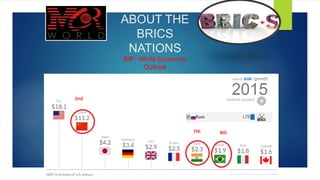
BRICS is an international organization consisting of five major emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. Formed in 2009, BRICS aims to enhance cooperation between these countries in multilateral forums and promote economic and political ties. The organization has led to the establishment of new institutions like the New Development Bank and Contingency Reserve Arrangement that allow BRICS nations to challenge the influence of Western financial bodies like the IMF and World Bank. With nearly half the world's population and a growing share of global GDP, BRICS represents a significant geopolitical force.