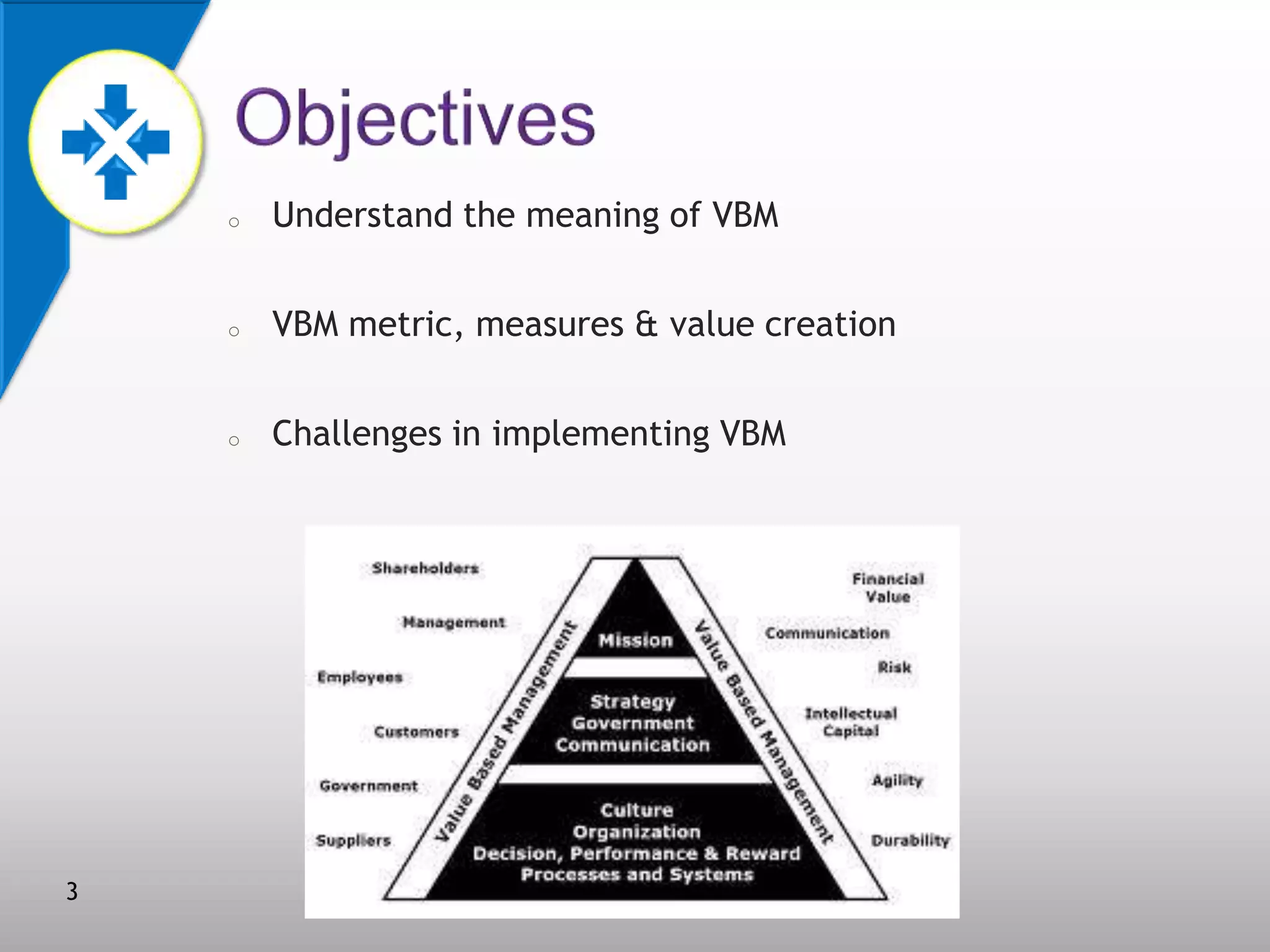
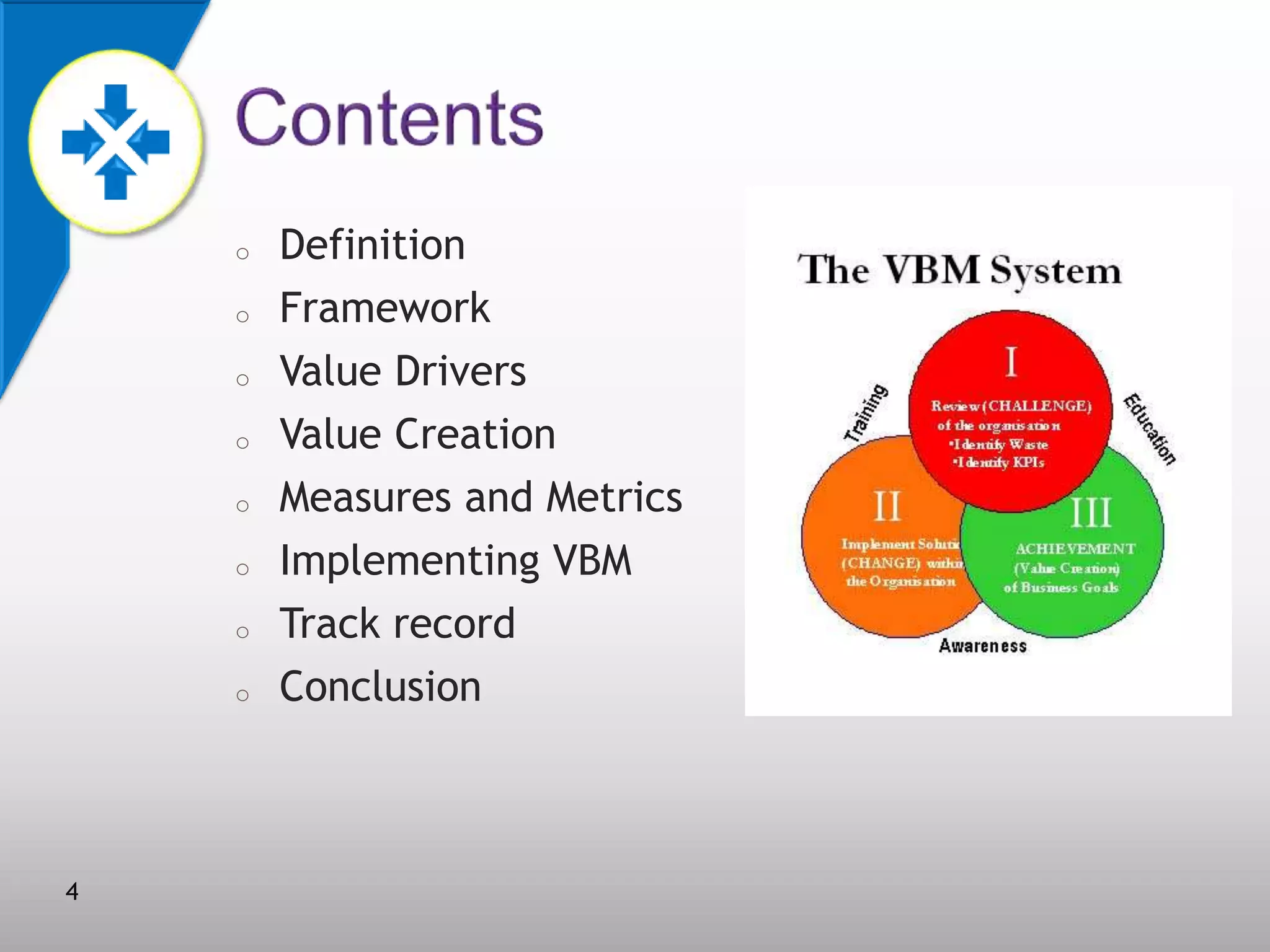
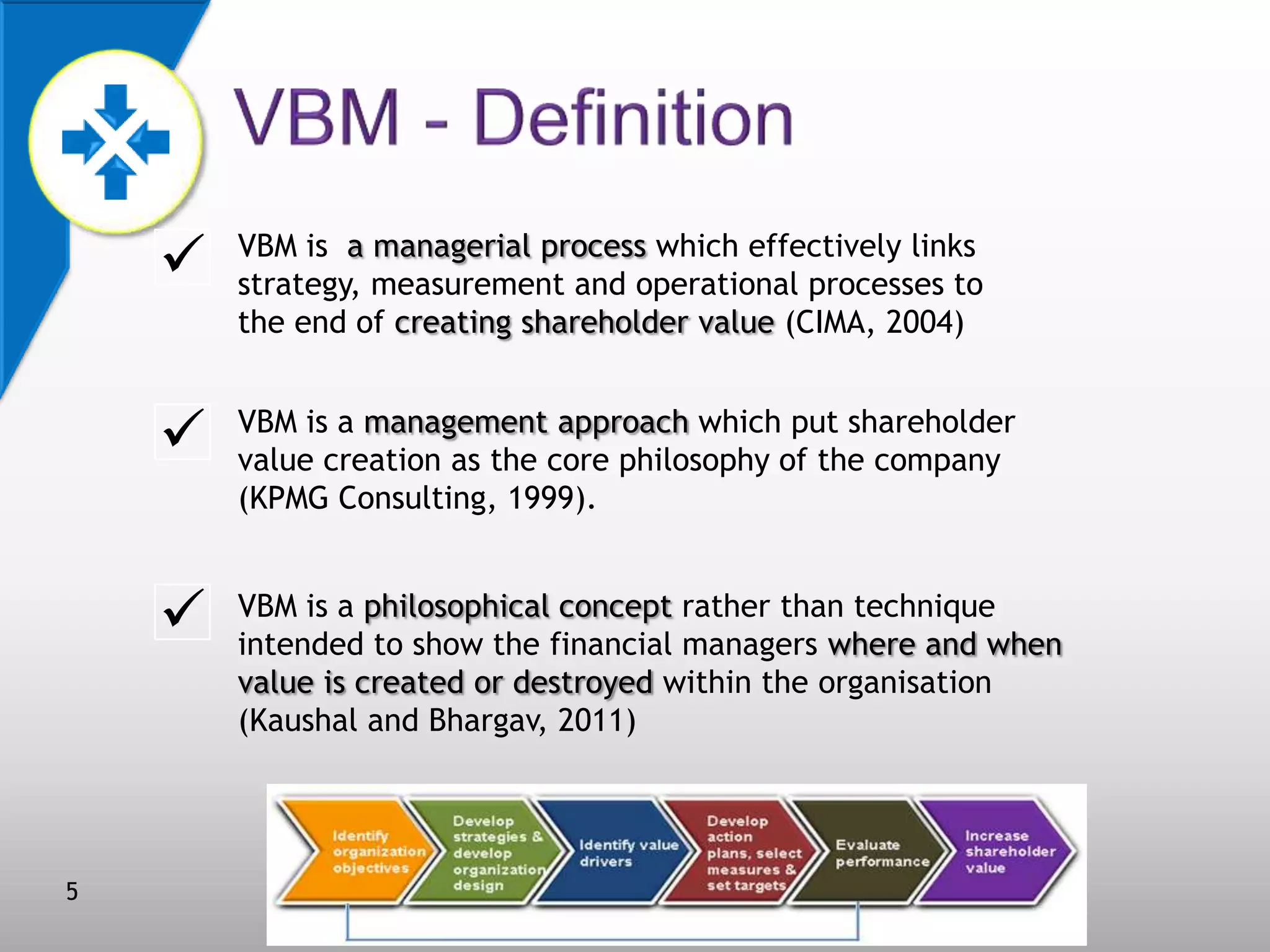
