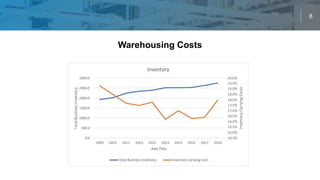
The document discusses the evolving landscape of warehouse technology, highlighting the integration of automation and robotics to enhance efficiency and productivity. Key technologies mentioned include drones, robots, and warehouse management systems (WMS), which significantly impact operational costs and workflows. The future of warehousing relies on continued investments in technology while maintaining the need for human workers alongside automation.