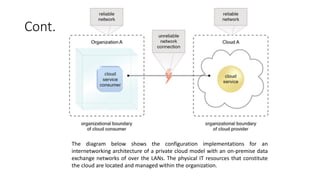
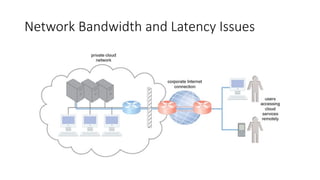
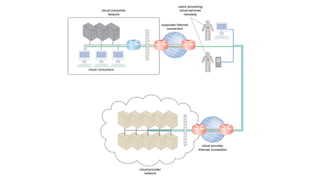
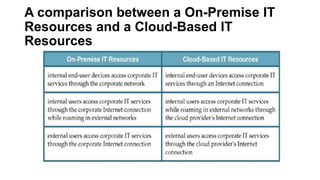
The document outlines the technical and business considerations organizations must evaluate before adopting cloud computing, highlighting important factors such as bandwidth, latency, and the selection of cloud carriers and providers. It discusses risks associated with service level agreements (SLAs), the challenges of cloud migration, and the need for network security and operational governance. Additionally, it touches upon legal issues related to data storage and privacy across different jurisdictions.