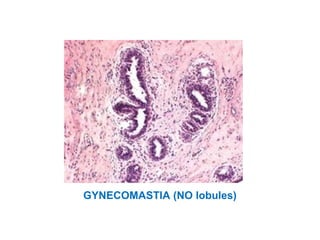
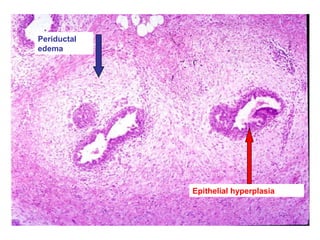
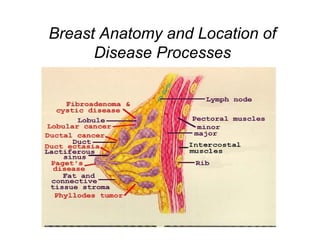
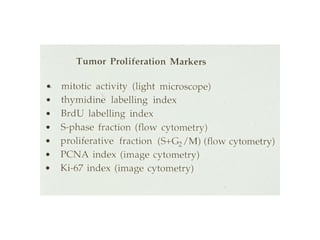
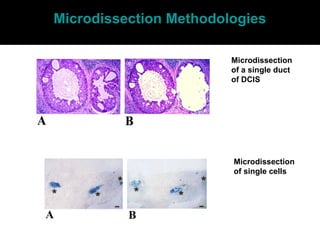
This document discusses breast cancer, including:
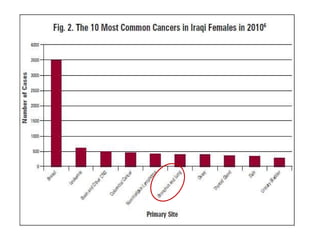
1. Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in the United States, and the second most common cause of cancer death in women. One in eight women will get breast cancer.
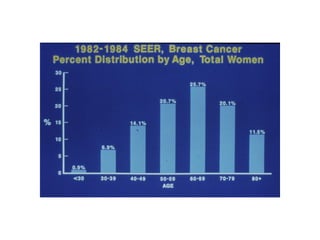
2. Risk factors for breast cancer include age, family history, benign breast disease, reproductive history, and environmental/lifestyle factors.
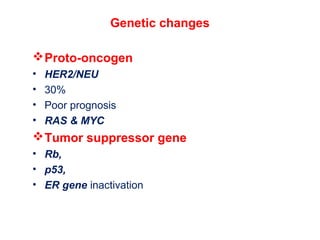
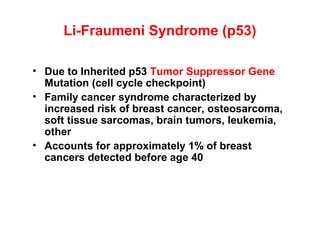
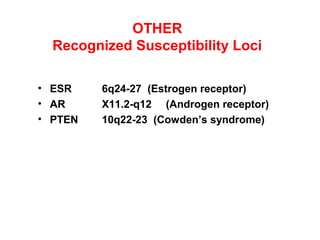
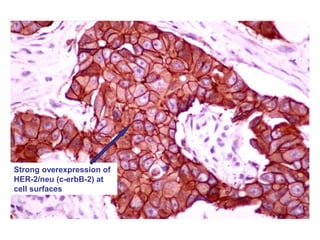
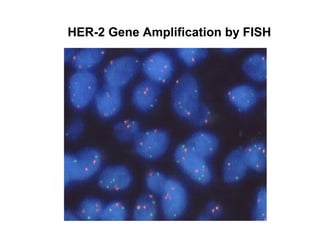
3. Genetic changes like mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, and p53 genes can increase the risk of breast cancer.
