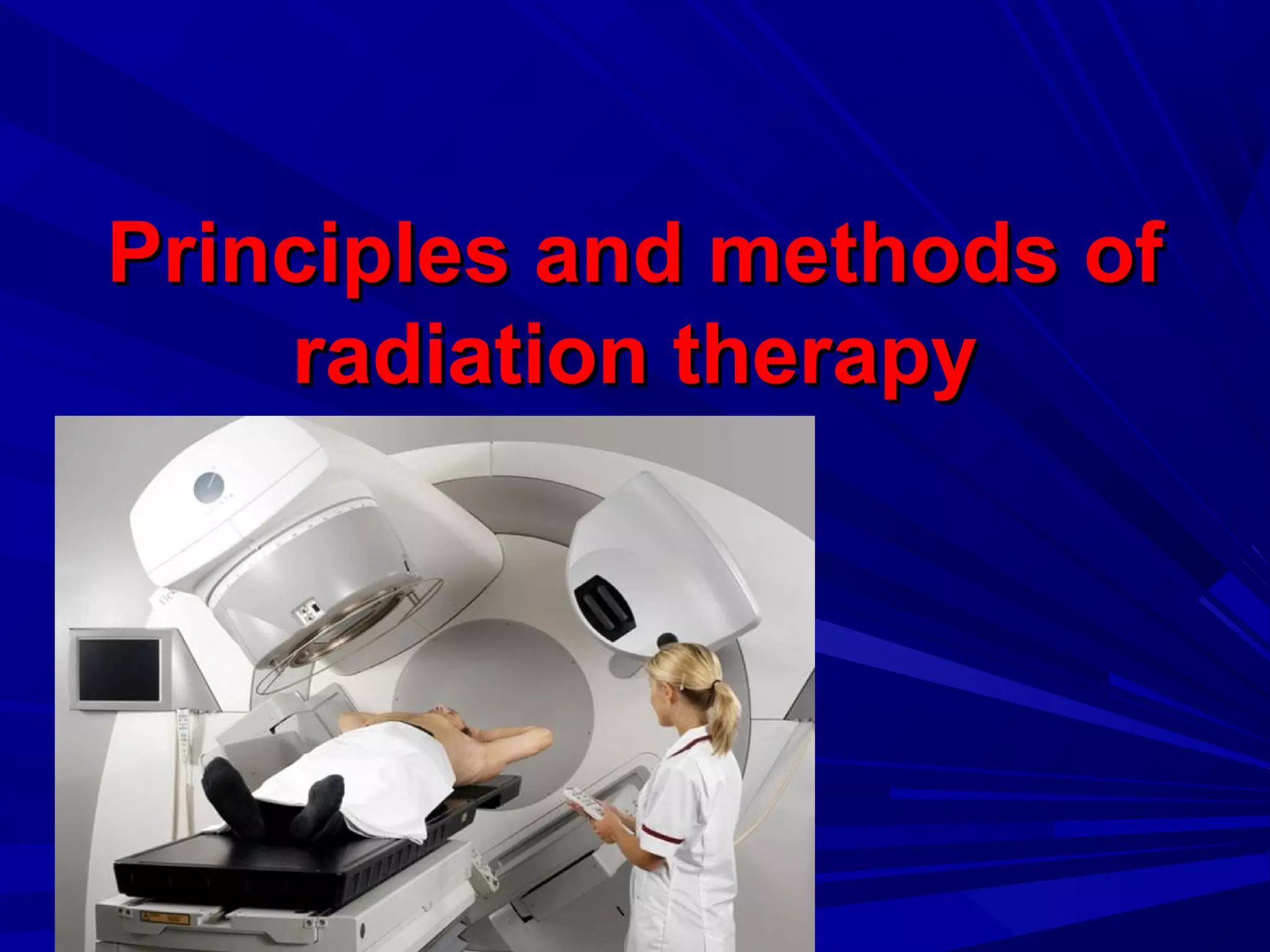
