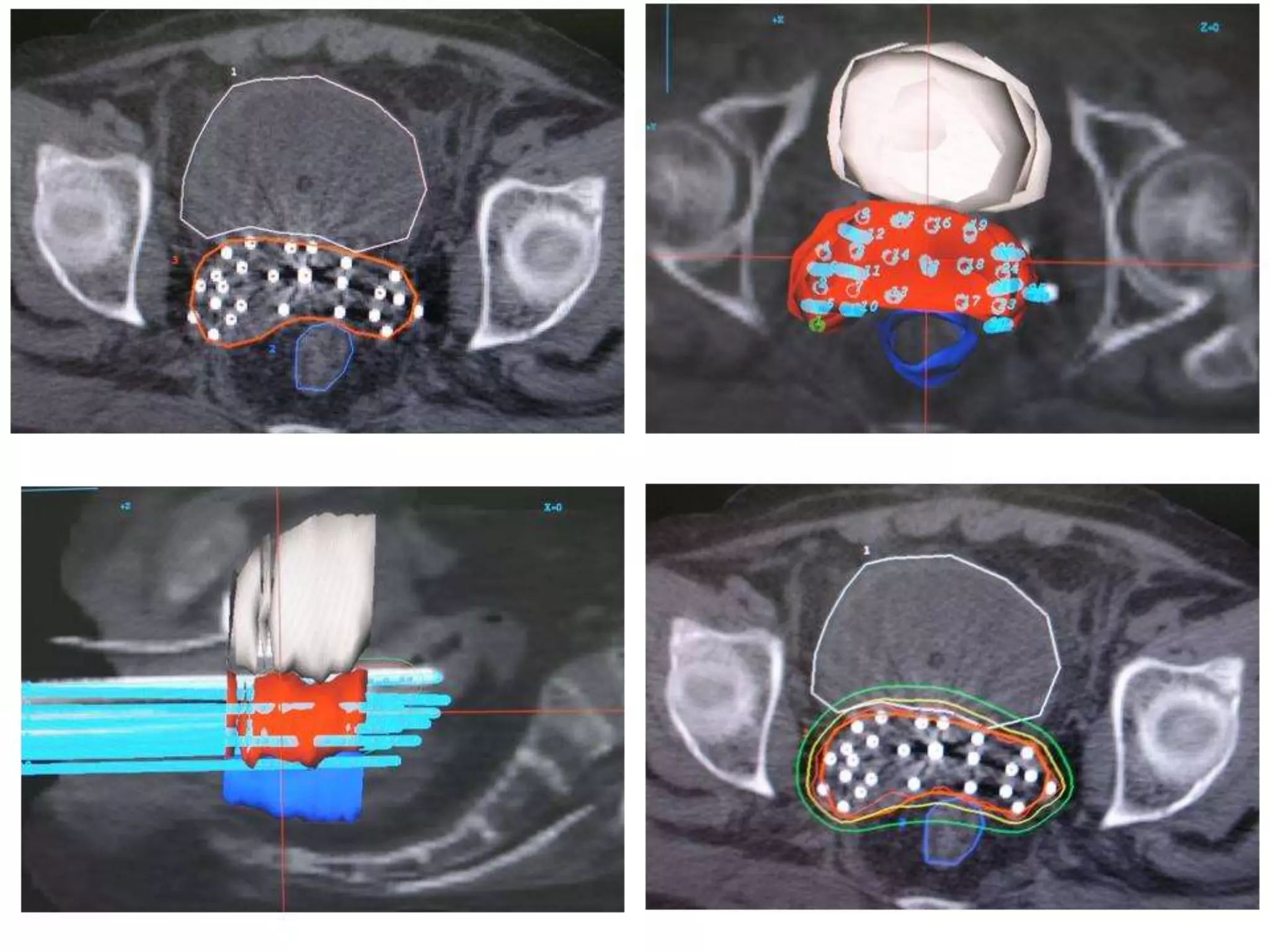
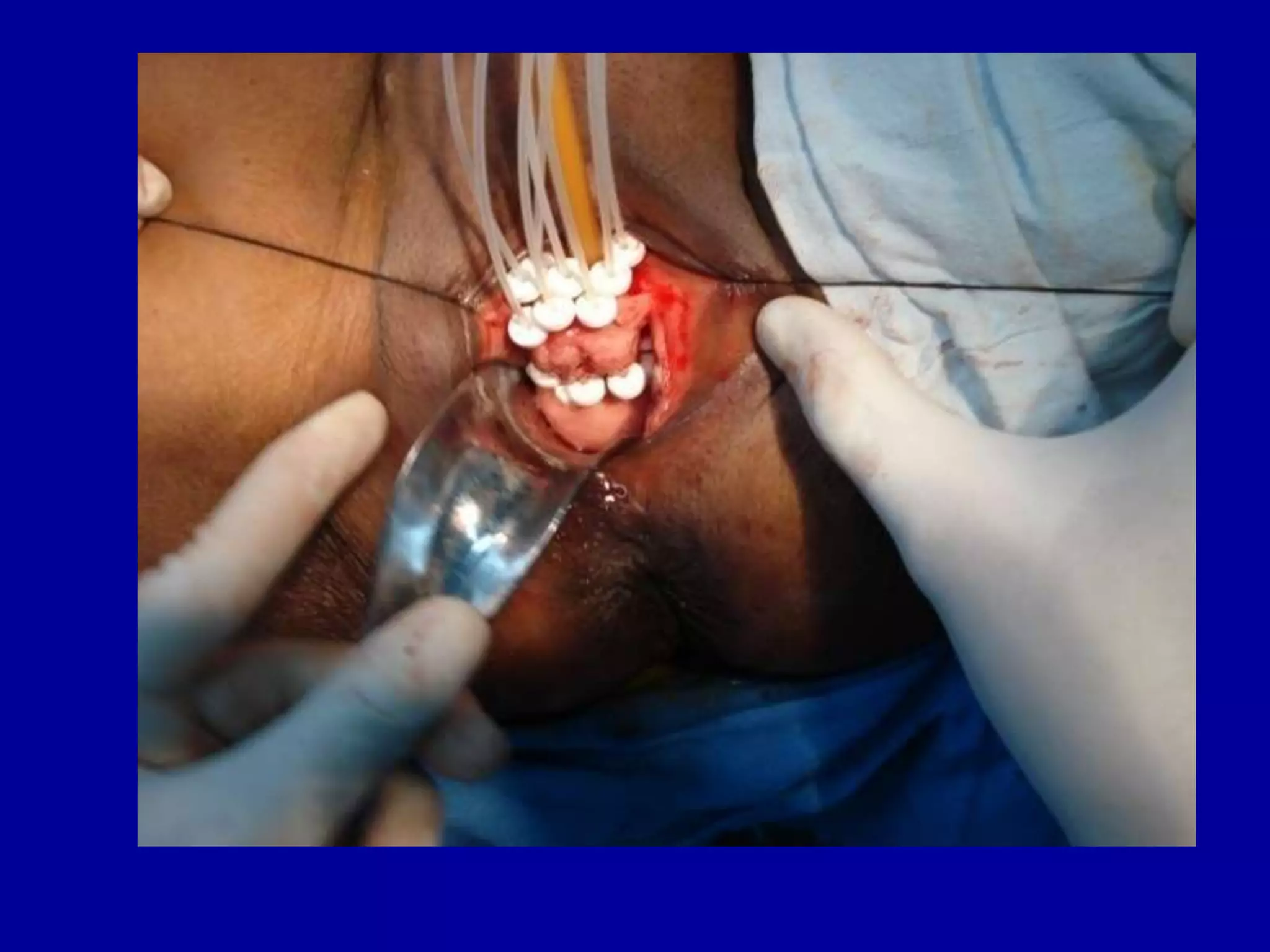
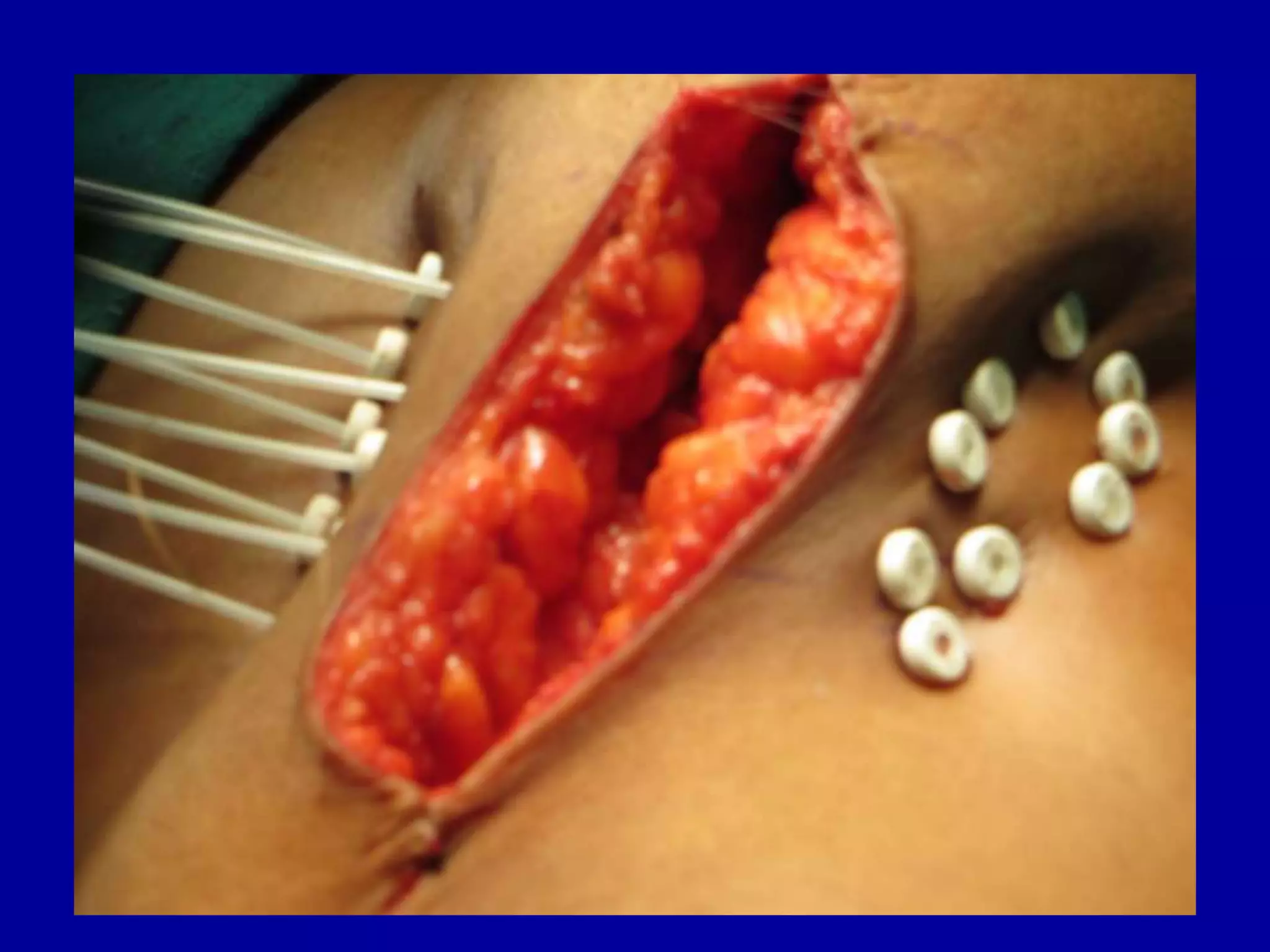