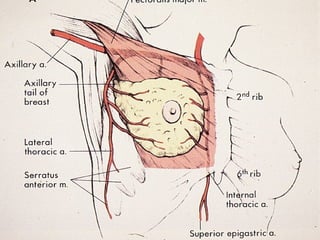
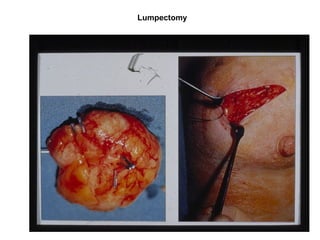
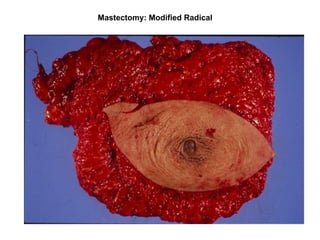
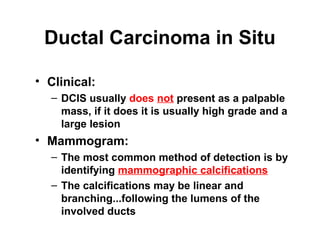
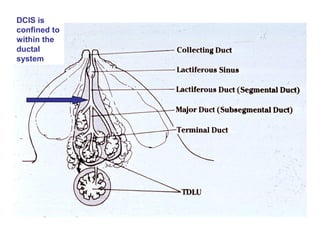
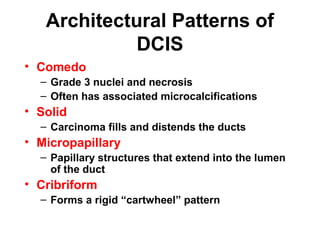
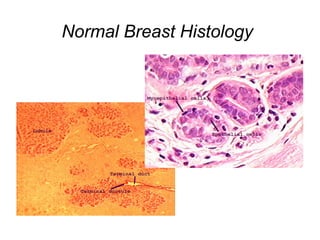
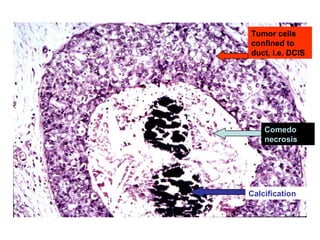
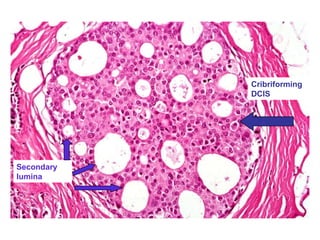
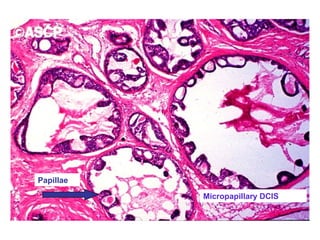
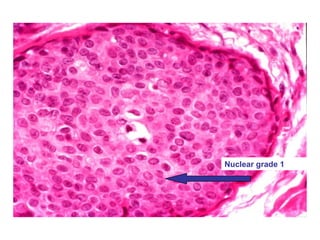
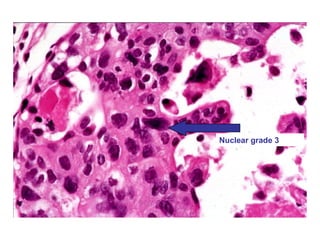
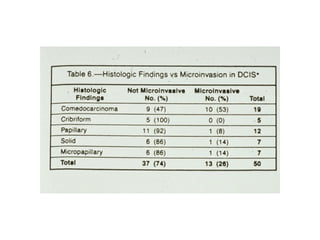
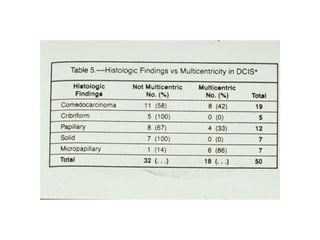
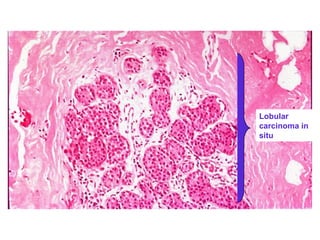
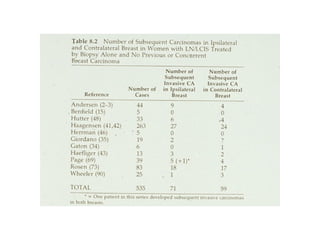