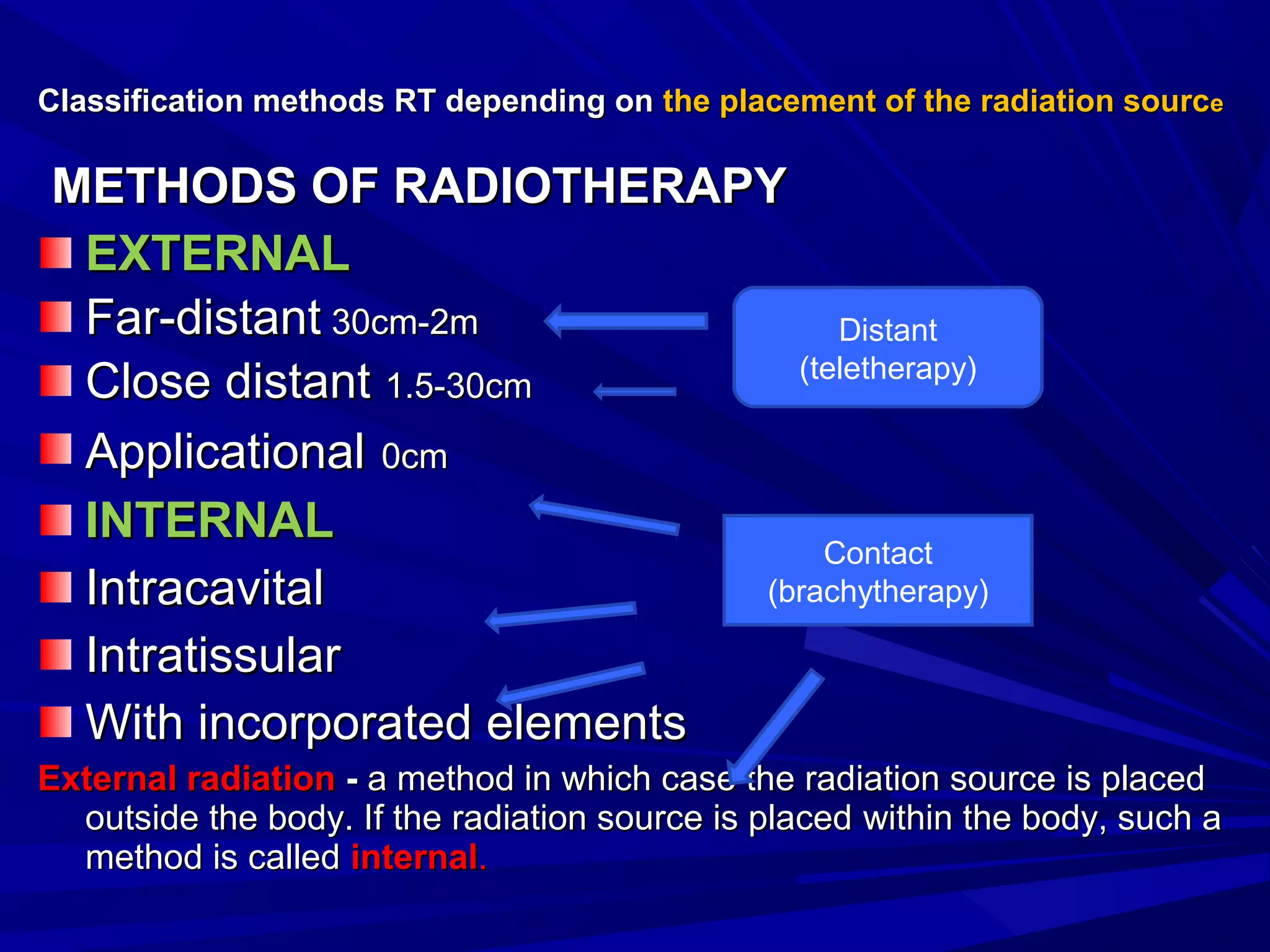
