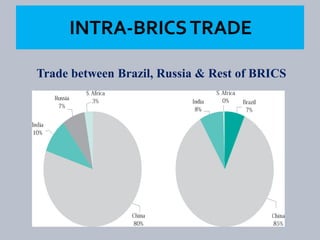
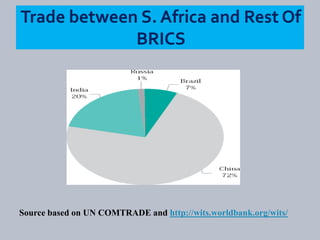
The document discusses BRICS, an international organization consisting of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. It notes that BRICS was formed in 2001 and accounts for over 40% of the global labor force. The organization allows member countries to exchange views, identify areas for cooperation, and influence the global agenda. South Africa joined in 2010, changing the name from BRIC to BRICS. Key goals of BRICS include regional development, economic growth, education improvement, and utilizing their comparative advantages.