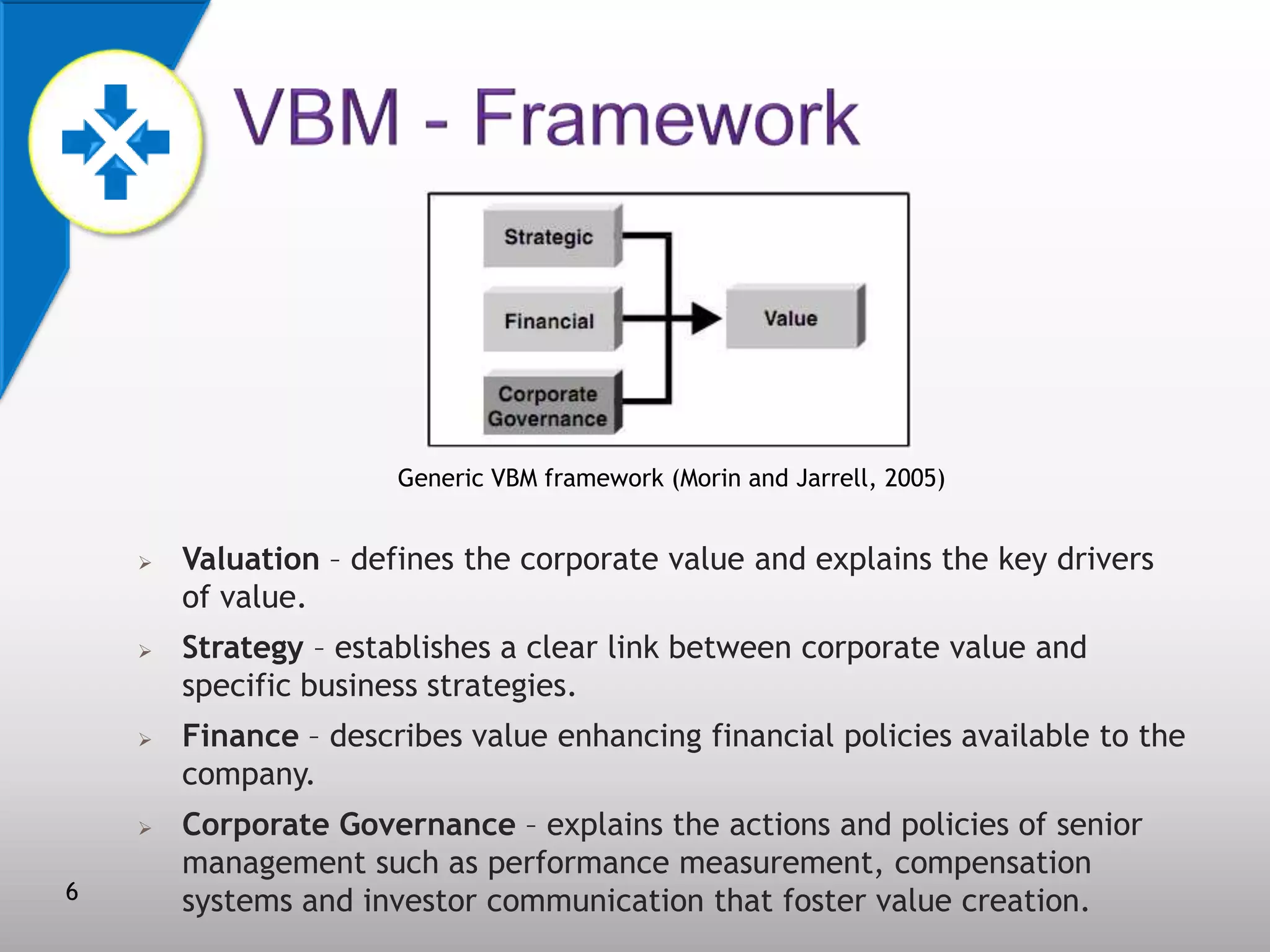
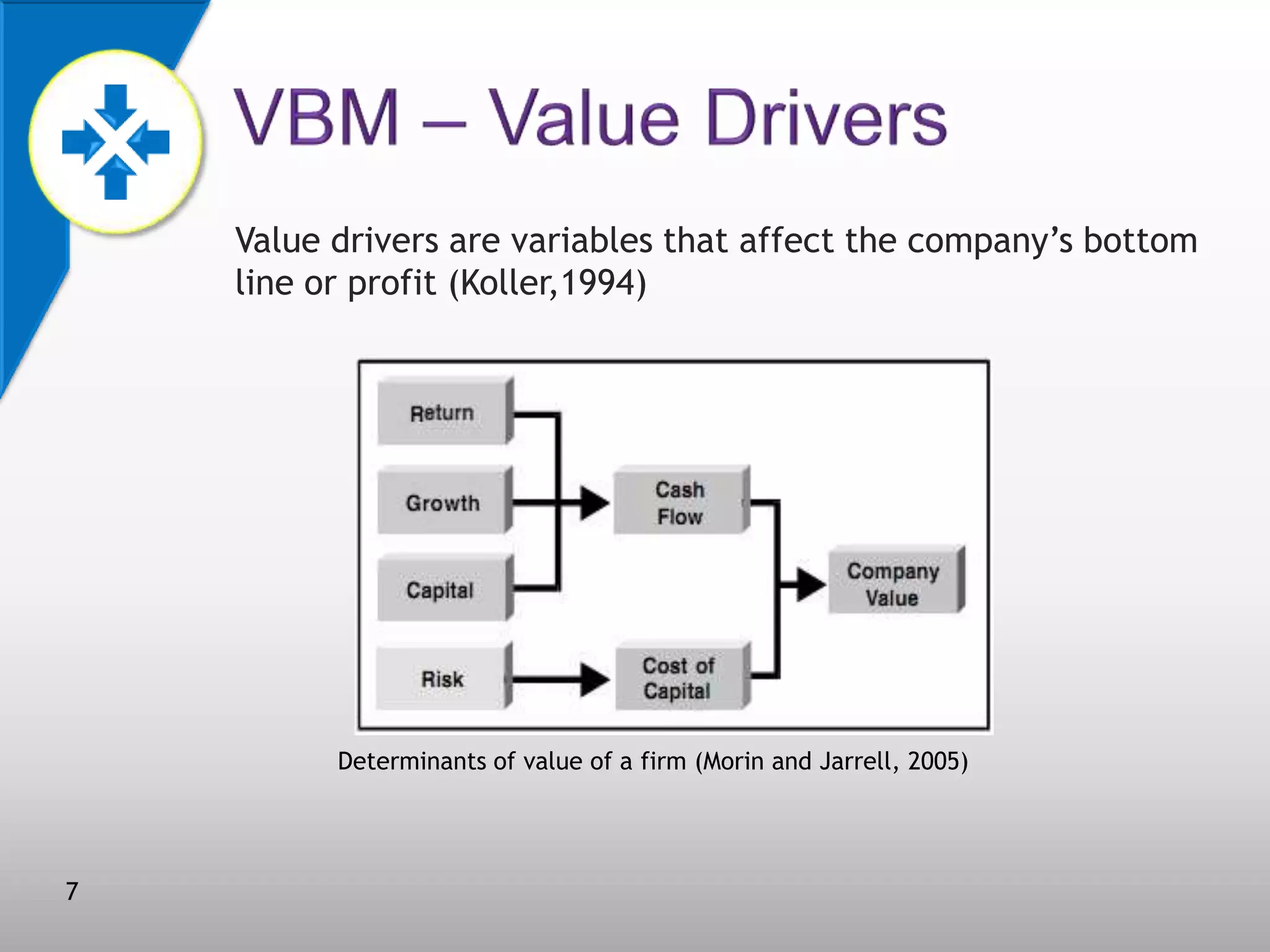
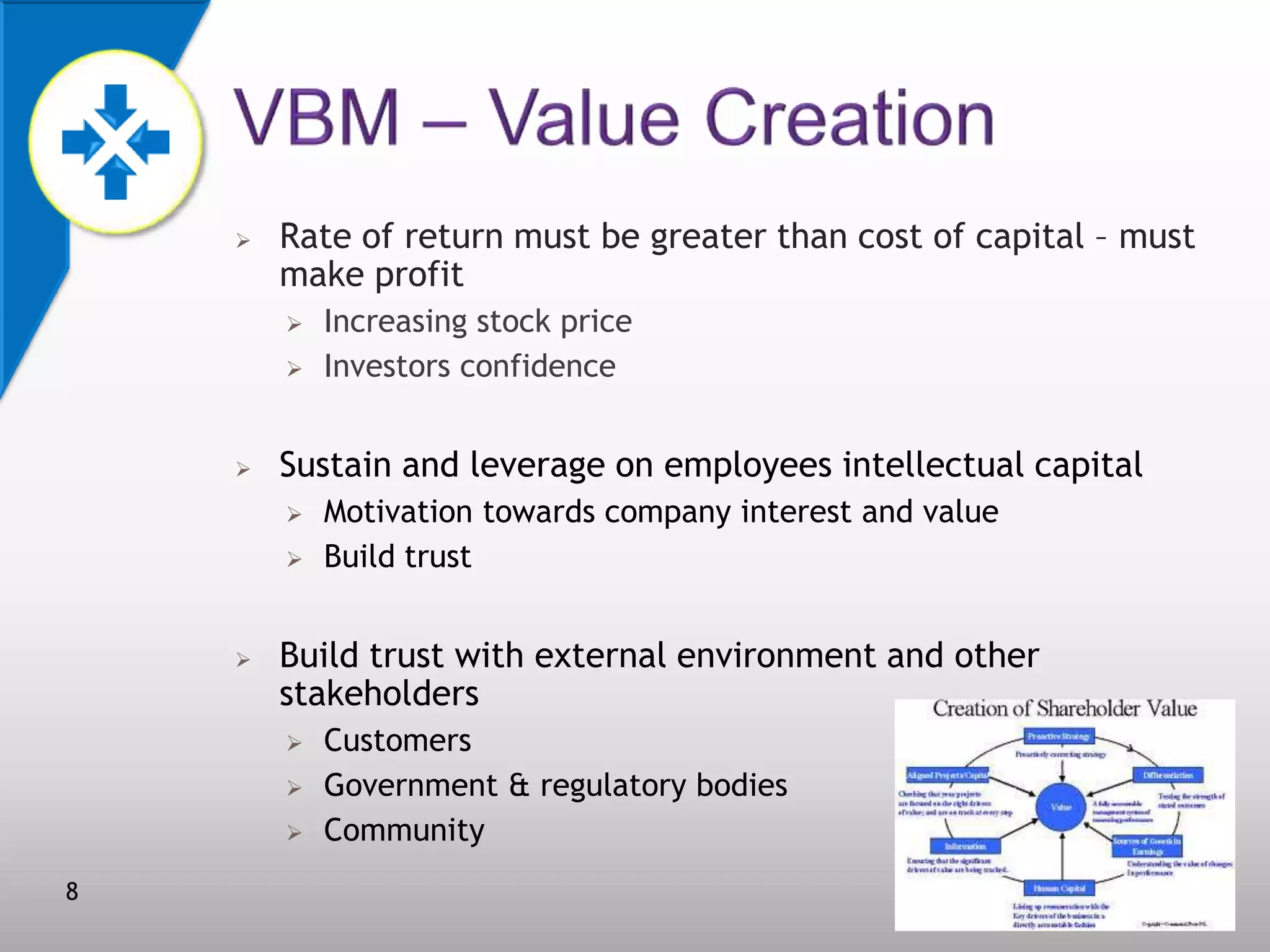