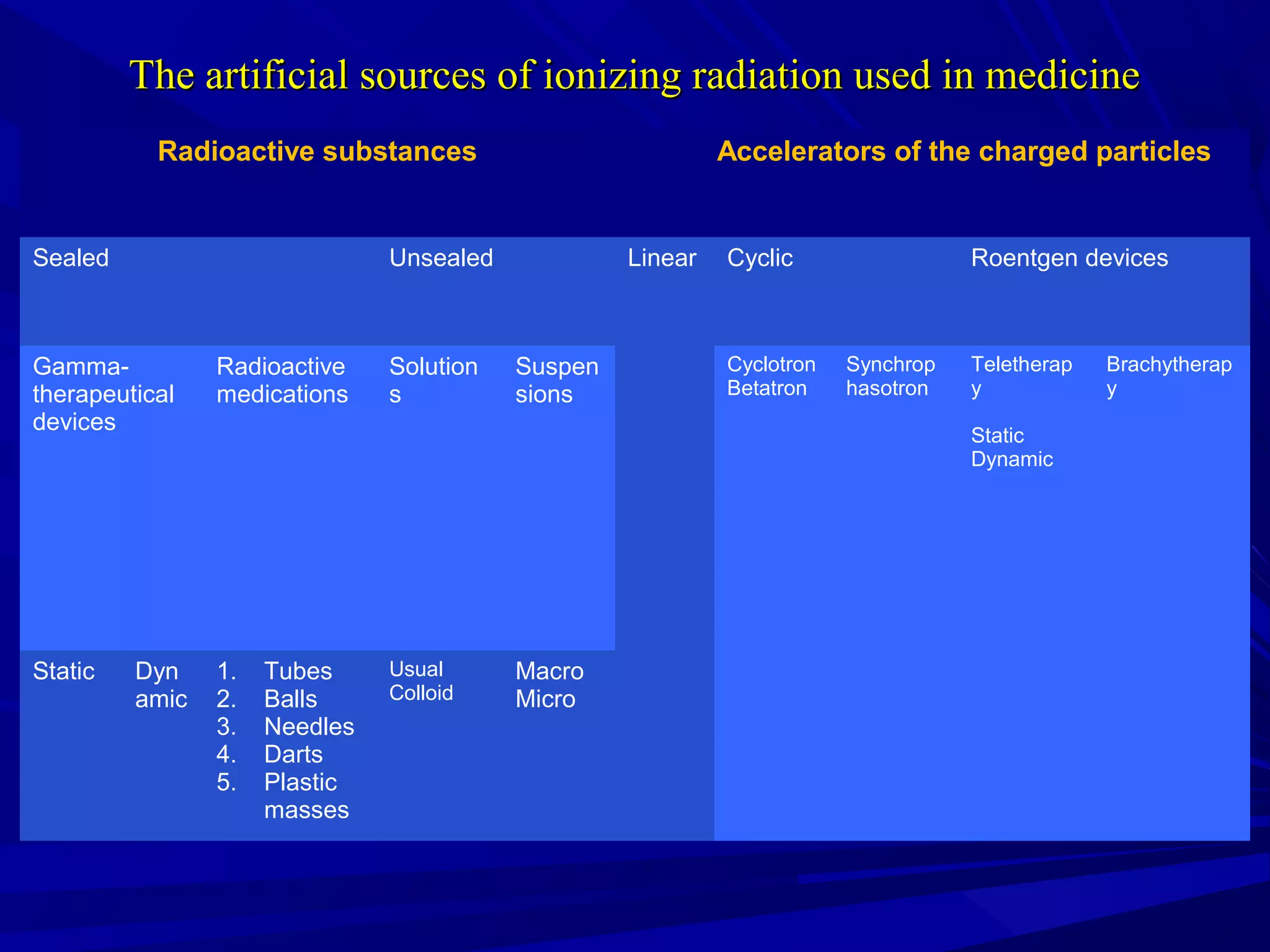
