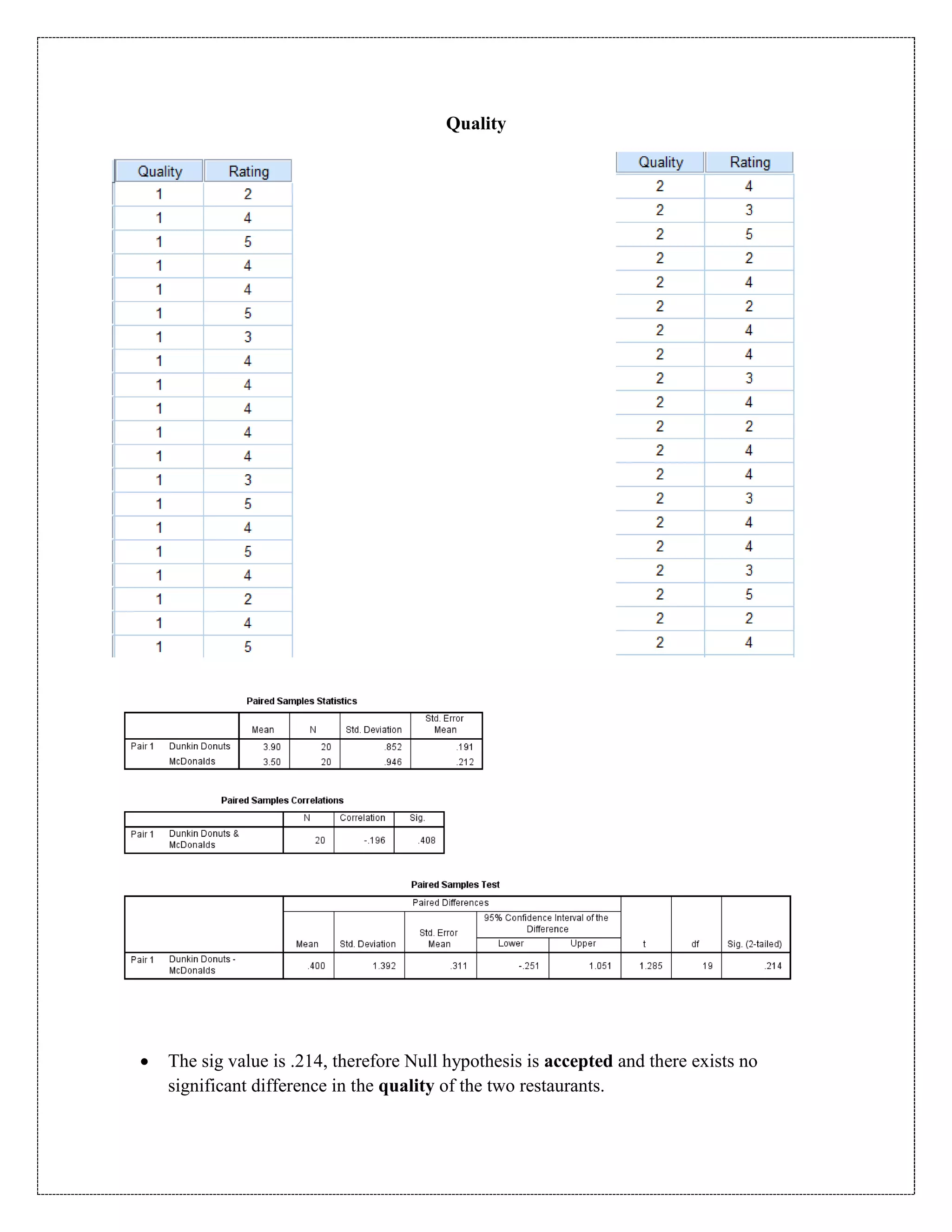
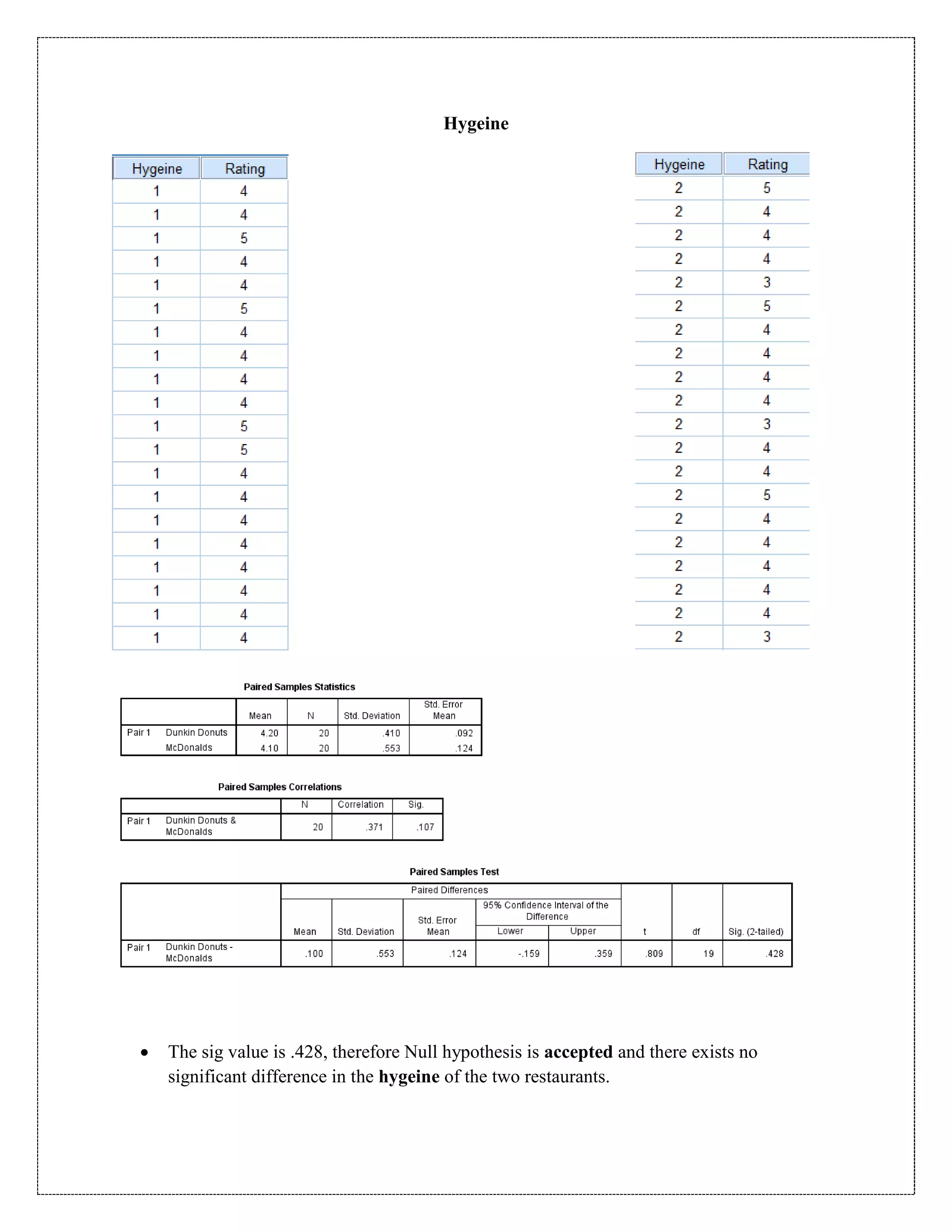
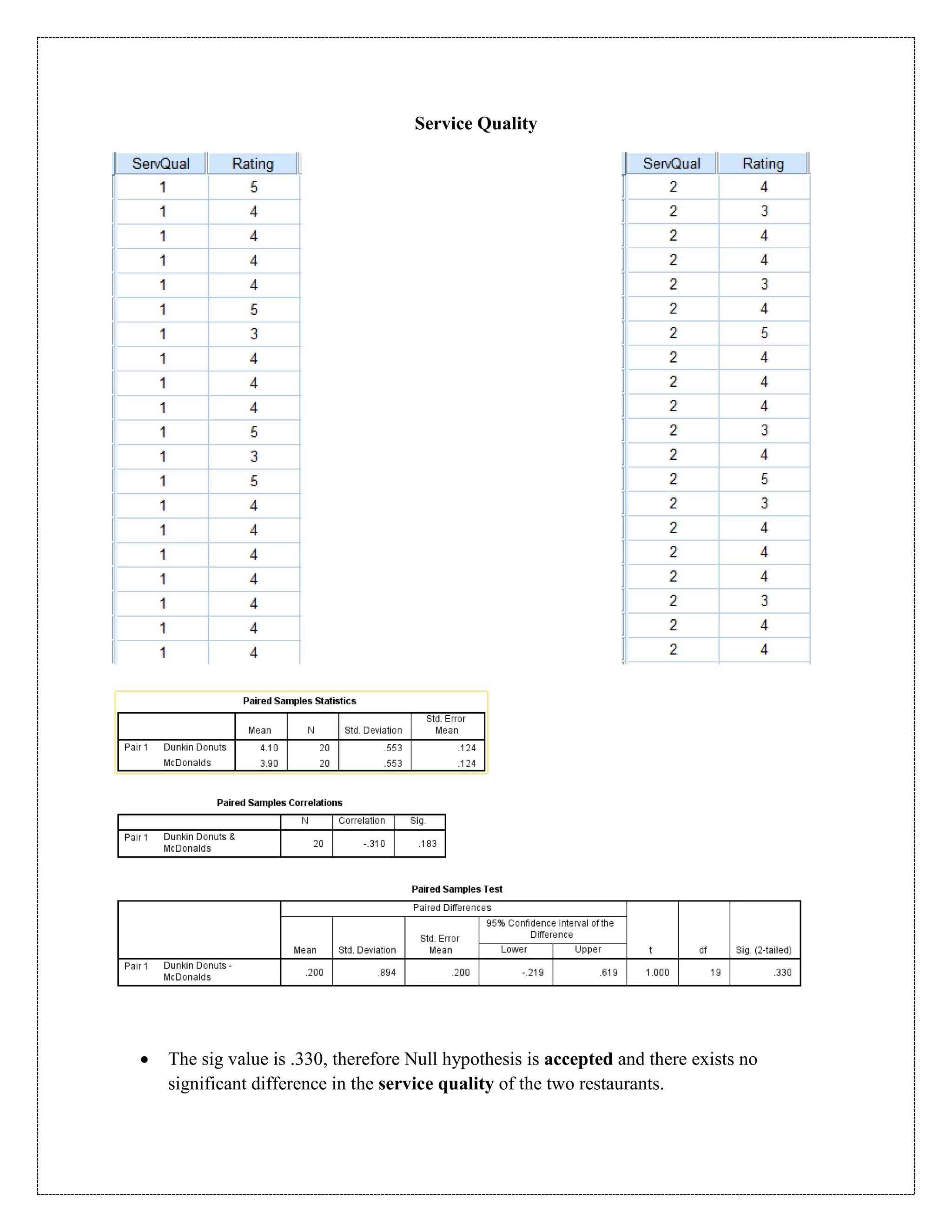
