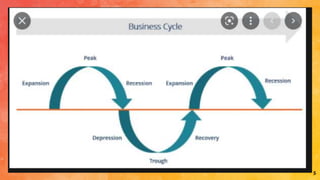
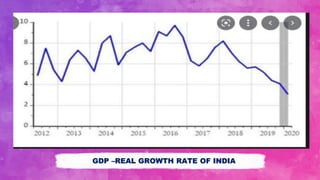
The business cycle is defined as the fluctuations in gross domestic product (GDP) around its long-term growth rate, encompassing stages of expansion, peak, contraction, trough, and recovery. Each stage represents different economic indicators and activities, where expansion shows growth and peak marks saturation, followed by recession and depression characterized by declining economic performance. Recovery initiates a turnaround, leading to renewed economic activity as demand and production begin to increase.