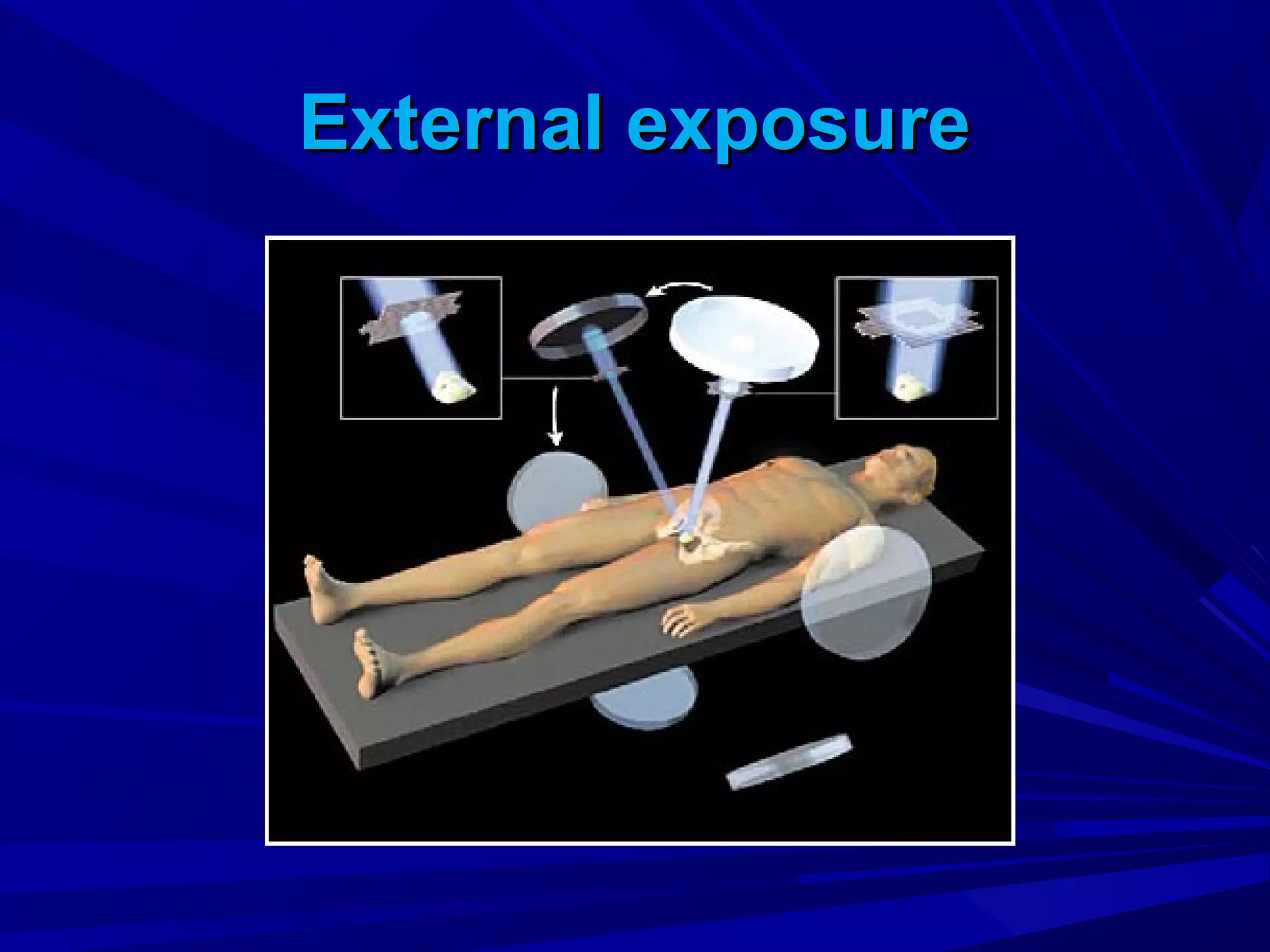
