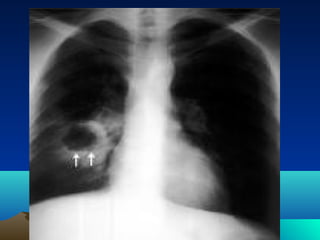
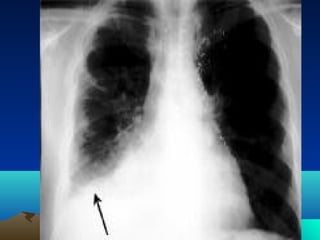
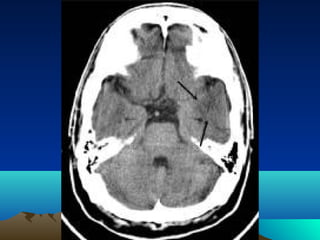
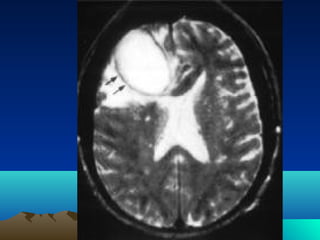
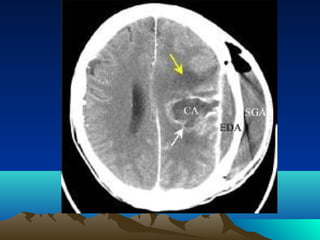
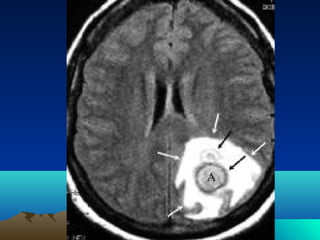
Cerebral and spinal abscesses are infections that can develop in the brain or spinal cord. Cerebral abscesses are usually caused by bacteria spreading from nearby infections through the bloodstream or openings in the dura. Clinical diagnosis involves patient history, symptoms like headache or seizures, and imaging tests like CT or MRI scans. Treatment may involve antibiotics alone or in combination with surgical drainage procedures. Outcomes depend on the patient's neurological condition, with mortality as high as 60% in cases of brain herniation. Spinal abscesses can be epidural, subdural, or intramedullary in nature and usually require both medical and surgical treatment.