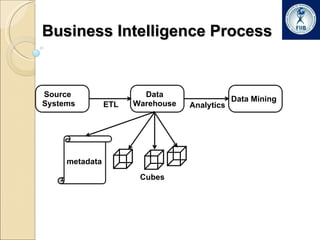
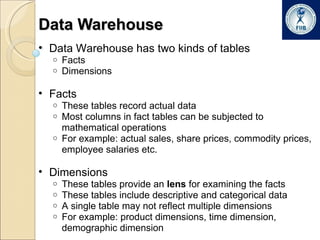
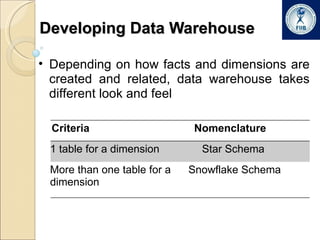
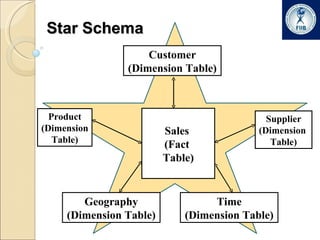
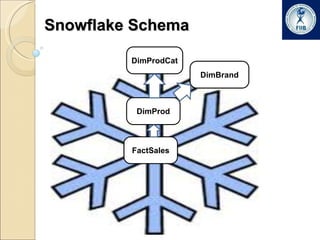
Business intelligence involves analyzing large datasets to help with decision making. It commonly used in retail, banking, IT security, and online marketing. The process involves extracting data from multiple sources into a data warehouse where it is transformed and organized. Data is then mined from the warehouse to generate insights through techniques like forecasting, segmentation, and market basket analysis. A data warehouse consists of fact and dimension tables. Facts contain measures while dimensions provide context for analyzing facts. Data warehouses can have a star or snowflake schema to organize this data.
![Business Intelligence: A Review Prof. Swanand Deodhar [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessintelligence-111209091321-phpapp01/85/Business-Intelligence-A-Review-1-320.jpg)