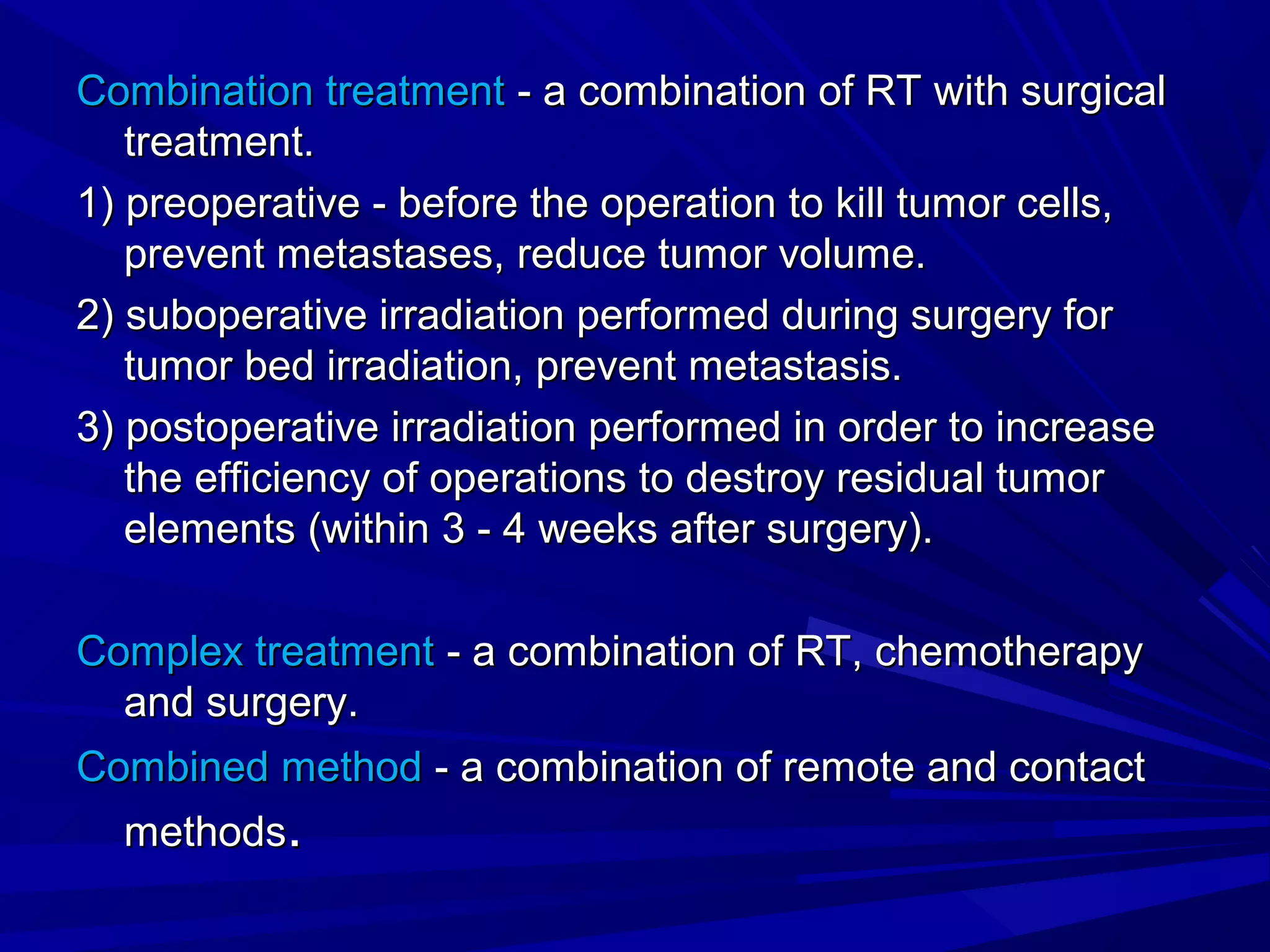
