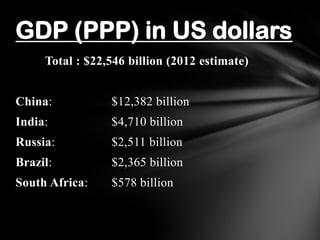
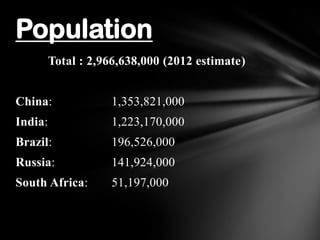
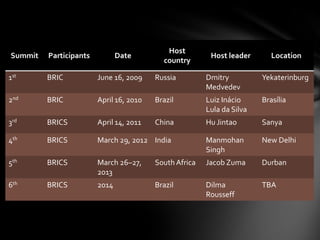
The document provides information on the BRICS nations (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa). It lists the current leaders and finance ministers of each country. It also provides key economic data including GDP, population, area, and other statistics for each BRICS nation as well as in total. The history and developments of the BRICS group are summarized, including details on the first 5 summits hosted between 2009-2013.