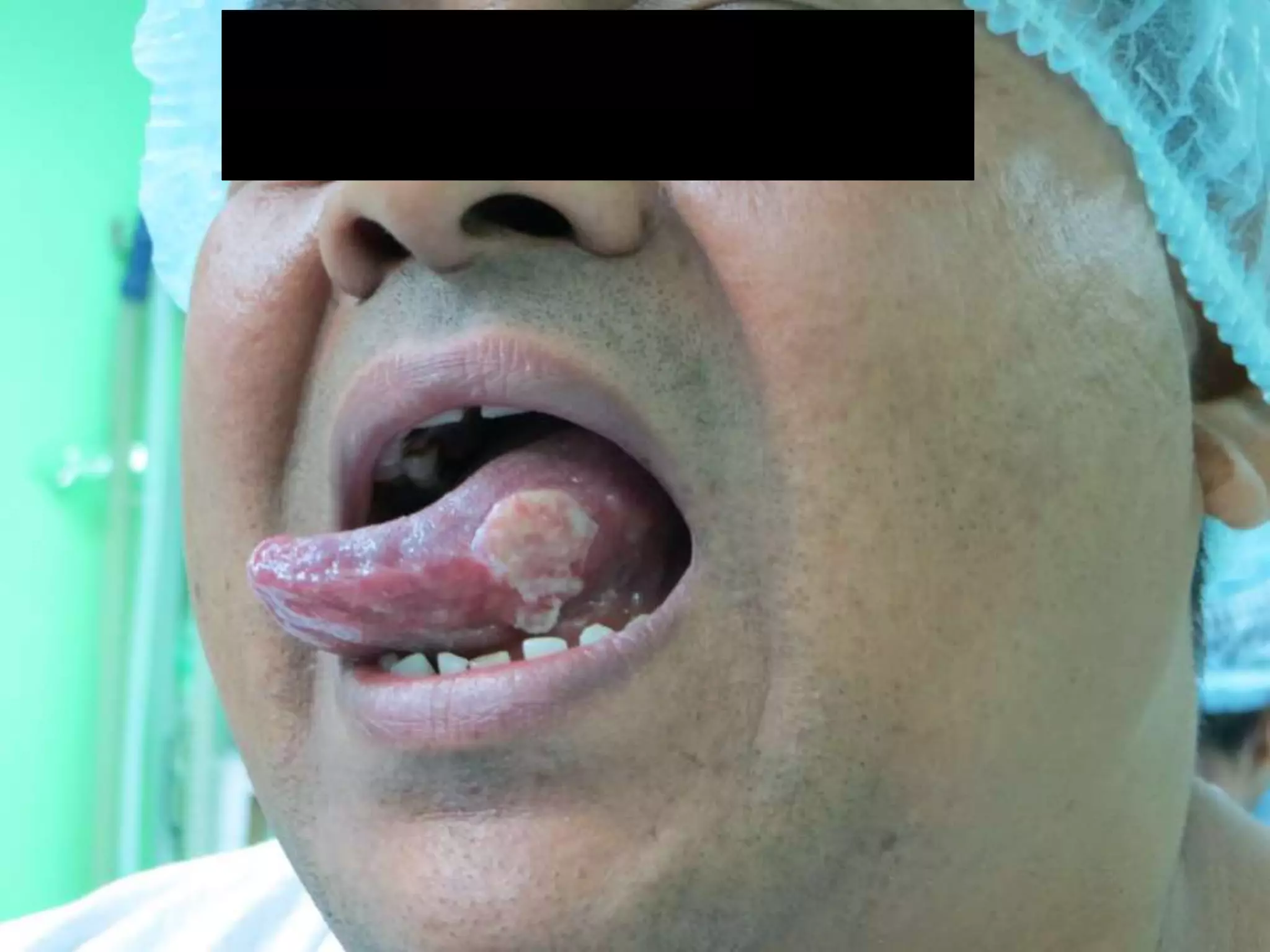
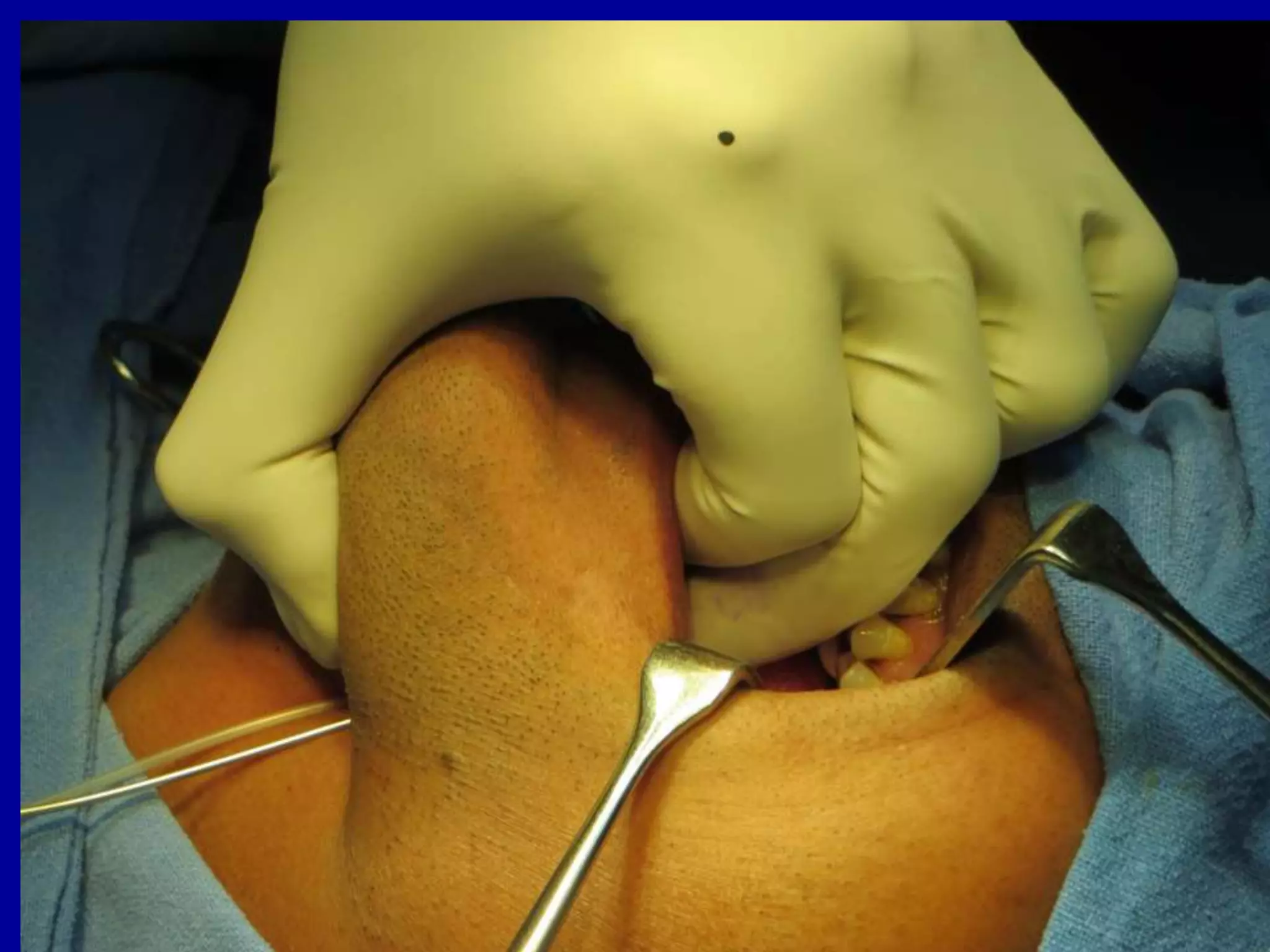
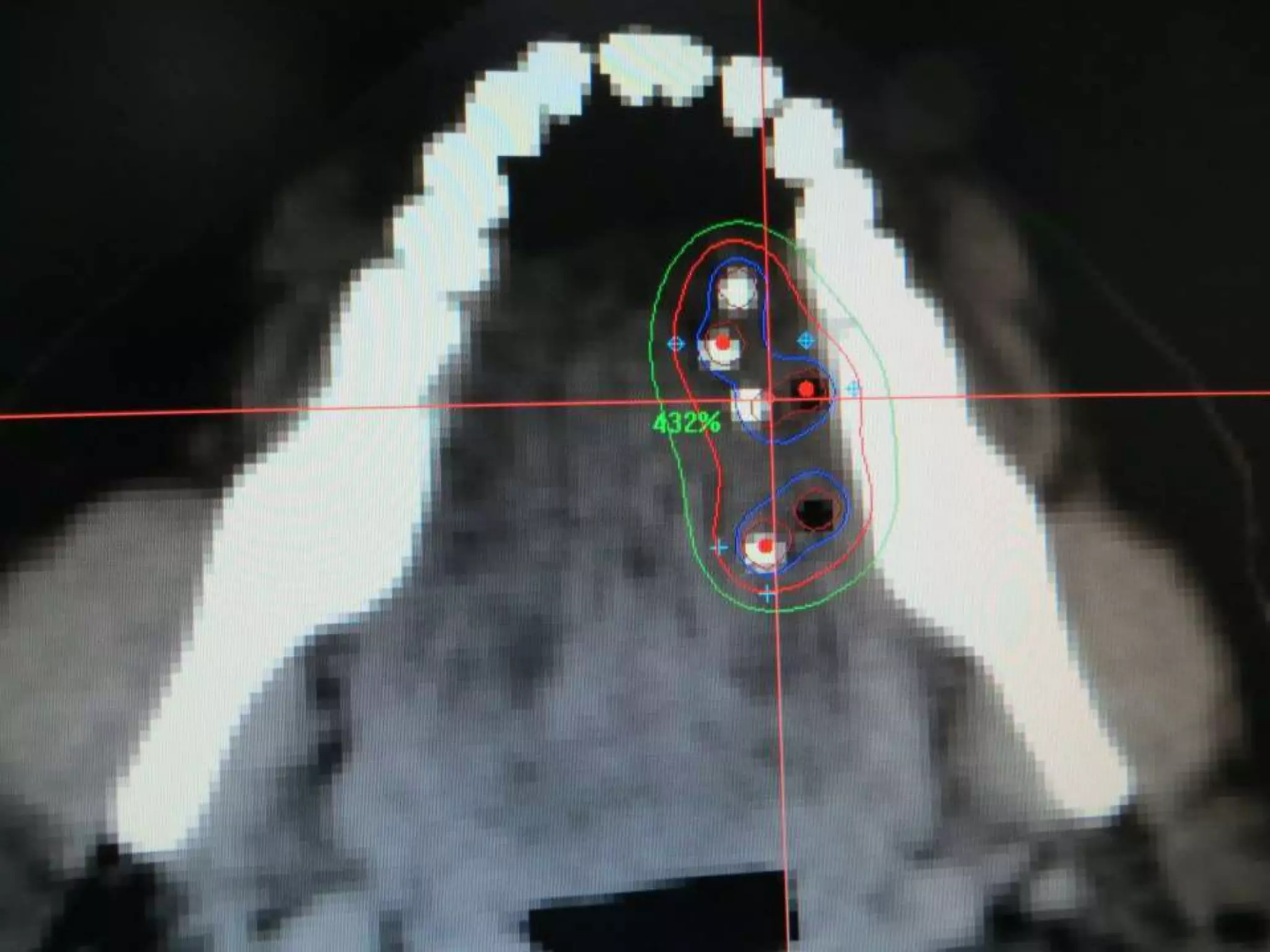
