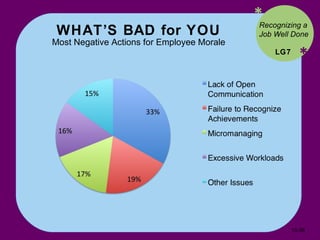
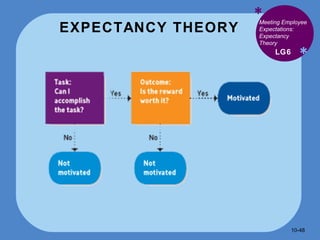
The document discusses various theories of motivation in the workplace, including:
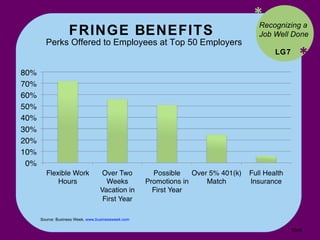
- Google founders motivate employees by allowing them to pursue their interests and providing amenities like colorful offices and food.
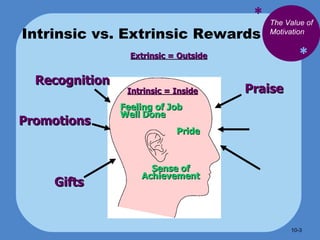
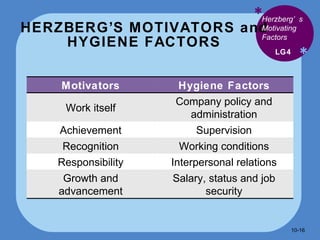
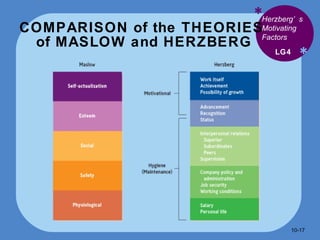
- Herzberg's theory distinguishes between intrinsic motivators like achievement and extrinsic motivators like pay that don't necessarily motivate.
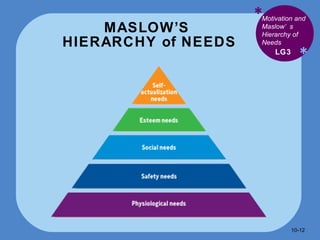
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs proposes that lower level needs must be met before higher ones motivate.
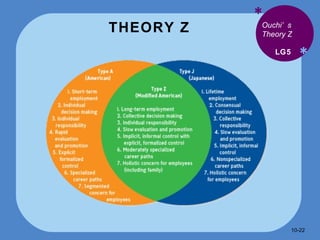
- McGregor's Theory X and Y describe assumptions managers have about motivating workers through fear versus commitment to goals.