The document discusses analysis of variance (ANOVA), covariance, and correlation. It provides the following key points:
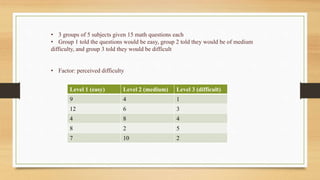
1. ANOVA is a statistical technique used to compare population means by examining variances within and between samples. If between-sample variation is larger than within, the population means are likely different.
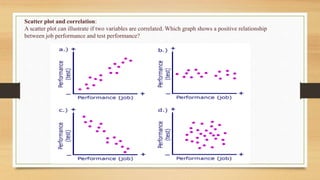
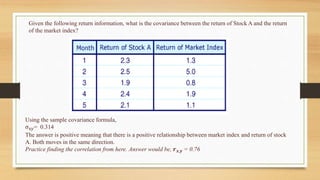
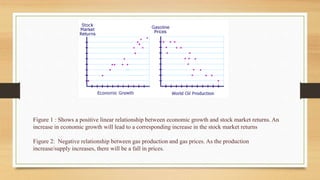
2. Covariance measures how two random variables relate and change together. Positive covariance means variables move in the same direction, while inverse covariance means they move opposite directions.
3. Correlation assesses the strength and direction of covariance. It ranges from -1 to 1, with 1 being total positive correlation and -1 being total negative correlation. Correlation indicates how strongly variable changes are associated.










![Covariance
- Indicates how two random variables are related to one another. Example, is there a linear increase in one
associated with a linear increase in another?
- Are they moving together or in the opposite direction?
- Variables are positively related if they move in the same direction.
- Variables are inversely related if they move in opposite directions.
- This relationship is called covariance and denoted by
𝜎𝑥𝑦 = Cov (x,y) =
∑𝑖=1
𝑁
𝑥𝑖 − 𝜇𝑥 𝑦𝑖 − 𝜇𝑦
𝑁
Cov(X,Y) = E [ (X- 𝜇𝑥) 𝑌 − 𝜇𝑦 ]
Expectation is simply the long run average value.
x = the independent variable
y = the dependent variable
n = number of data points in the sample
𝜇𝑥 = the mean of the independent variable x
𝜇𝑦 = the mean of the dependent variable y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bus1734-230612152220-92fc3c93/85/Bus-173_4-pptx-13-320.jpg)