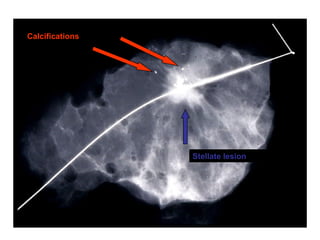
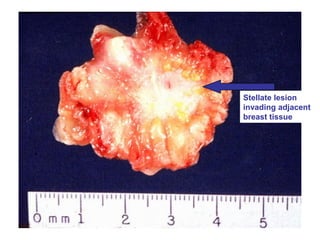
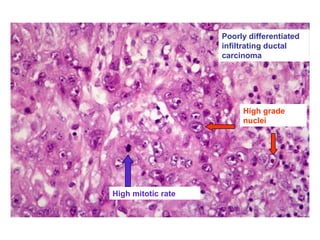
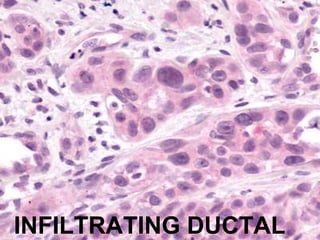
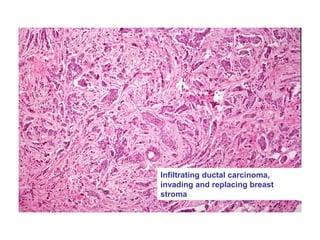
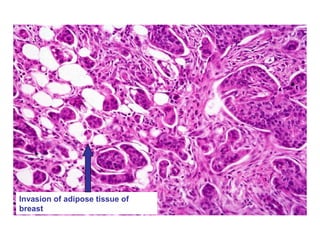
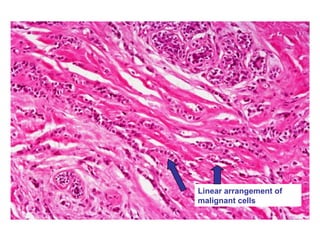
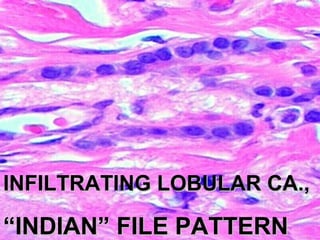
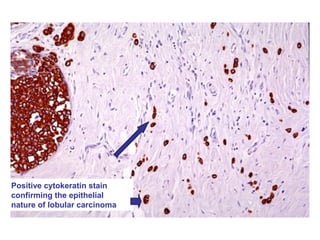
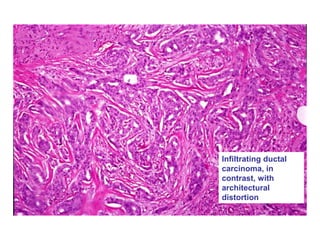
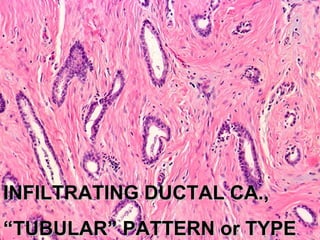
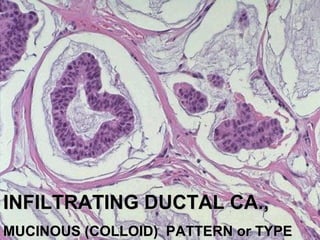
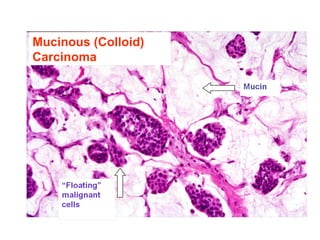
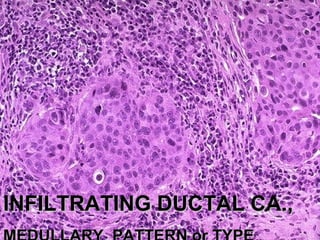
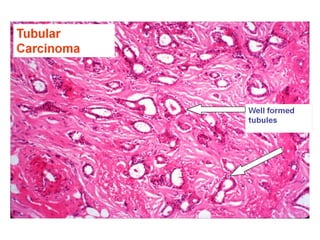
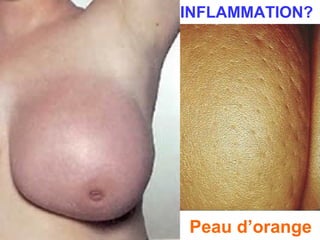
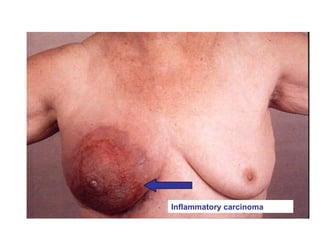
