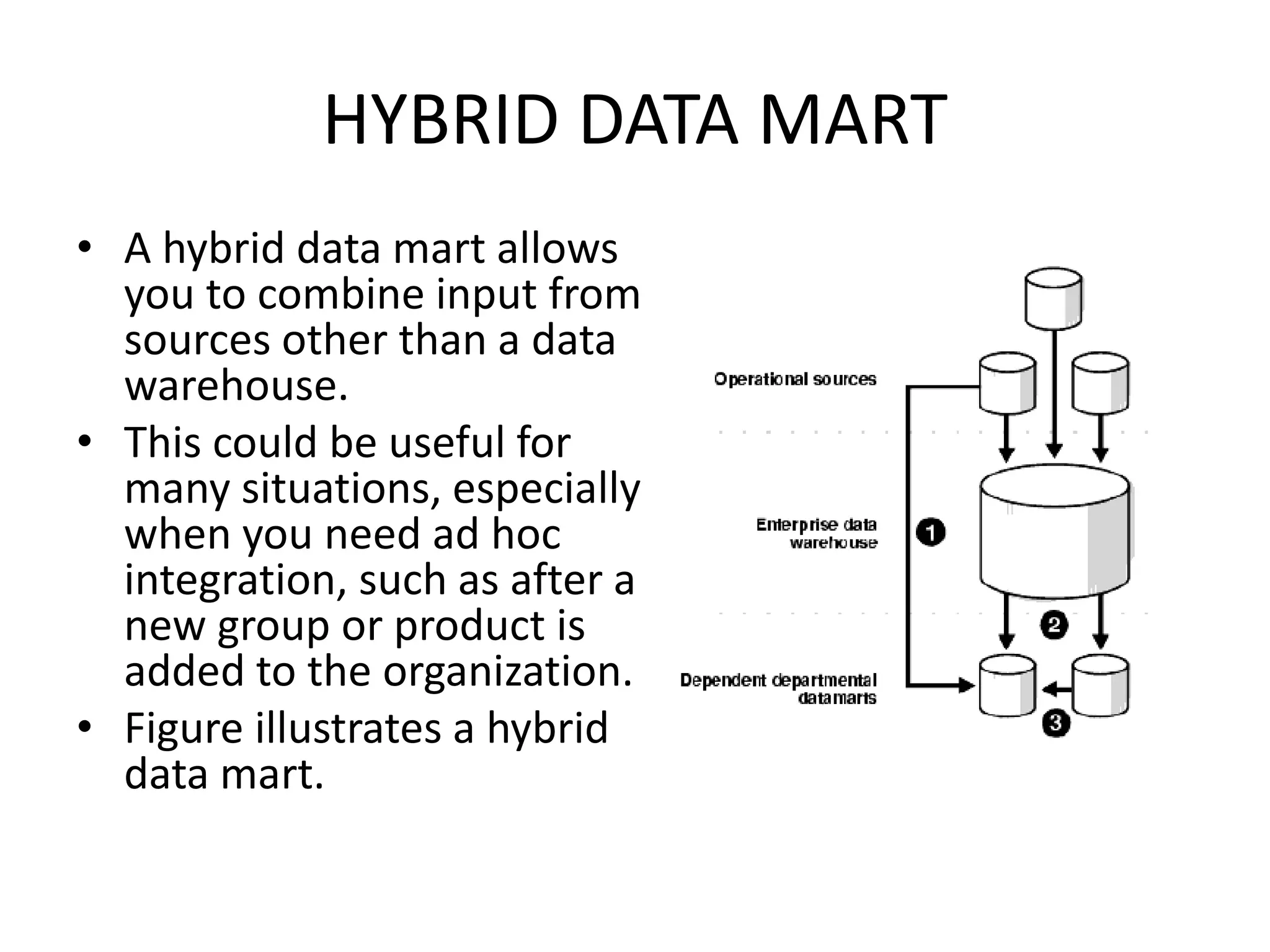
The document discusses different types of data marts:
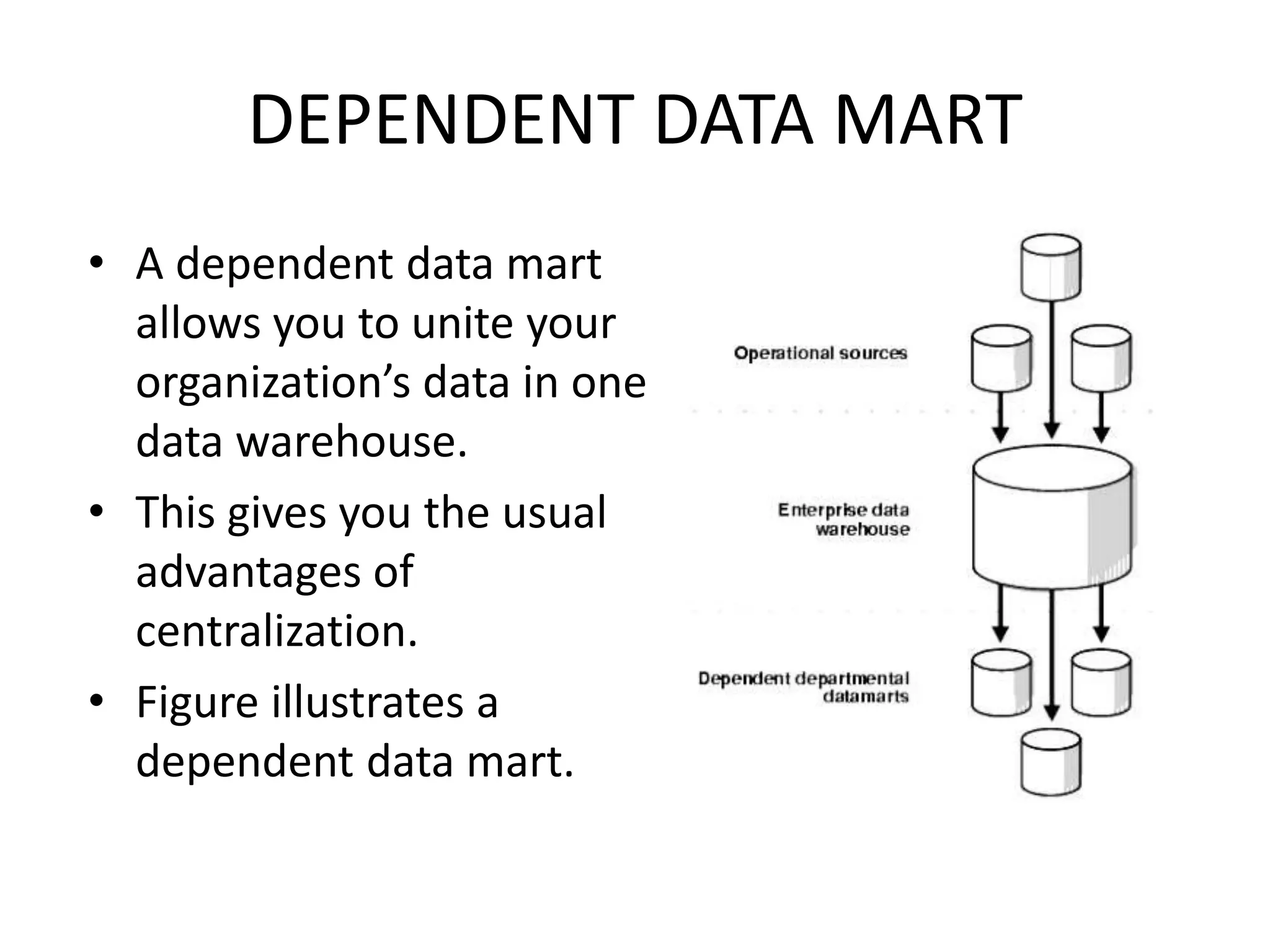
- Dependent data marts draw data directly from a centralized data warehouse, allowing for unified data access but with a focus on a specific group's needs.
