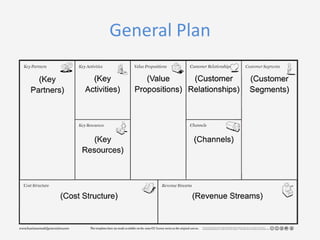
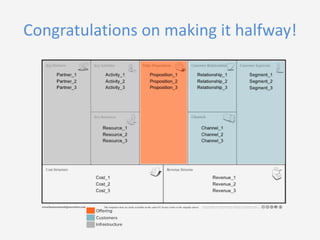
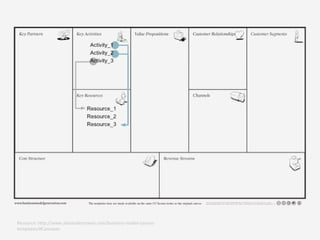
This document provides an overview of the Business Model Canvas tool for entrepreneurs. It outlines the 9 steps to complete a Business Model Canvas: 1) Customer Segments, 2) Value Propositions, 3) Channels, 4) Customer Relationships, 5) Revenue Streams, 6) Key Resources, 7) Key Activities, 8) Key Partnerships, and 9) Cost Structure. For each step, it provides brief explanations and questions to consider when evaluating that particular component of the business model. It also includes links to online tools that can be used to create a Business Model Canvas.