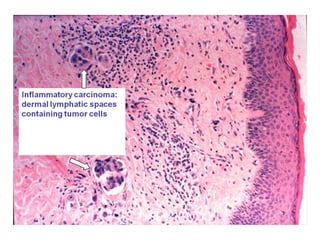
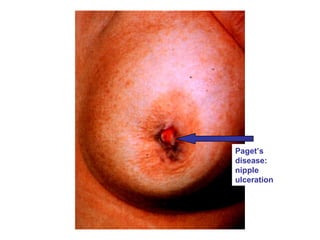
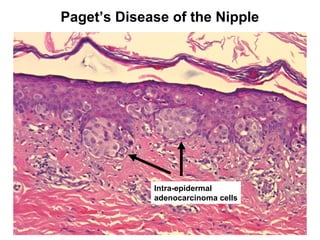
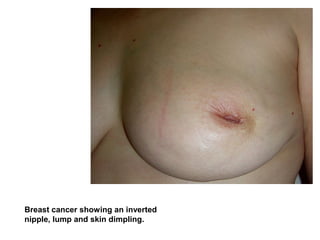
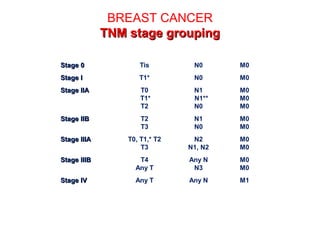
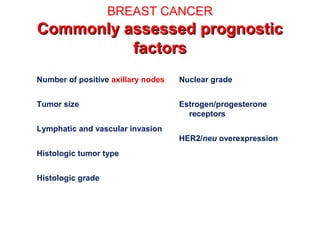
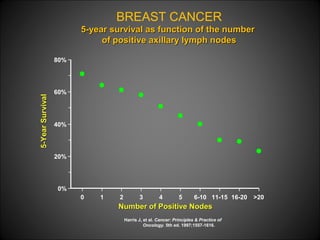
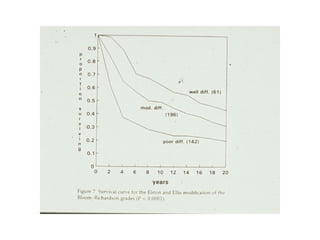
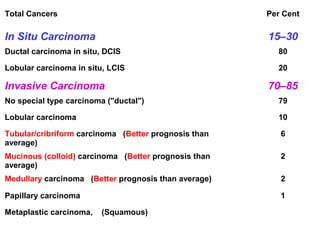
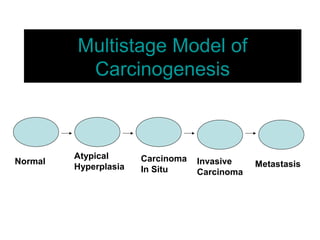
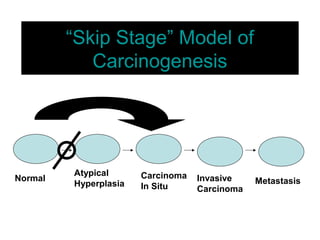
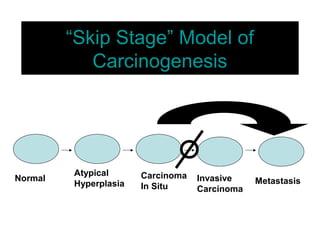
4. The main types of breast cancer are ductal carcinoma in situ, invasive ductal carcinoma, and invasive lobular carcinoma. Prognosis depends on cancer stage and characteristics.