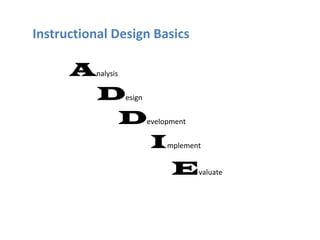
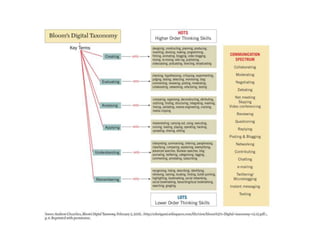
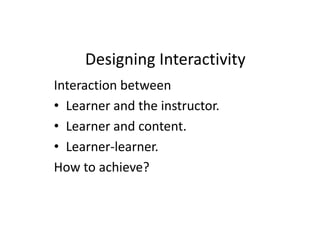
The document provides guidance on building effective online courses by starting with course goals and the instructor's teaching style, using a learner-centered approach, and ensuring clear organization and interaction. It emphasizes understanding students, applying principles of good teaching, and using instructional design steps that include analysis, design, development and evaluation of the course. The document also discusses engaging students through varied content delivery, collaboration activities, and addressing different learning needs.