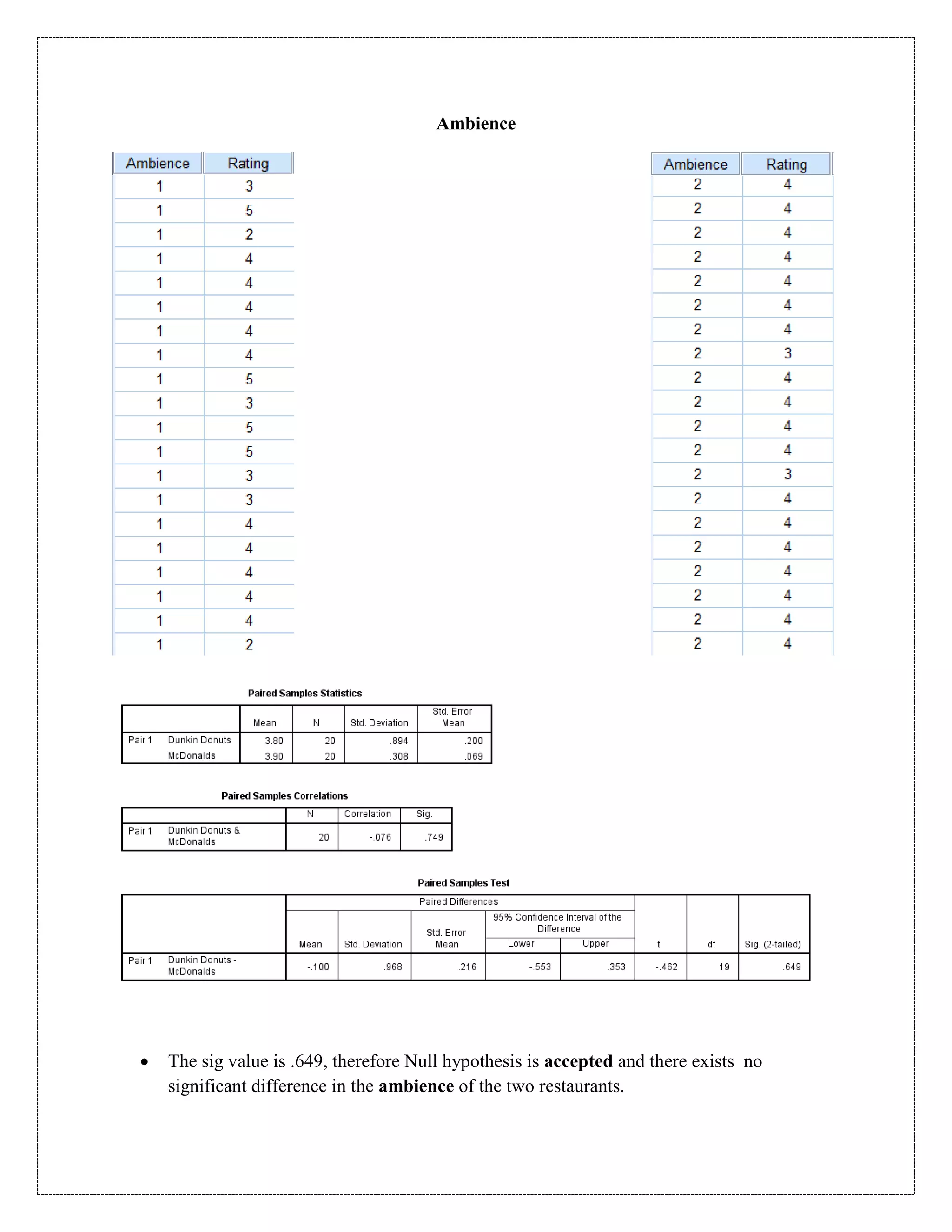
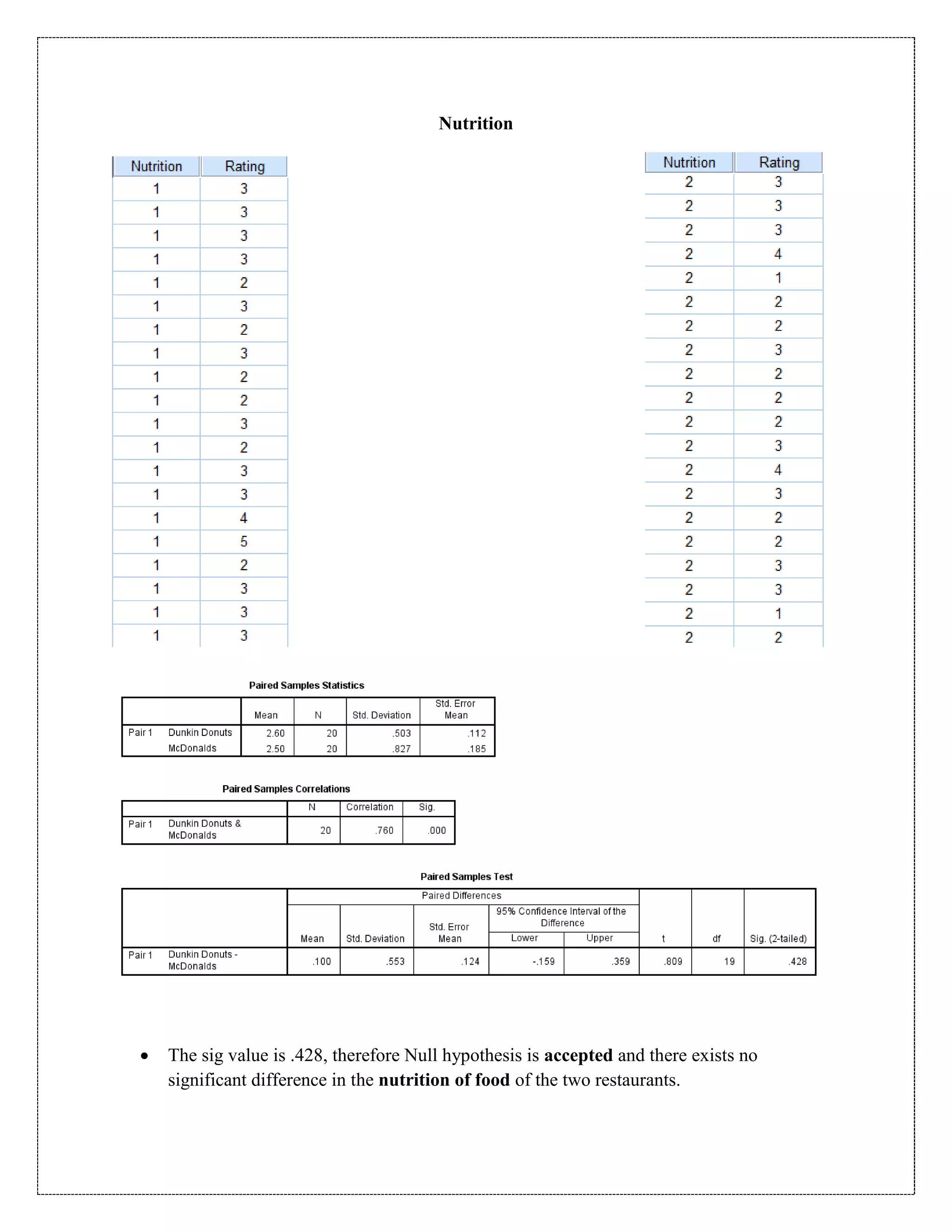
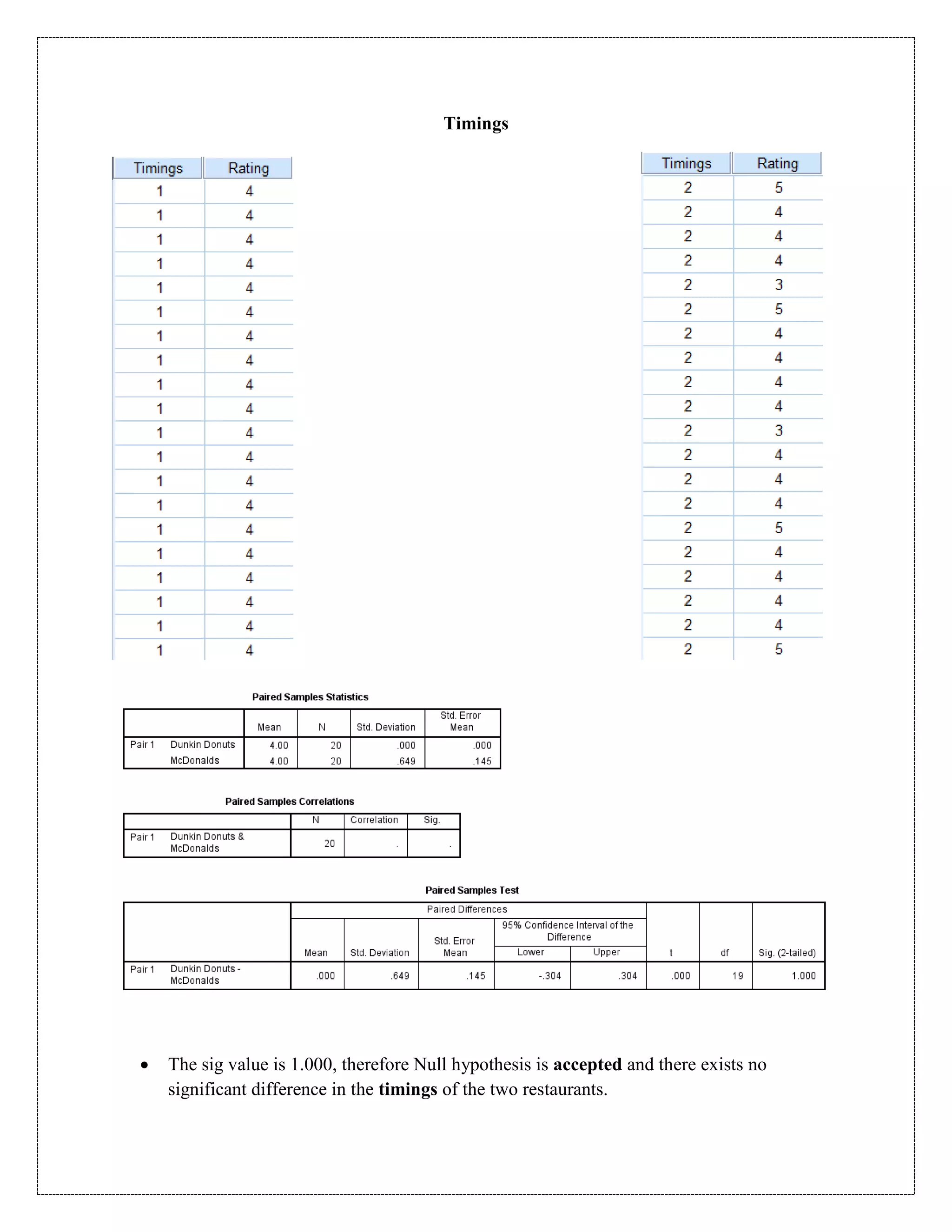
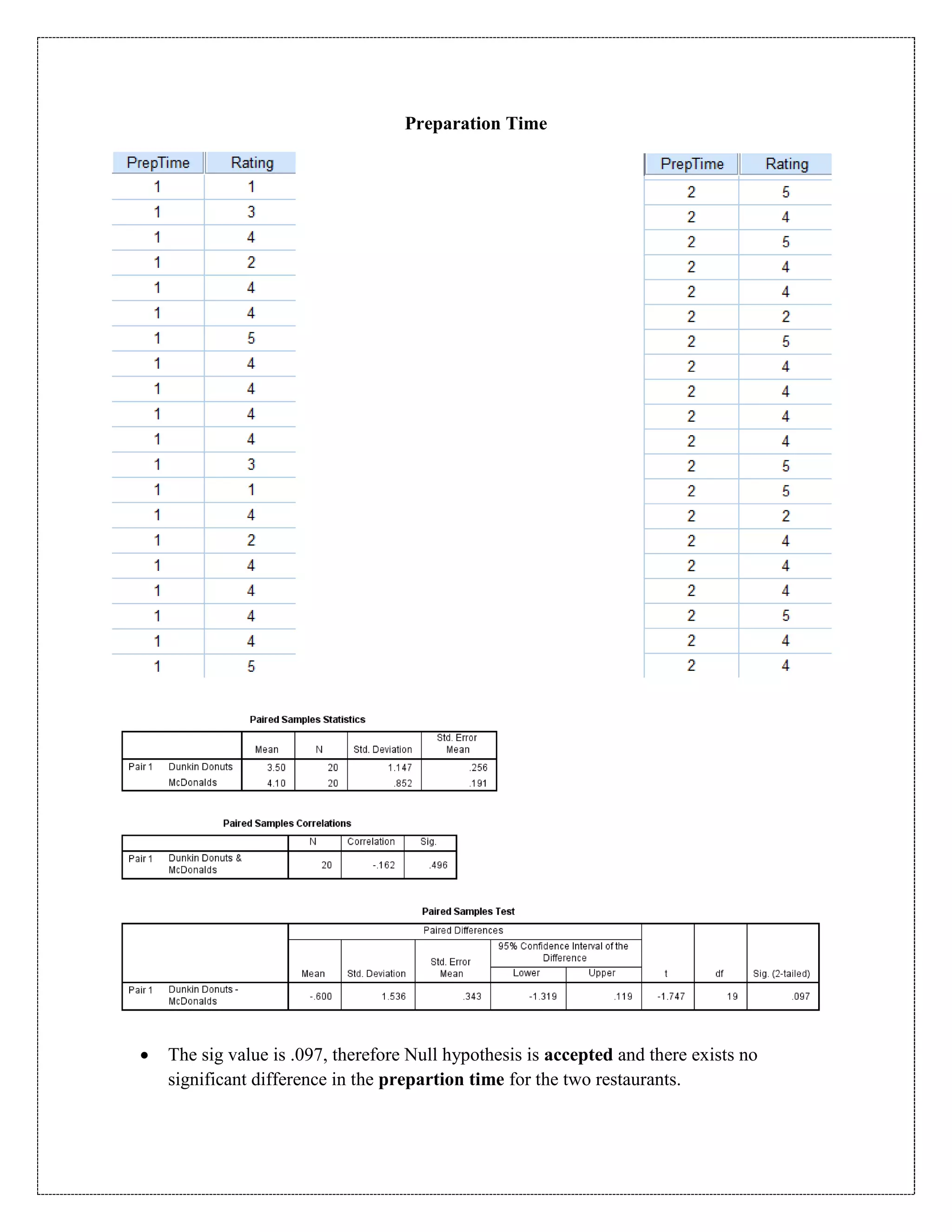
