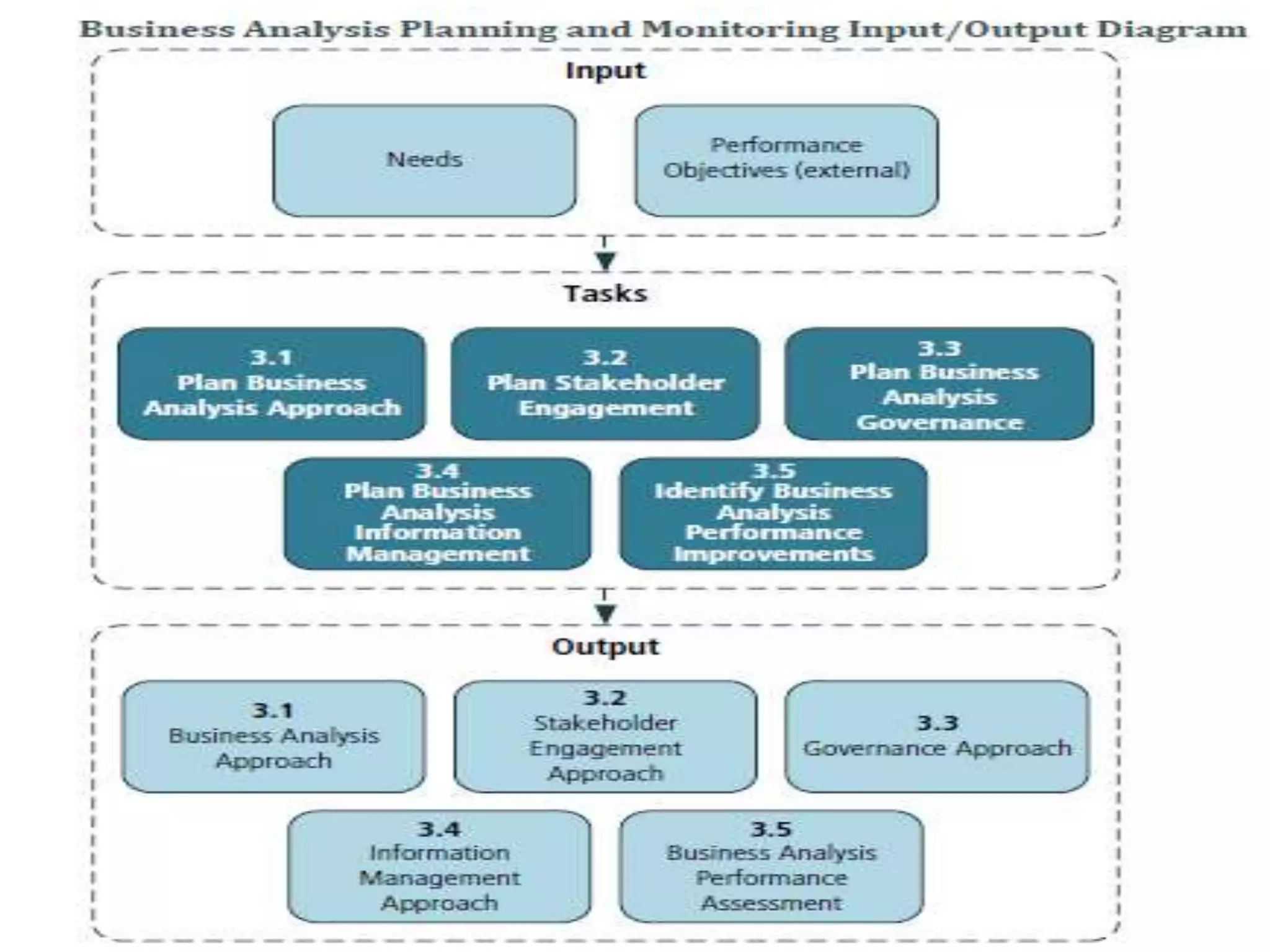
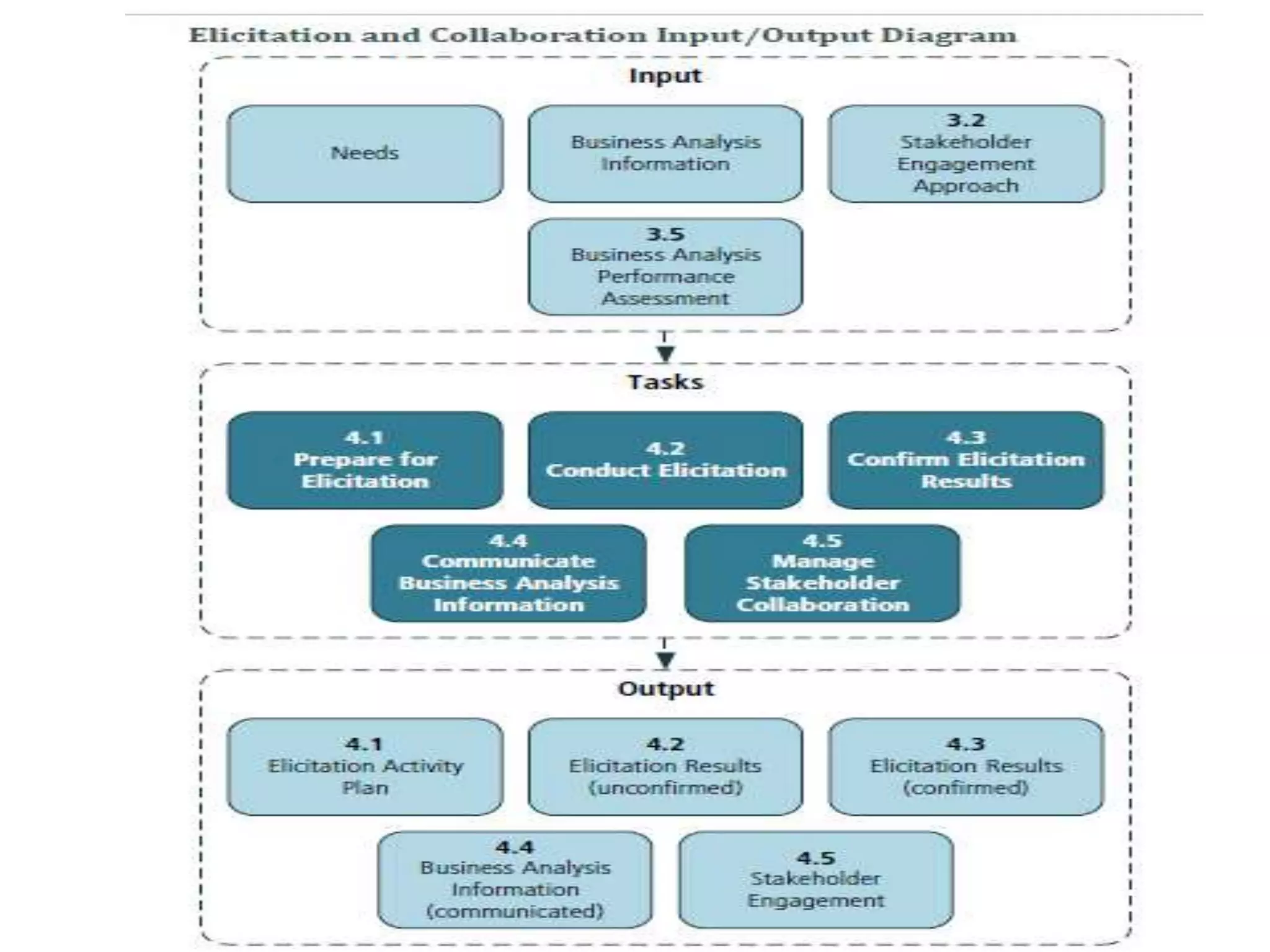
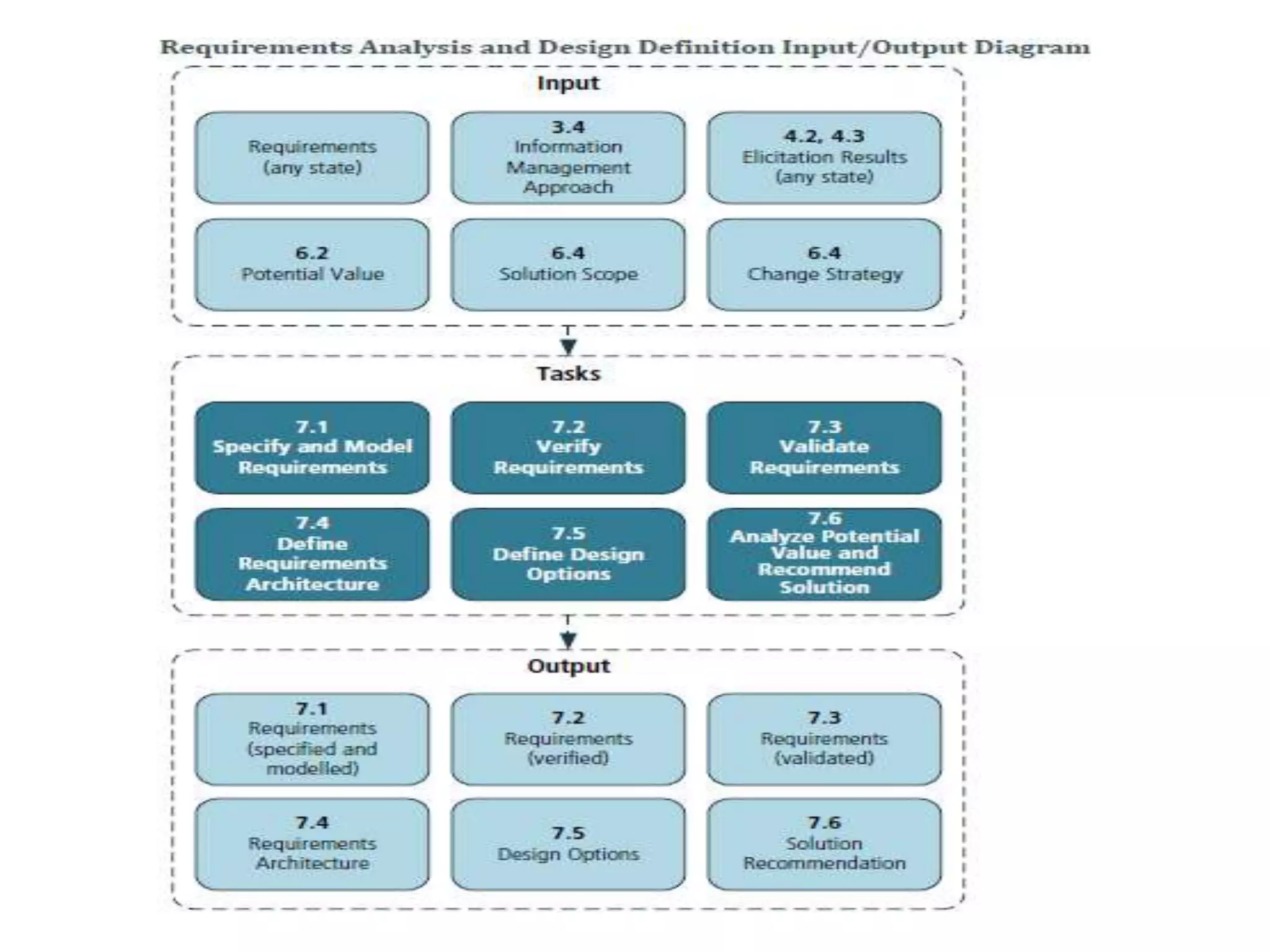
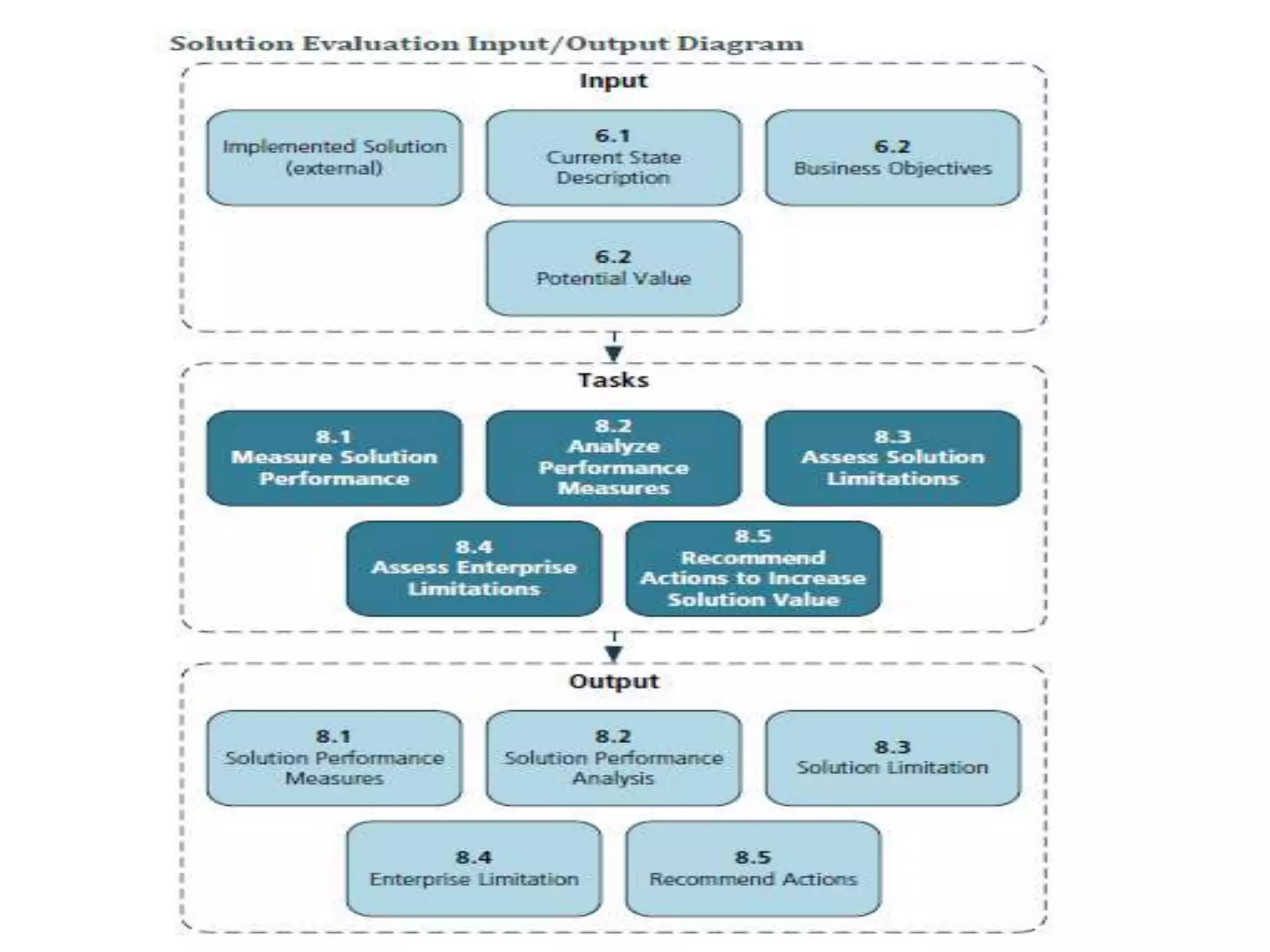
The document discusses the core standard knowledge areas of business analysis as defined by the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA). It outlines the six core knowledge areas which are: business analysis planning and monitoring, elicitation and collaboration, requirements life cycle management, strategy analysis, requirements analysis and design definition, and solution evaluation. For each knowledge area, it lists the key tasks involved at a high level. It also provides additional details on some of the knowledge areas such as elicitation and collaboration and requirements life cycle management.