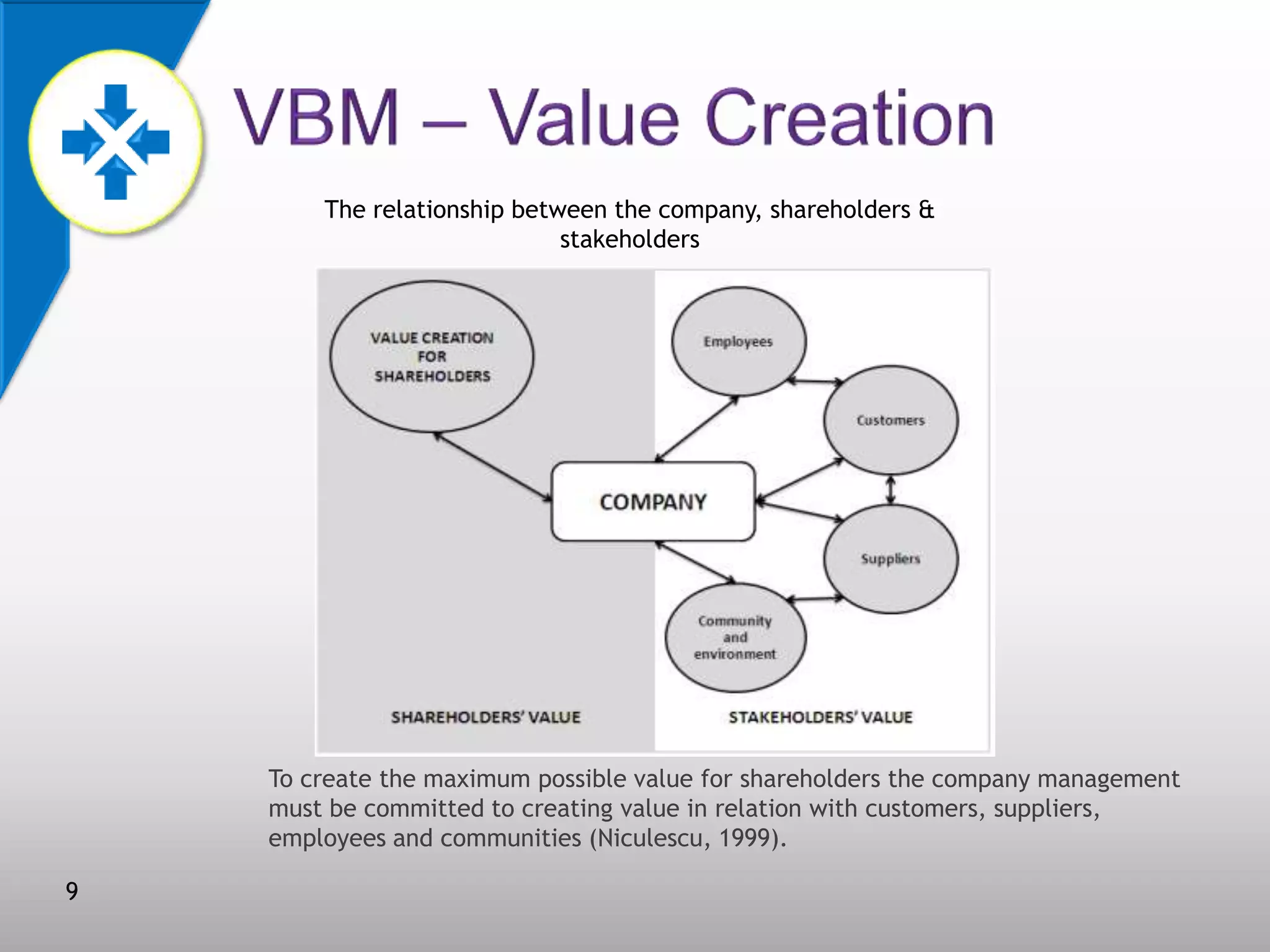
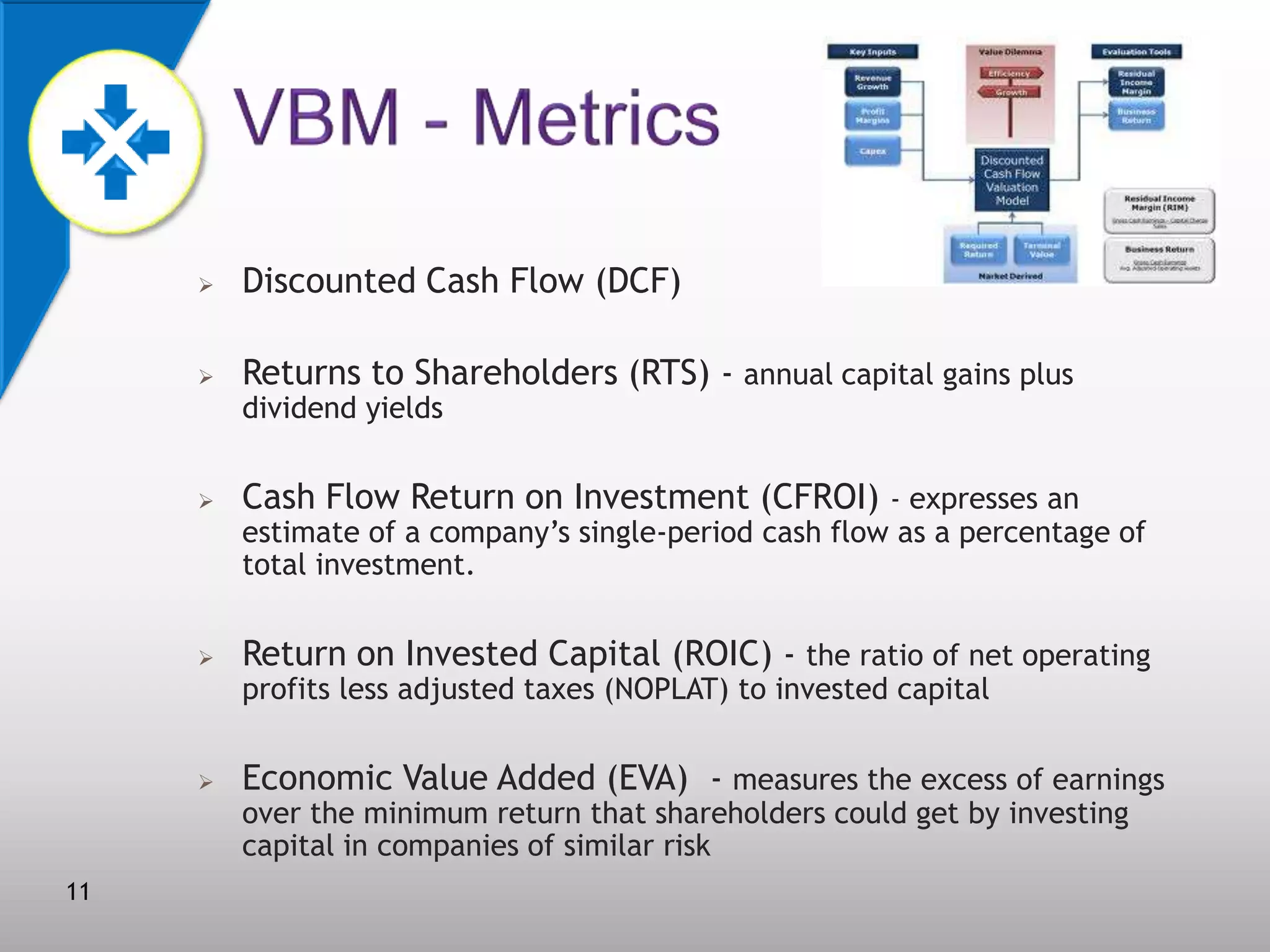
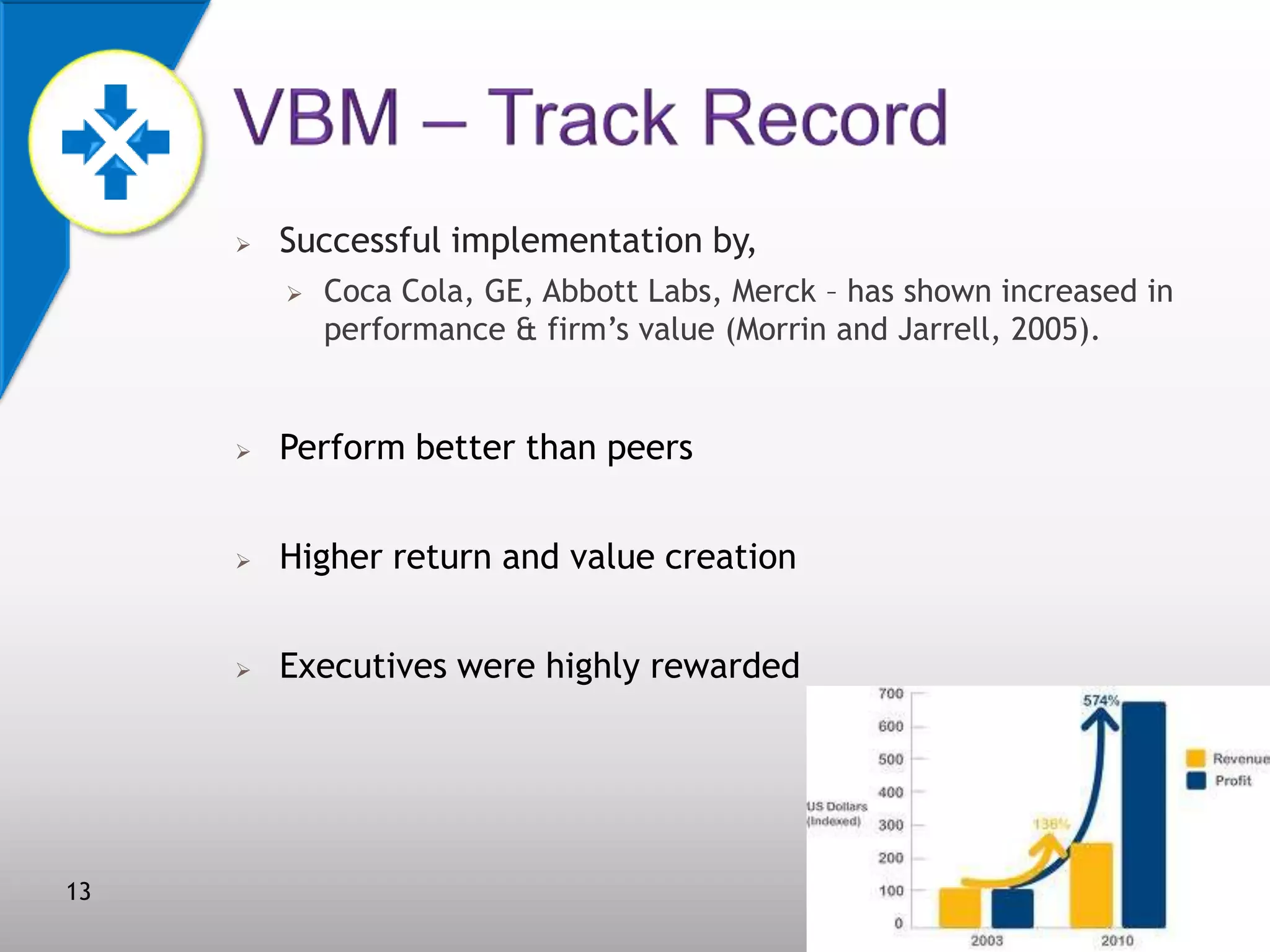
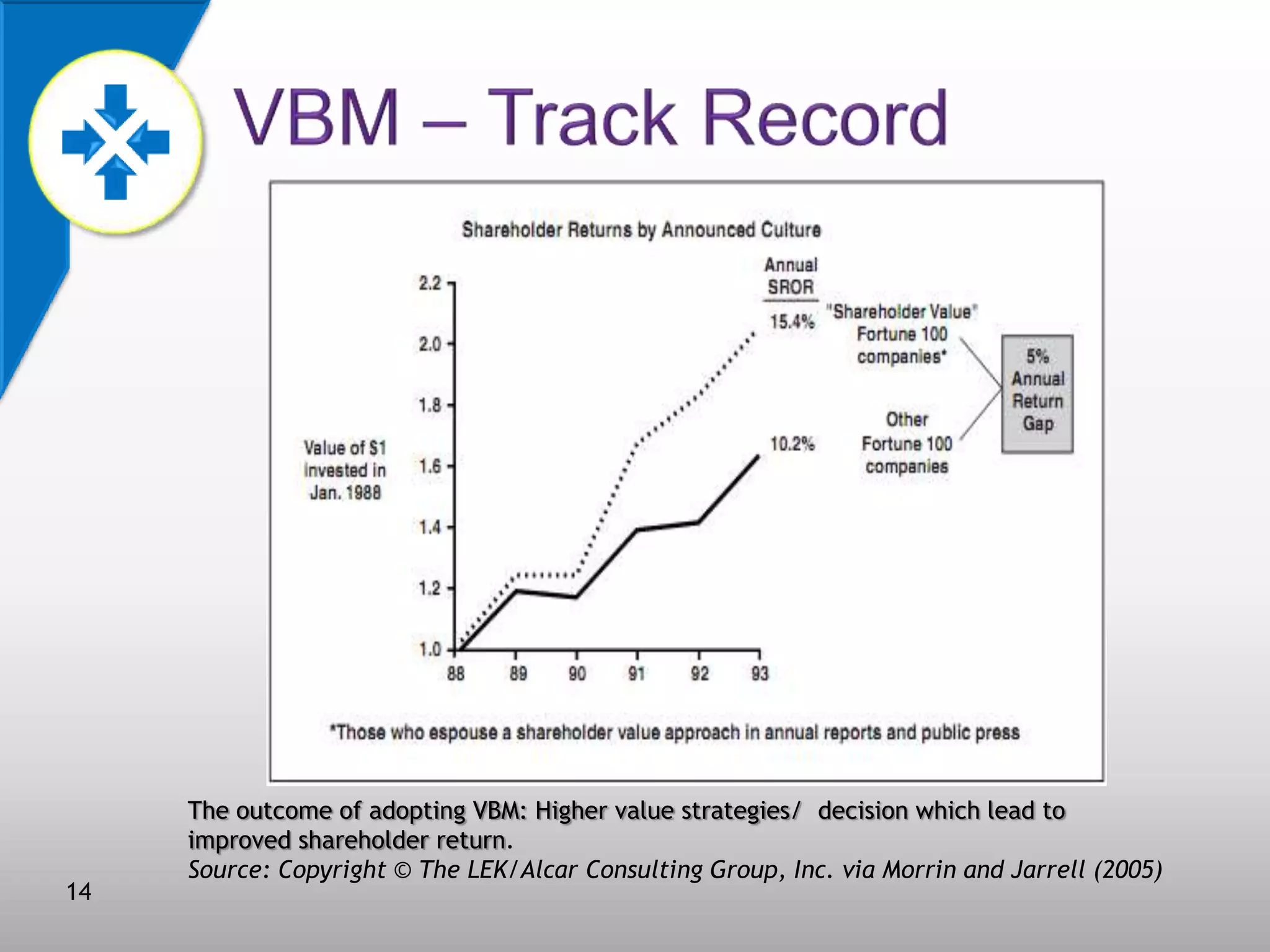