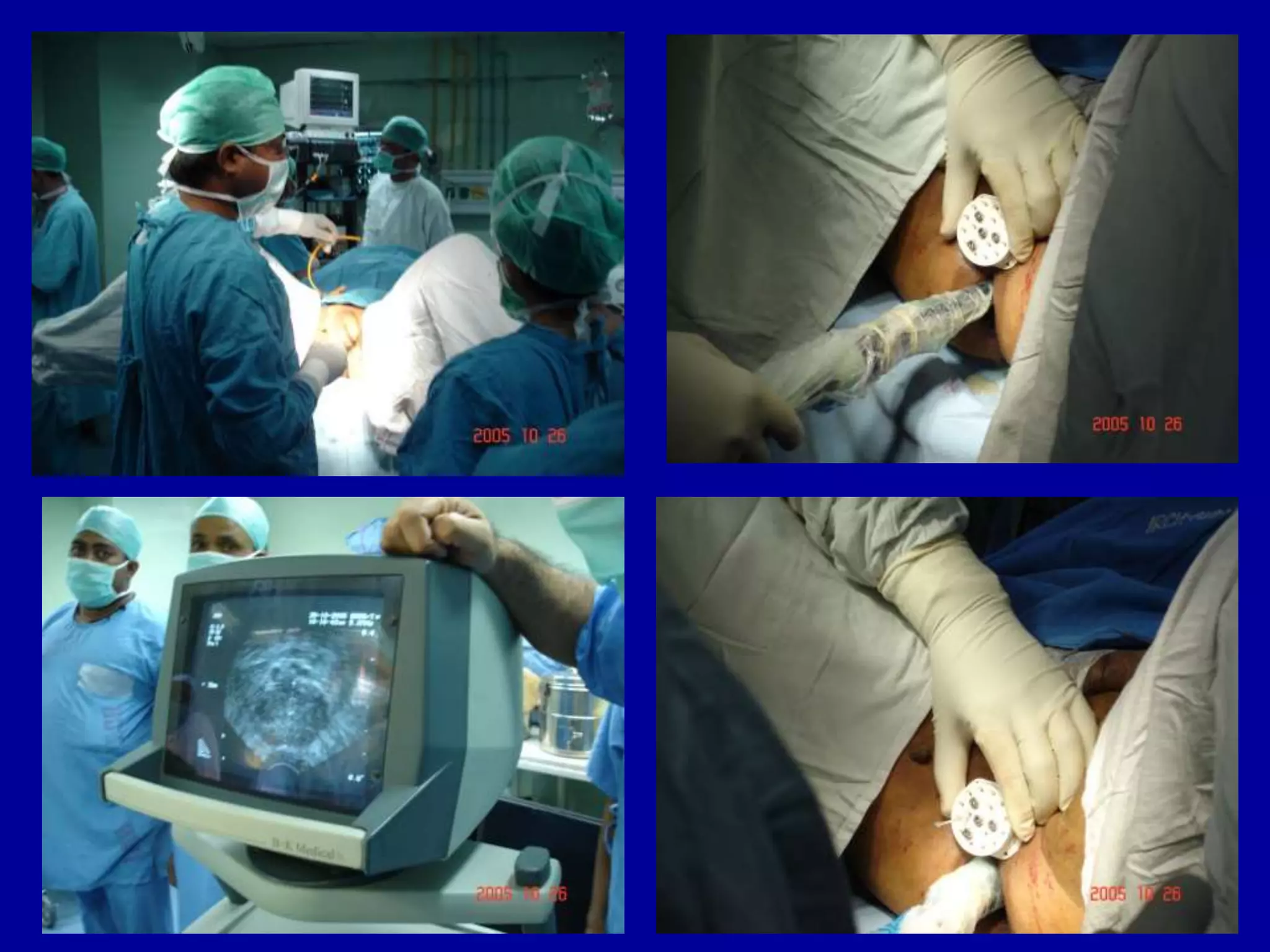
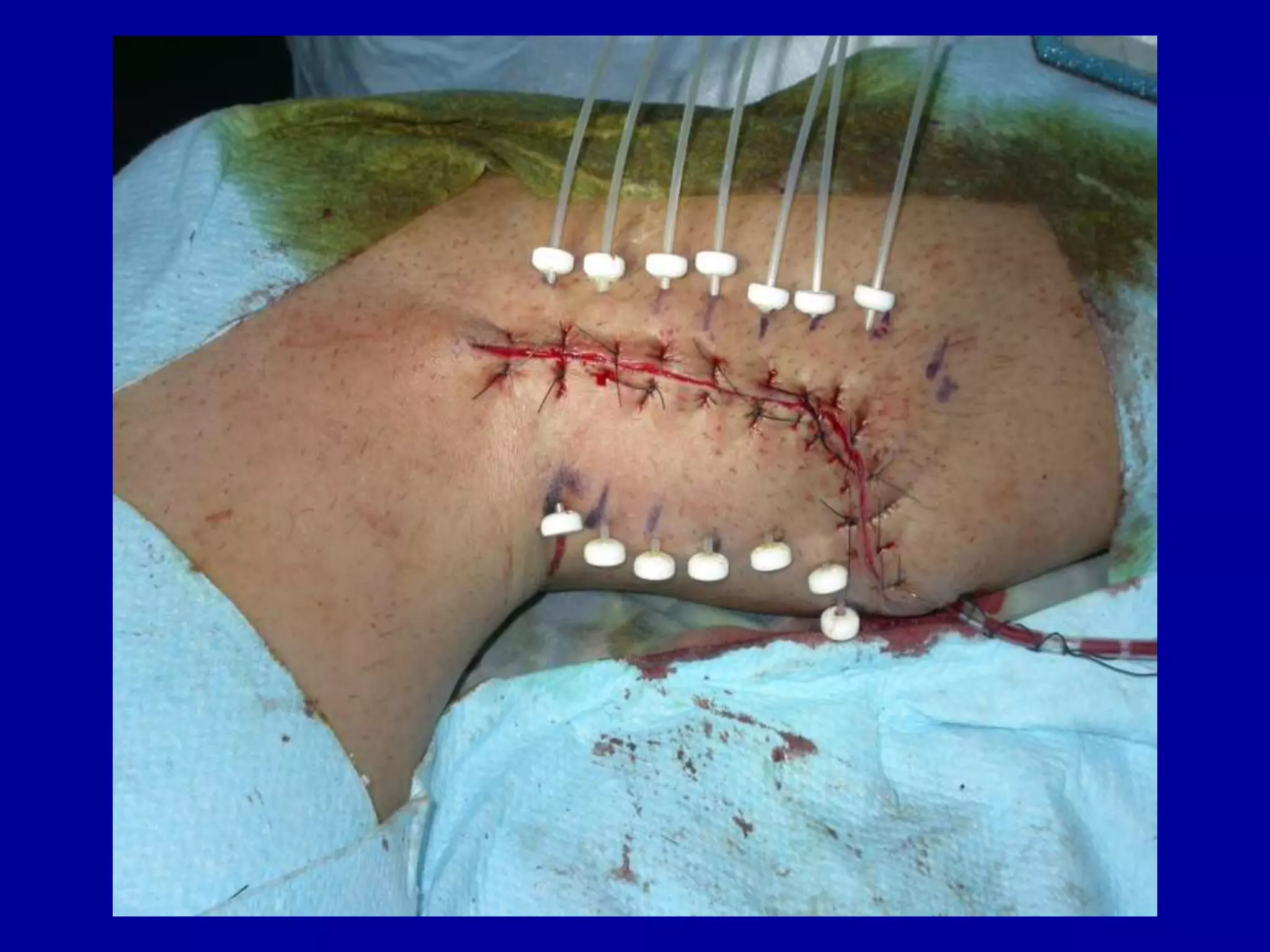