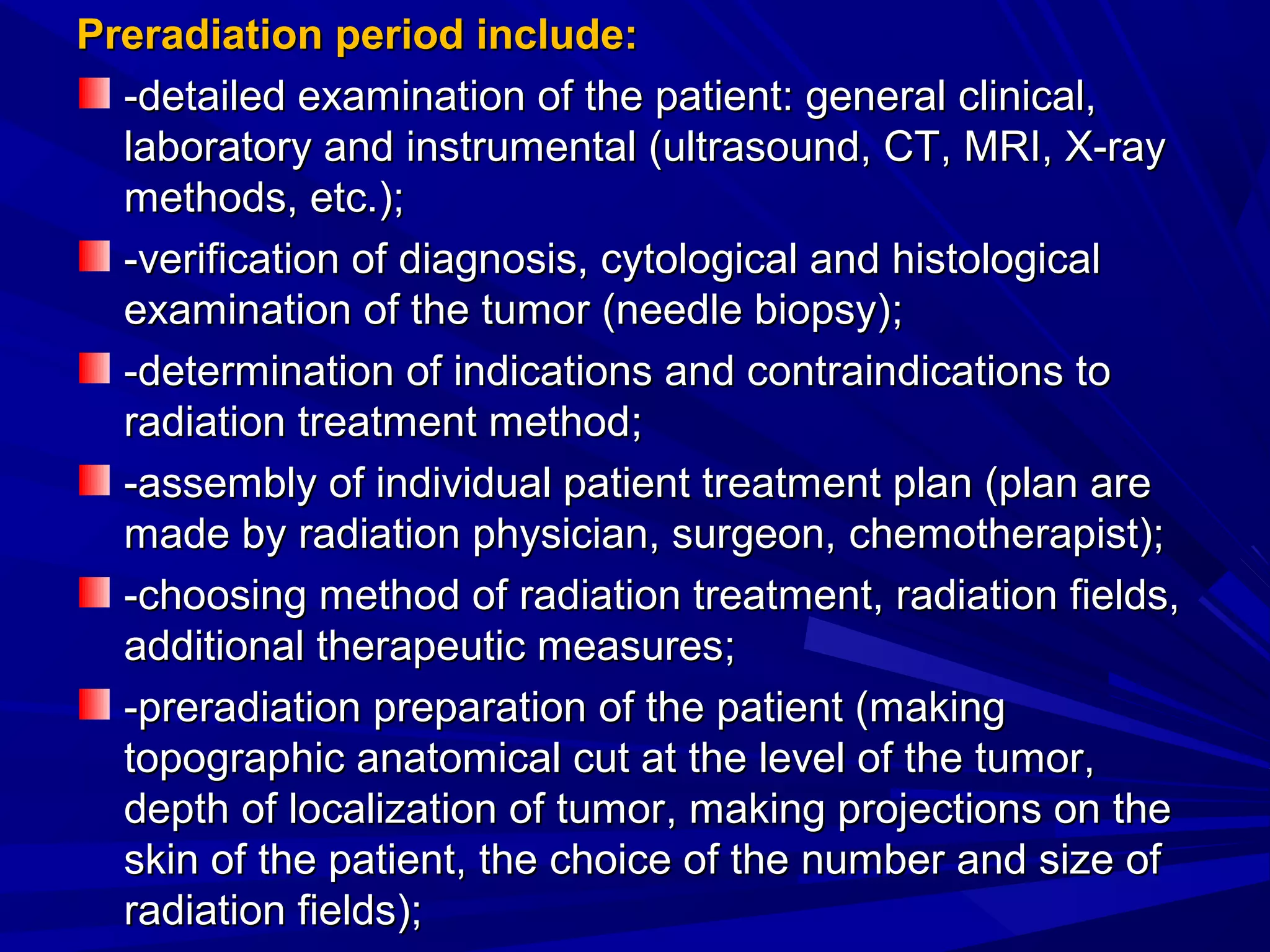
