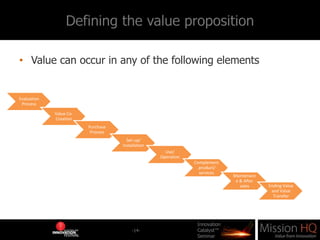
This document outlines a seminar on business model innovation presented by Marcus Tarrant of Mission HQ, detailing a framework for designing business models. It describes the importance of understanding value propositions, capabilities, partnerships, activities, costs, relationships, channels, revenue, and customer segmentation in business model design. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of business model design in facilitating planning and optimizing business concepts.