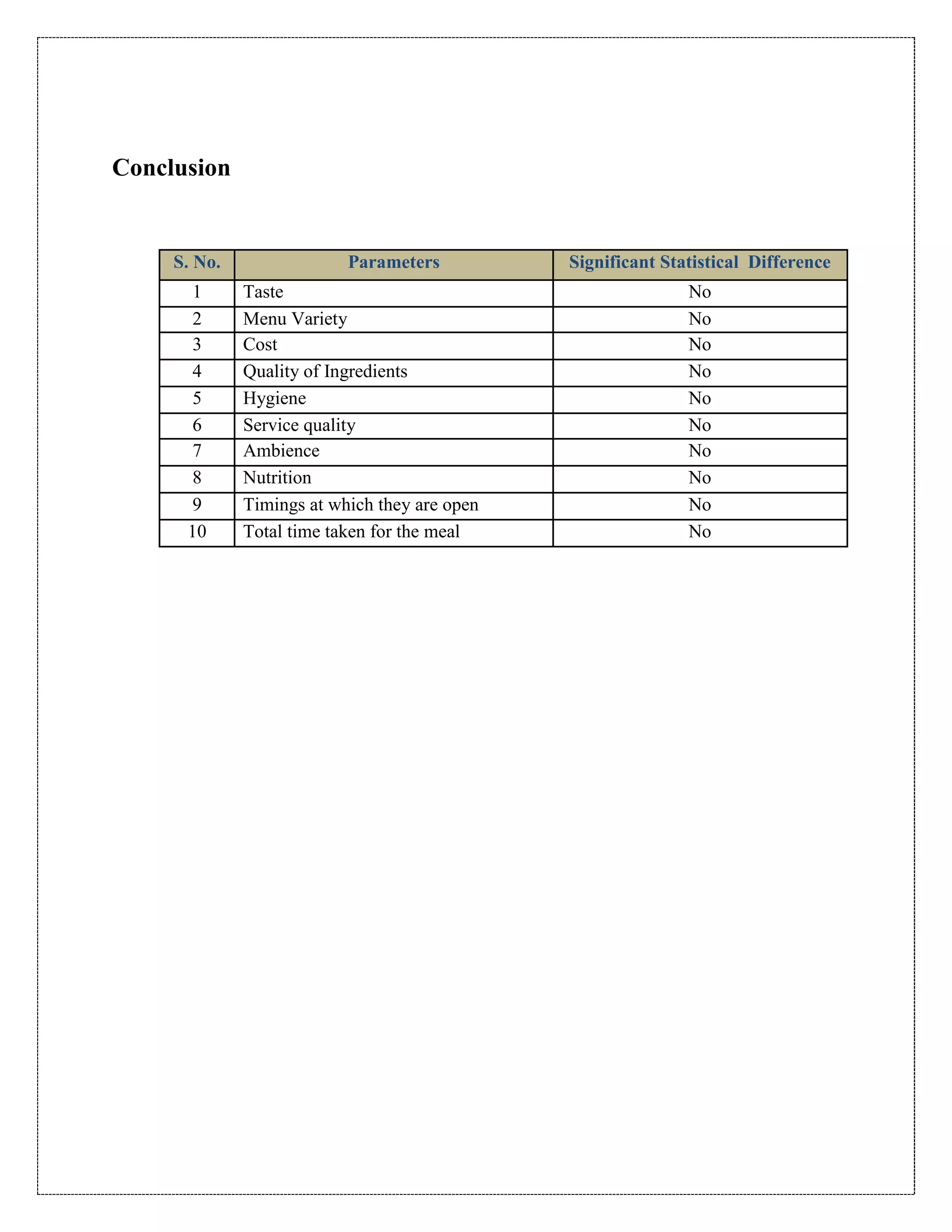
The document describes a study that used a paired t-test to compare various parameters of food quality and customer experience between Dunkin Donuts and McDonald's in Cyber City, Gurgaon. A survey was administered to employees who frequented both locations, rating 10 parameters on a scale of 1 to 5. SPSS analysis found no statistically significant differences between the restaurants on any of the 10 parameters, including taste, menu variety, cost, quality, hygiene, service, ambience, nutrition, operating hours, and time to receive food. The null hypothesis of no difference between restaurants was accepted for all comparisons at the 5% significance level.