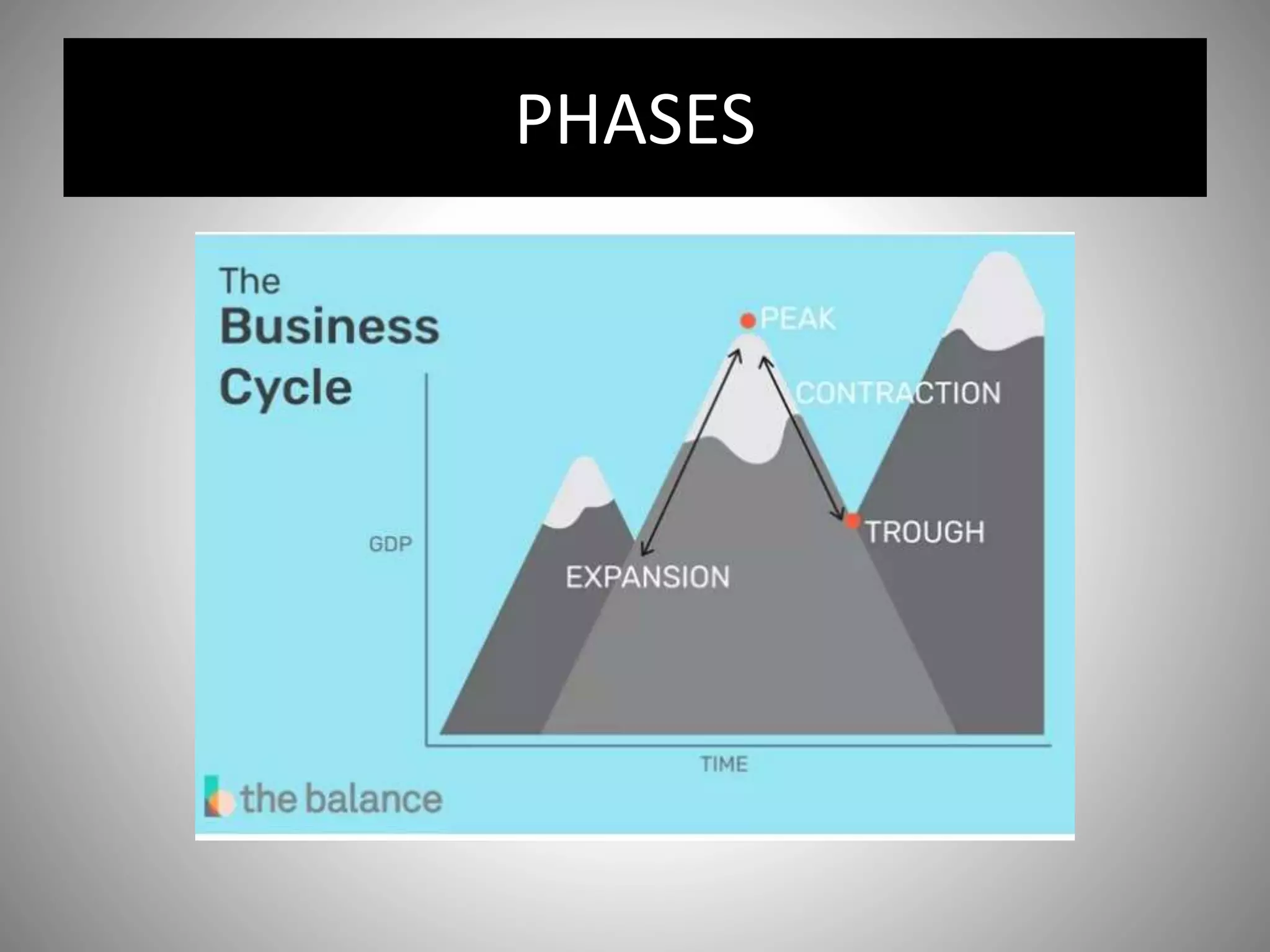
The business cycle, also known as the economic cycle, consists of periods of expansion, peak, contraction, and potential recession or depression, characterized by fluctuations in employment, income, prices, and output. During expansion, economic indicators show positive growth with low unemployment, while contractions lead to layoffs and increased unemployment. To manage the business cycle, governments utilize monetary policy, fiscal measures, and price controls; however, full control remains challenging.