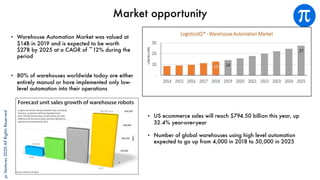
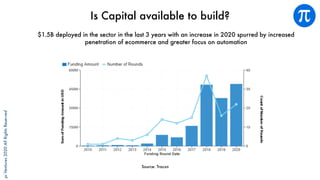
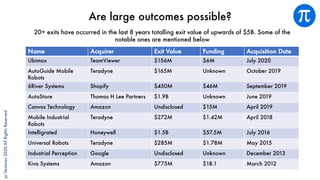
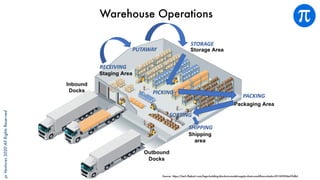
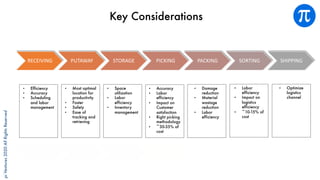
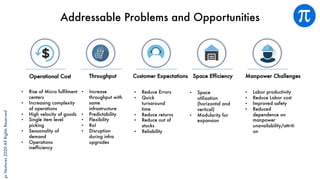
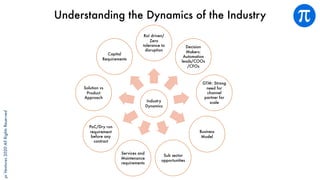
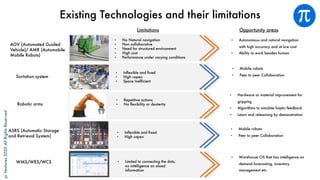
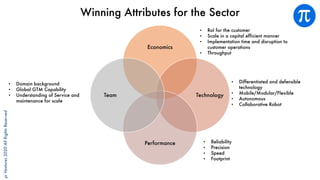
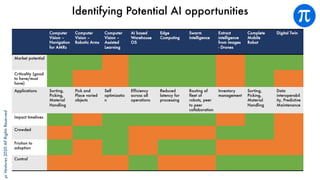
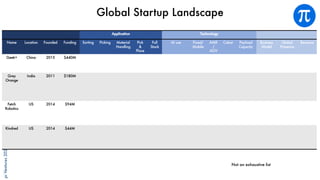
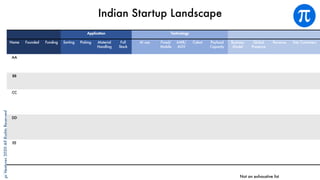
The document discusses building an investment thesis for warehouse automation. It identifies the large and growing market opportunity in warehouse automation driven by increasing ecommerce, labor challenges, and demand for efficiency. The document maps out the key operations in a warehouse and problems that can be addressed through automation. It analyzes the existing technologies used in warehouses and gaps that startups can address, such as developing autonomous mobile robots and collaborative robots. The document presents an investment thesis around warehouse automation and identifies attributes of startups that are well-positioned to succeed in this space, such as having differentiated technology, performance, and a strong team with domain expertise and go-to-market strategy.