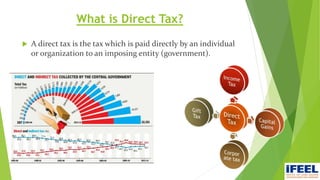
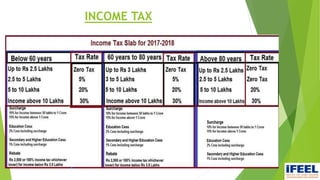
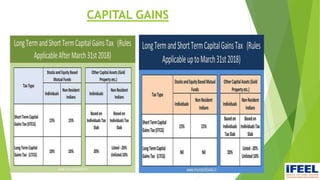
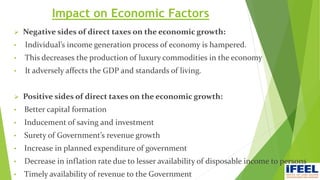
Group 6 presented information on direct taxes in India. The group members are Snehal Nemane, Sayli Mahalle, Shruti Adyalkar, and Vrushabh Agarwal. Direct taxes are taxes paid directly by individuals and organizations to the government. Major changes in direct taxes included no changes to income tax rates but a new 4% health and education cess. Corporate tax rates were reduced to 25% for companies with turnover less than Rs. 250 crore. Long-term capital gains on equity shares and funds will be taxed at 10%.