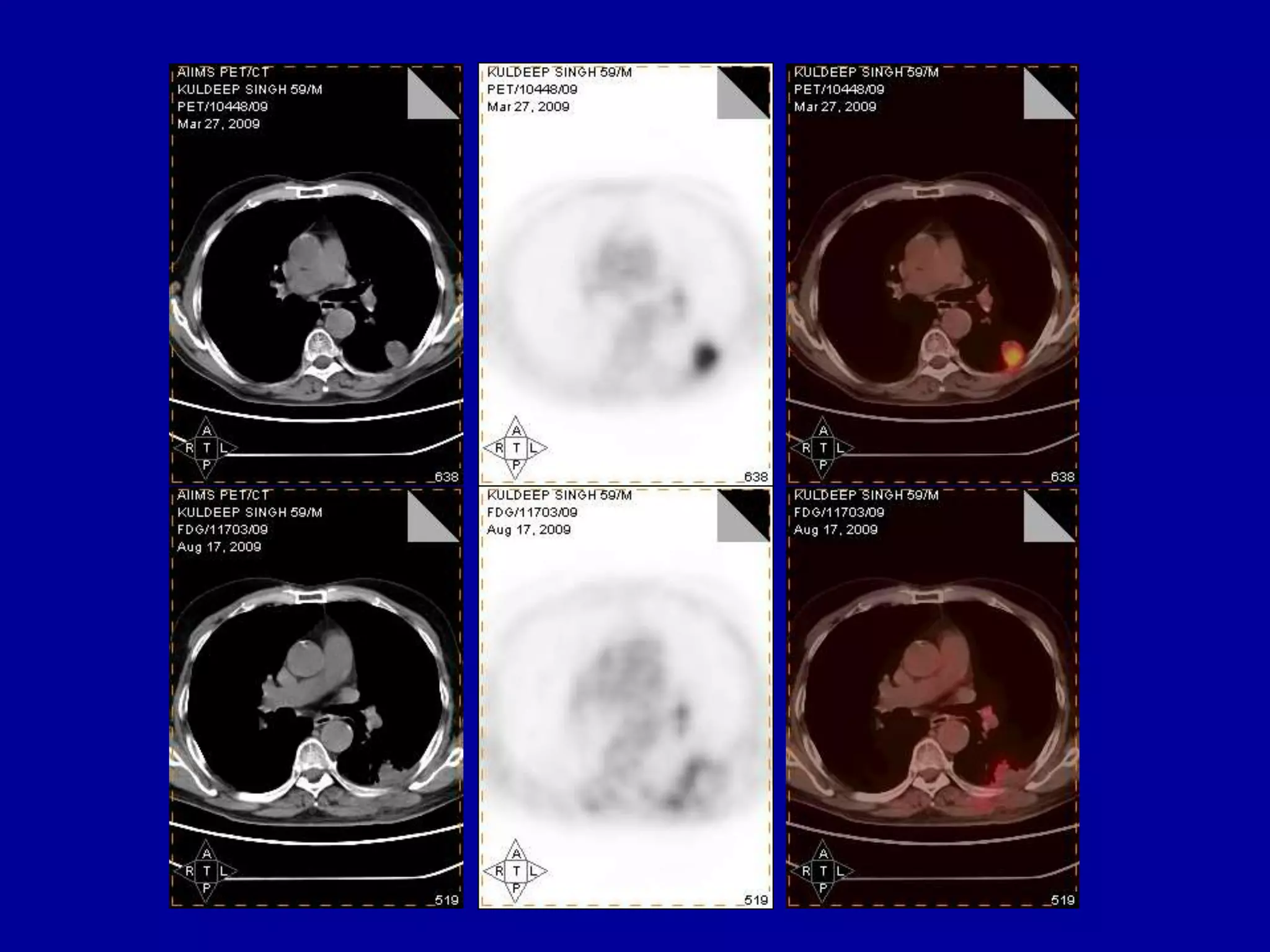
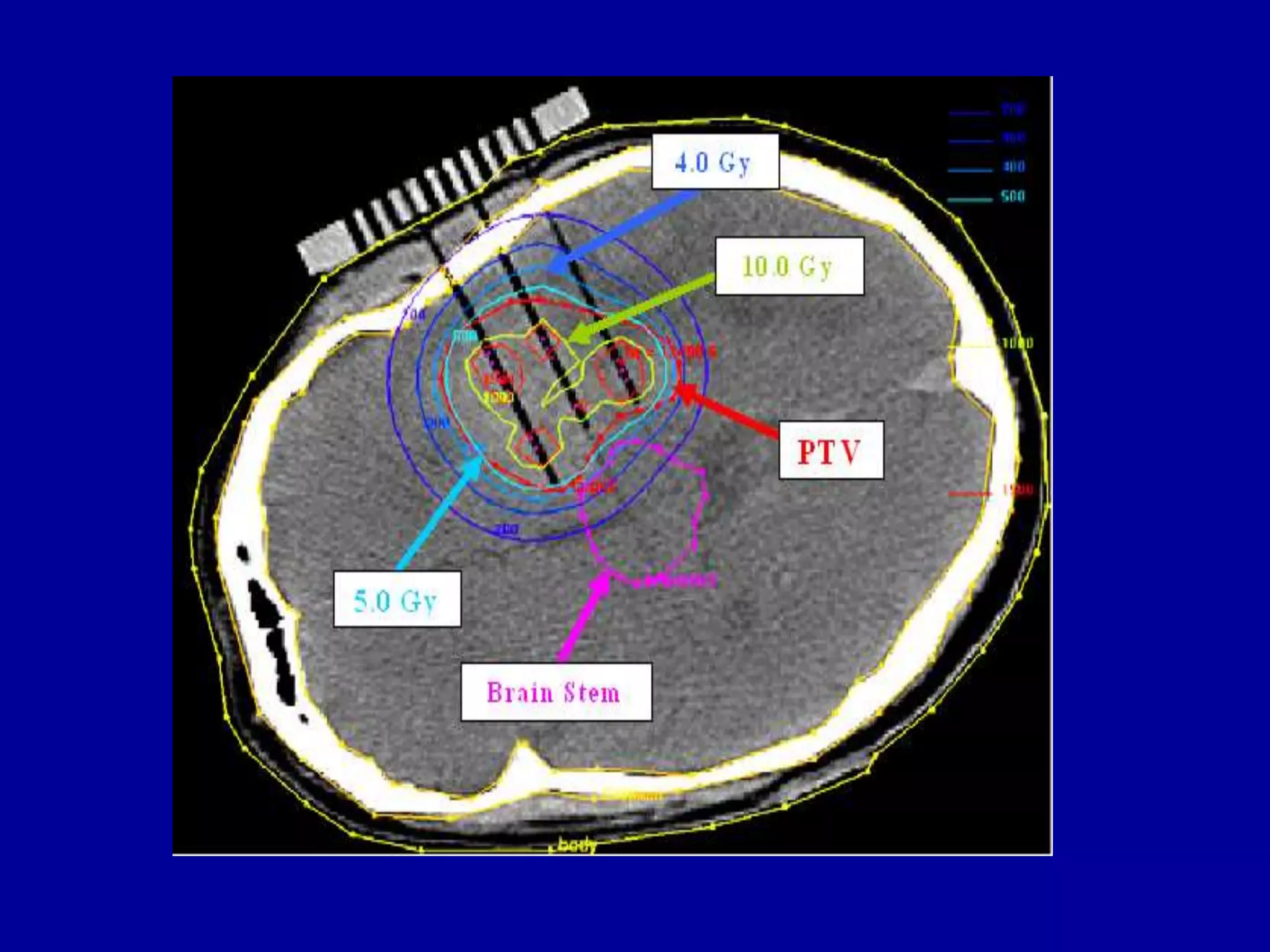
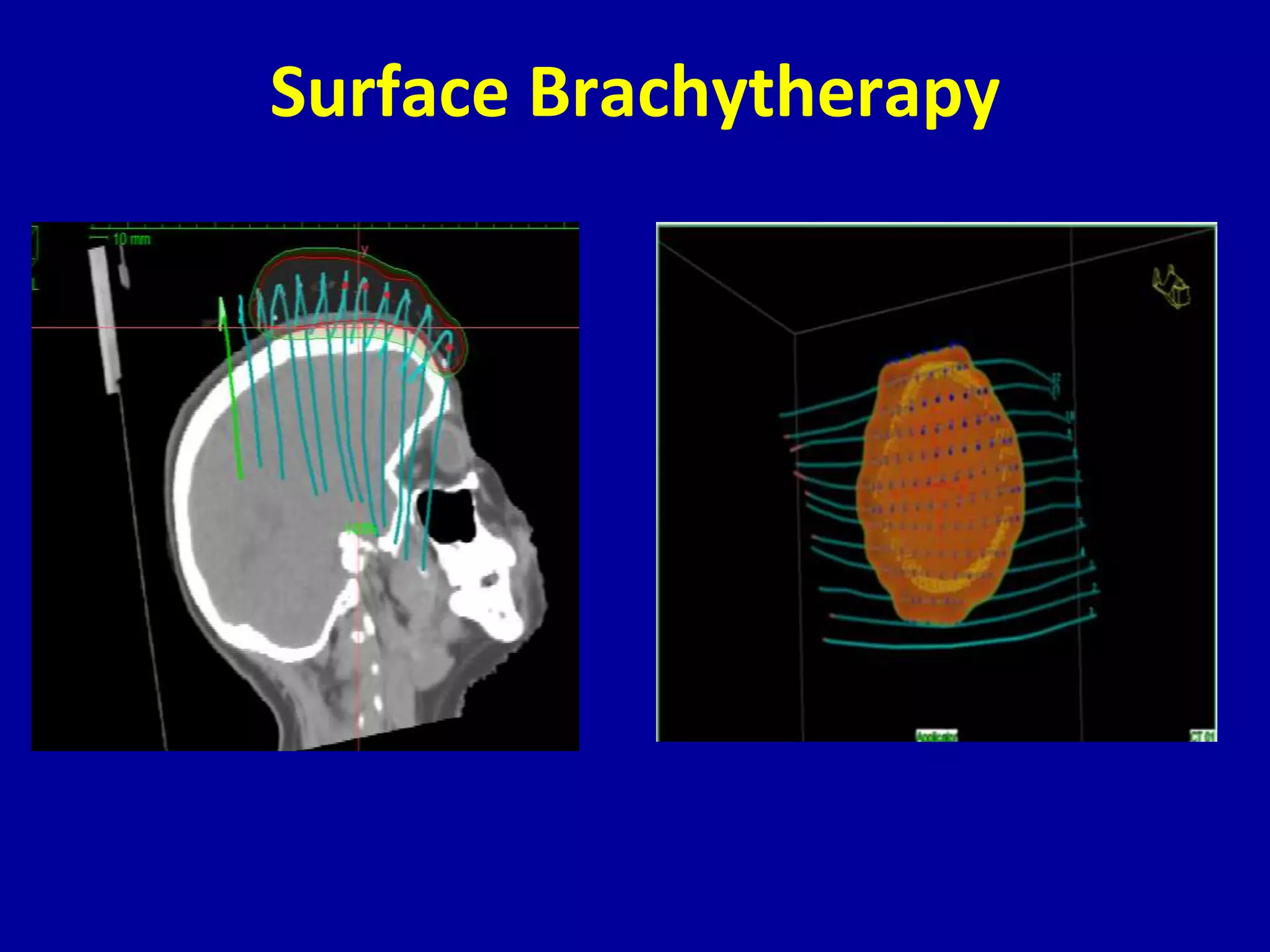
Brachytherapy involves placing radioactive sources inside or near a tumor to deliver radiation therapy. It is a type of radiotherapy that allows for a high dose of localized radiation to be administered to the tumor area while sparing surrounding healthy tissues from radiation exposure. Brachytherapy treatments are typically short in duration compared to external beam radiotherapy but require specialized equipment and skilled medical professionals for administration.