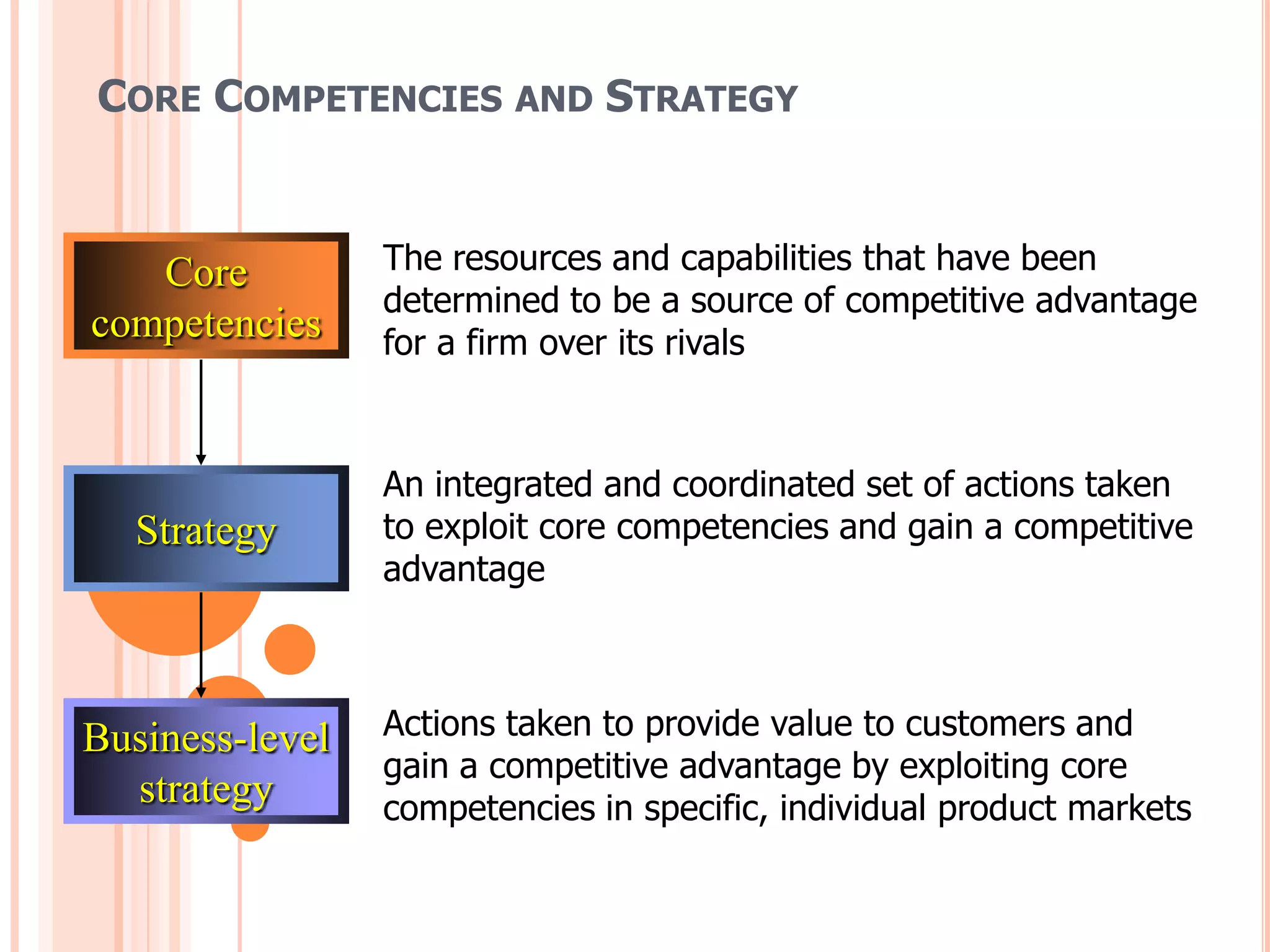
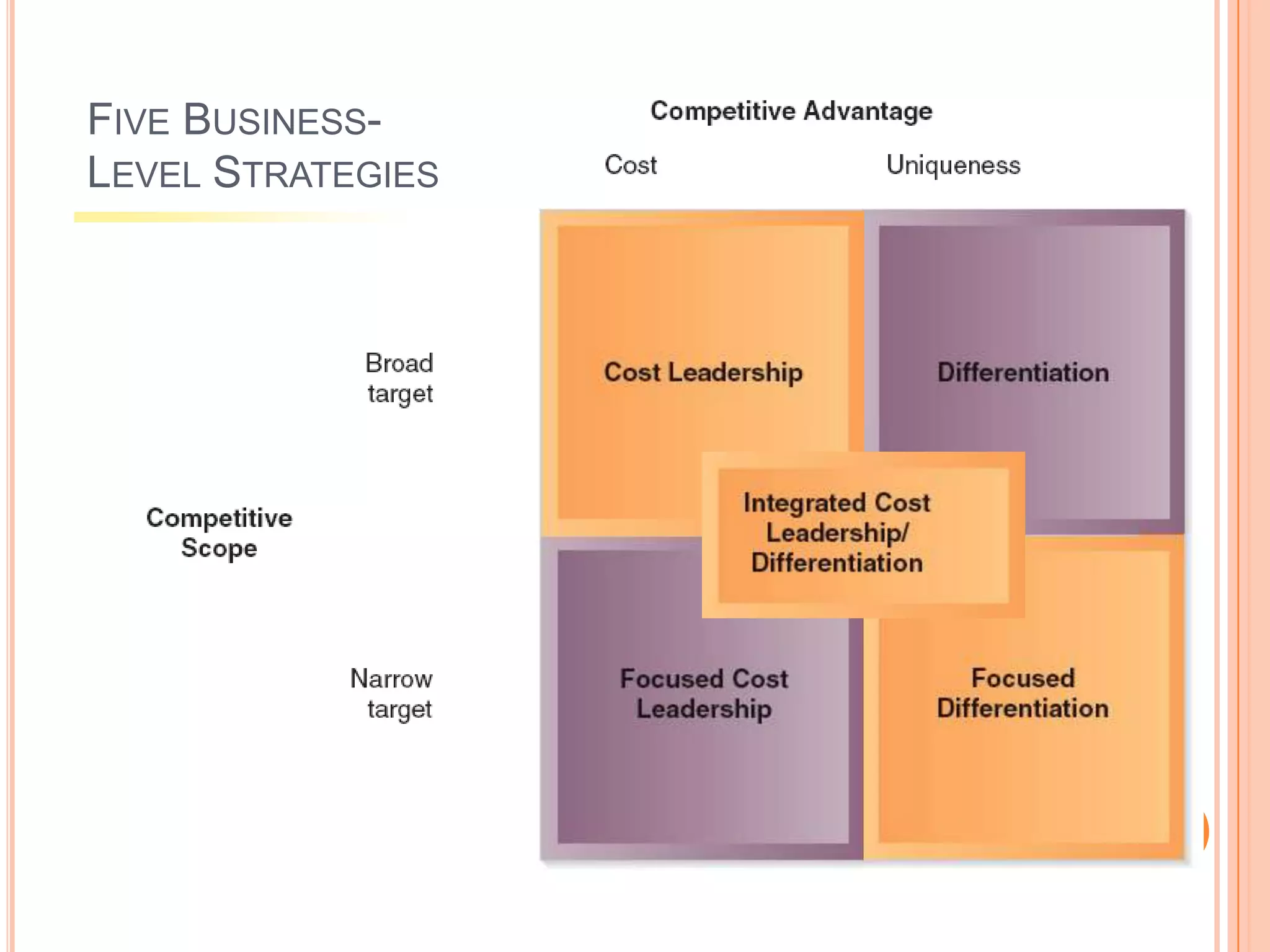
This document discusses different business level strategies including cost leadership, differentiation, focus, and an integrated cost leadership/differentiation strategy. It defines core competencies and business level strategy. It then examines each of the five strategies in more detail, outlining their objectives, keys to success, characteristics, and potential failures. The document provides an overview of strategic analysis at the business level.