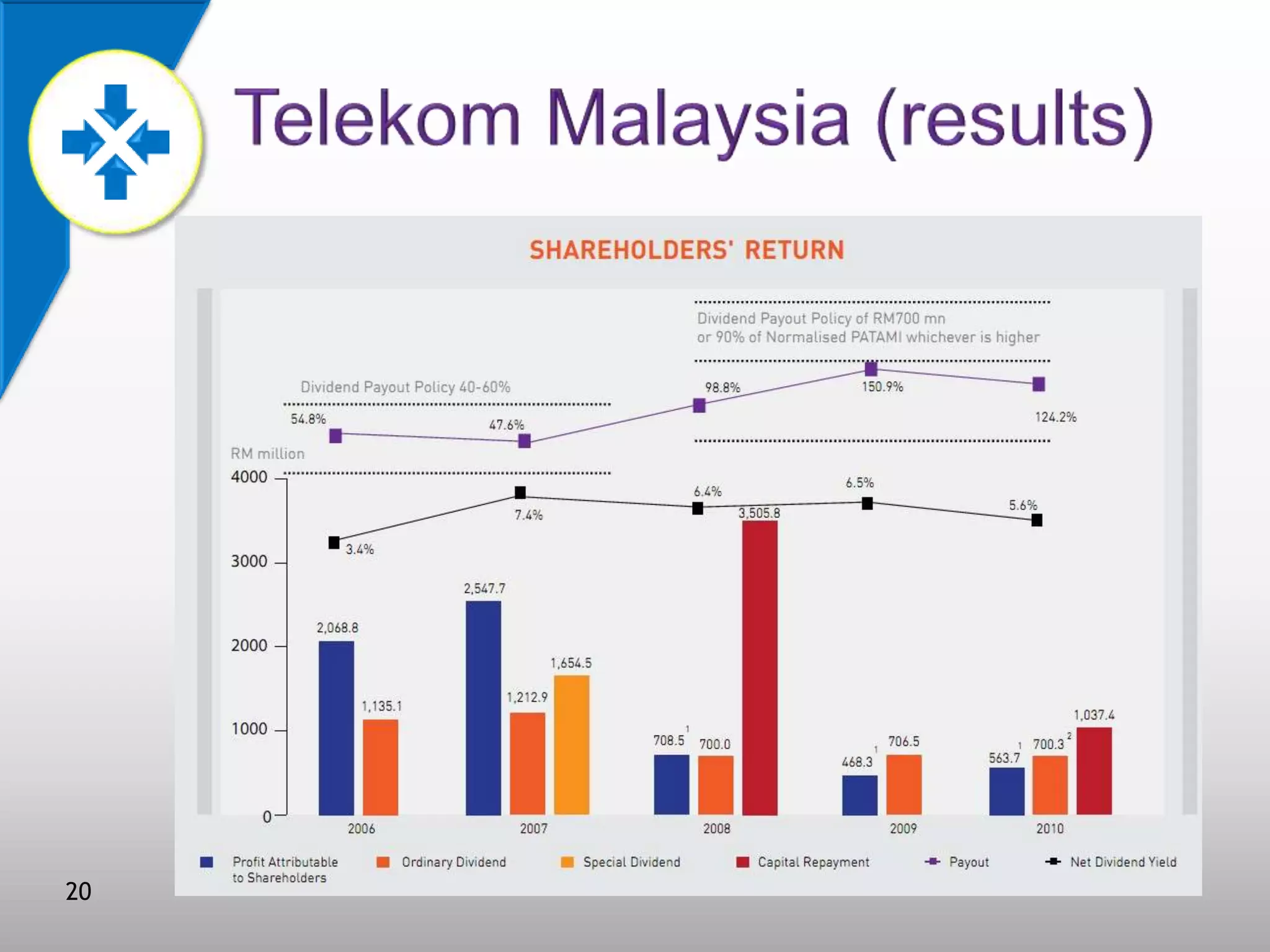
This document discusses value-based management (VBM) and its implementation. It defines VBM as a management approach that puts shareholder value creation as the core philosophy. VBM is intended to effectively link strategy, measurement, and operations to create shareholder value. The document outlines the generic VBM framework, key value drivers, example metrics like EVA and ROIC, and challenges in implementing VBM like gaining manager buy-in. It provides examples of successful VBM implementations at companies like Coca-Cola and notes that top management support is critical to smooth adoption of VBM.