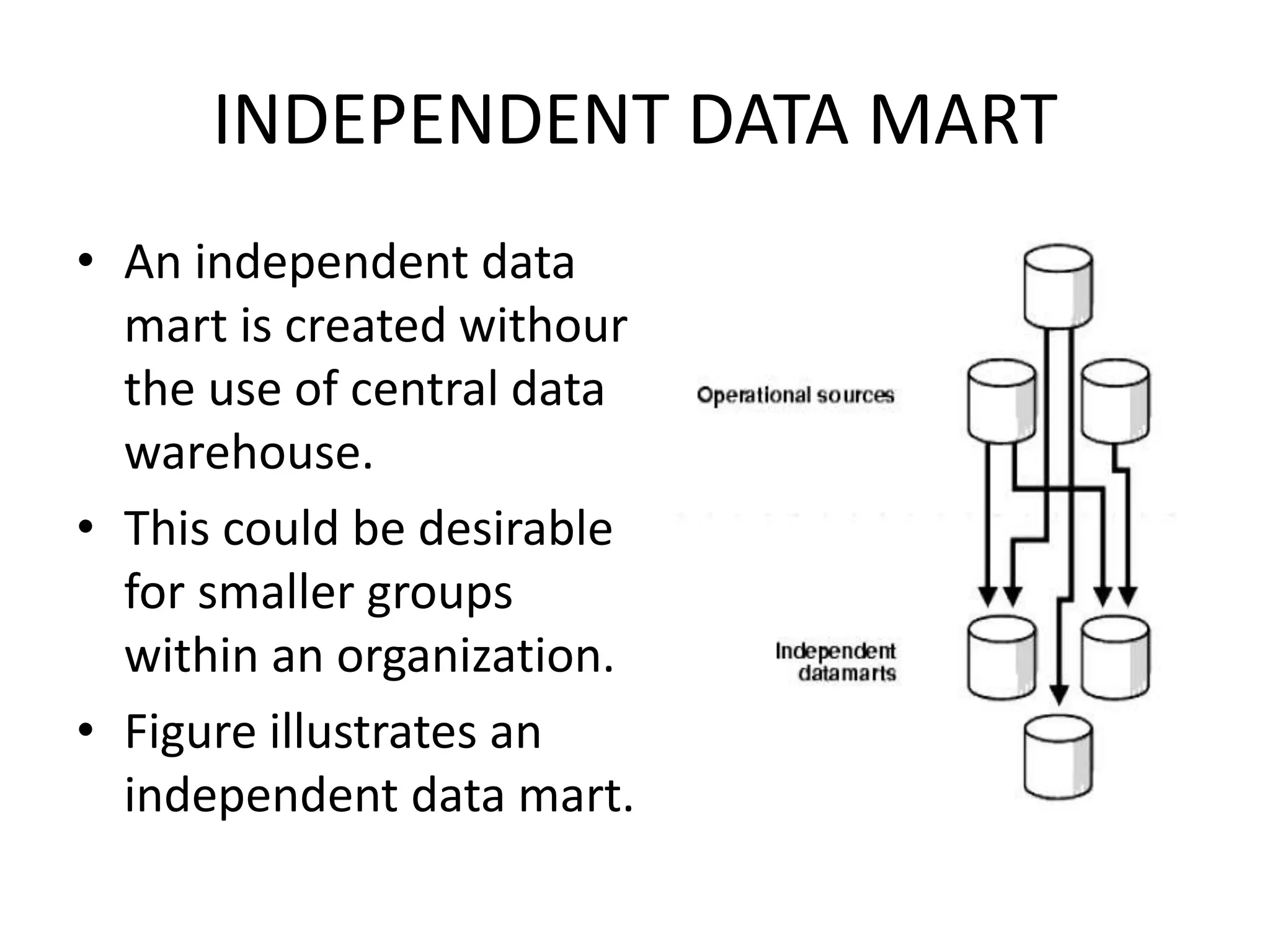
- Independent data marts are standalone systems built from direct access to operational or external data sources without using a centralized warehouse. They are suitable for smaller groups.
- Hybrid data marts can integrate data from both a centralized warehouse and other sources, providing flexibility for ad hoc integration needs.