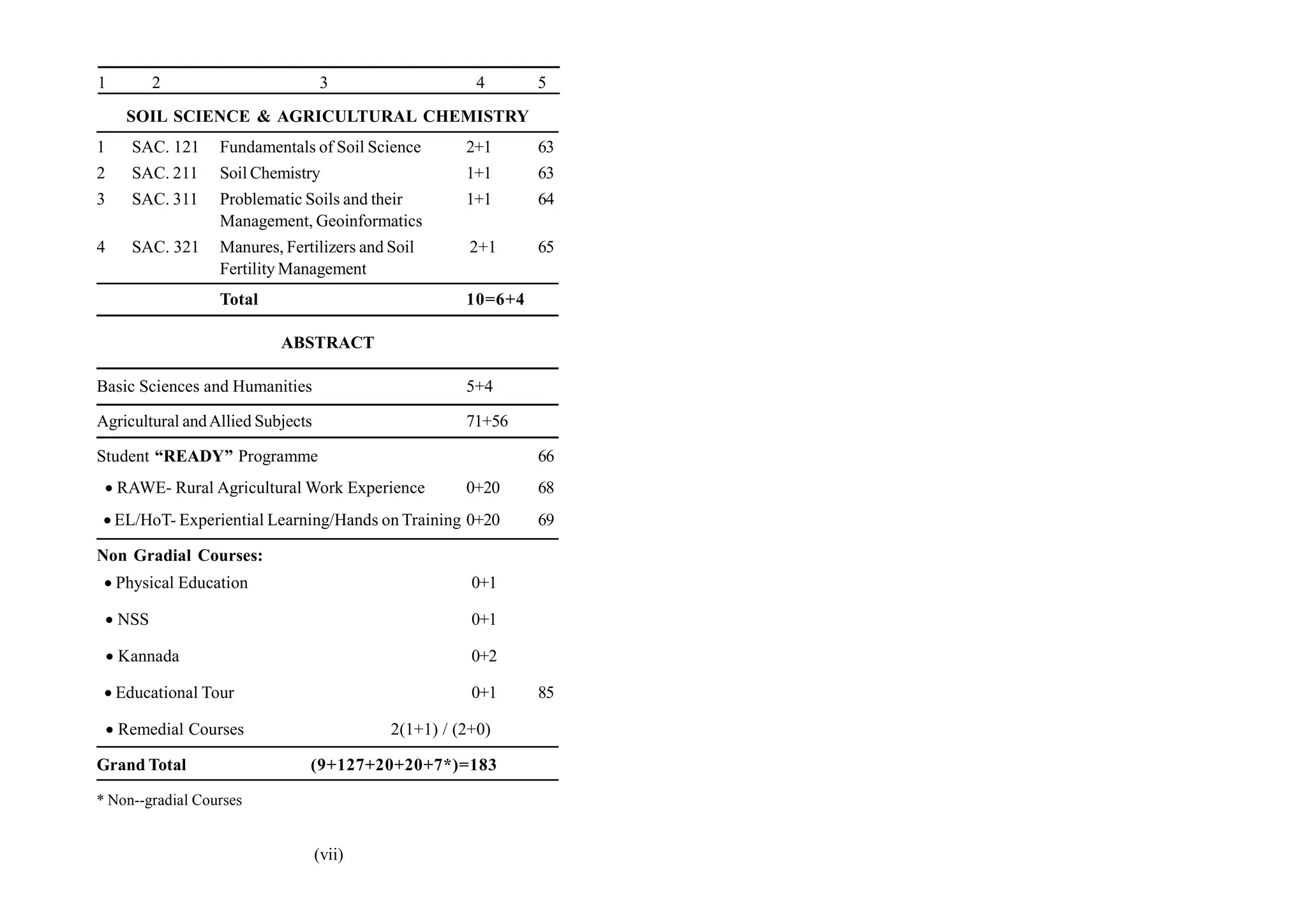
The document outlines the curriculum for the B.Sc. (Agriculture) degree program at the University of Agricultural Sciences in Bengaluru, highlighting course subjects across various disciplines including basic sciences, agricultural engineering, and more. It specifies course titles, credits, and structures such as theoretical and practical hours. Additionally, it emphasizes non-gradial courses, a student readiness program, and includes detailed descriptions of several courses related to agriculture and allied subjects.