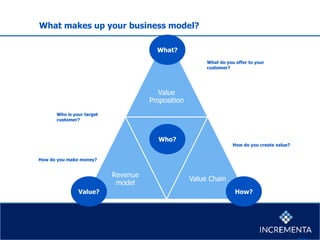
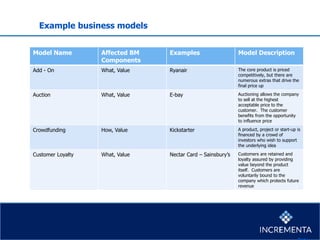
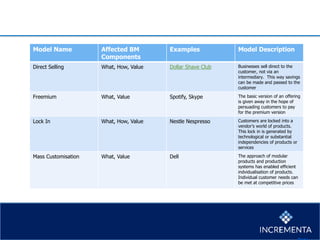
This document discusses different types of innovation including business model innovation, process innovation, product innovation, and service innovation. It then provides examples of how a business can generate revenue from a cow, including selling milk, cheese, yogurt, meat, and leather. The key components of a business model are defined as the value proposition, revenue model, customer segments, key resources and processes, and cost structure and profit potential. Barriers to business model innovation and example business models are also outlined.