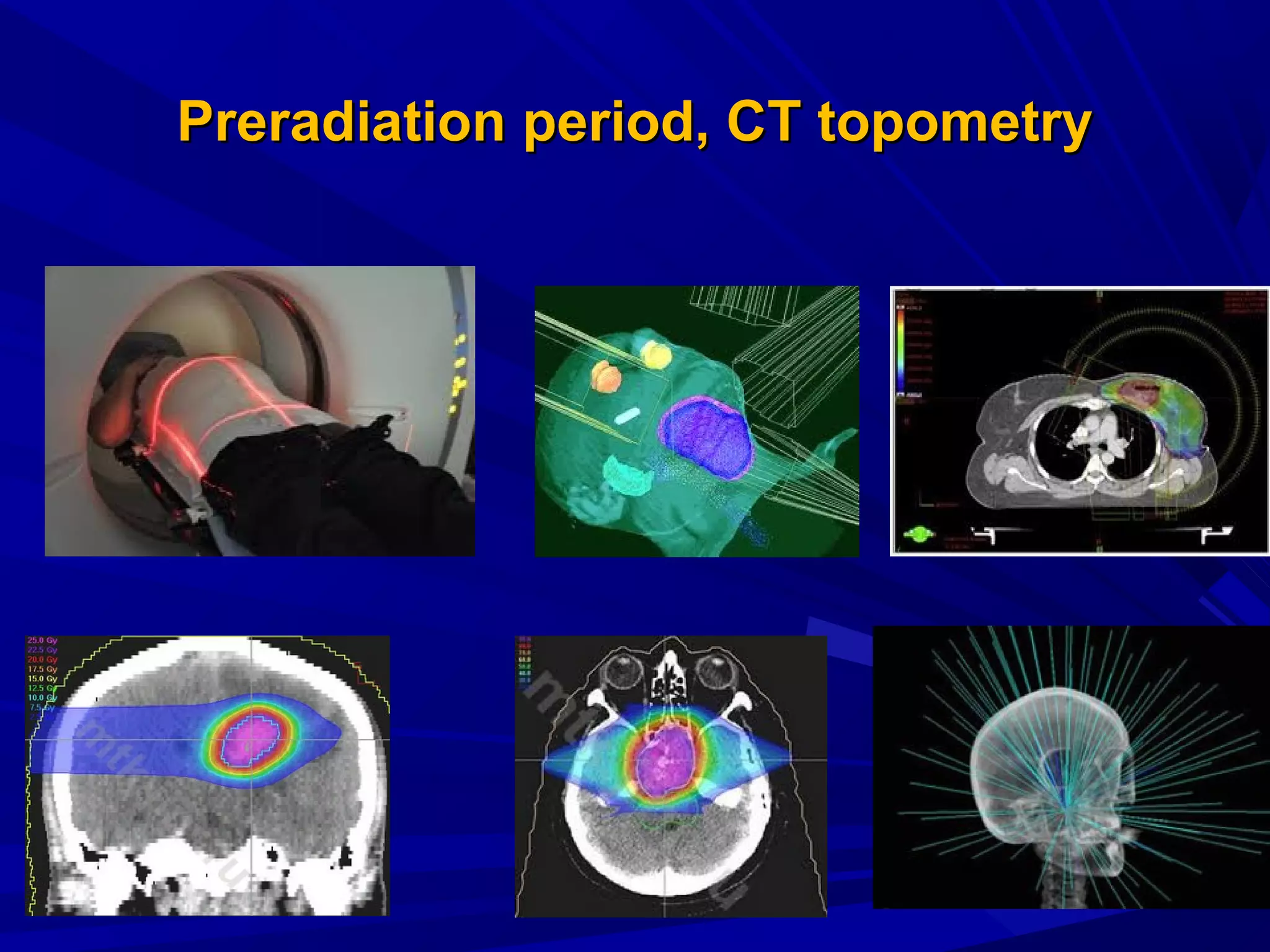
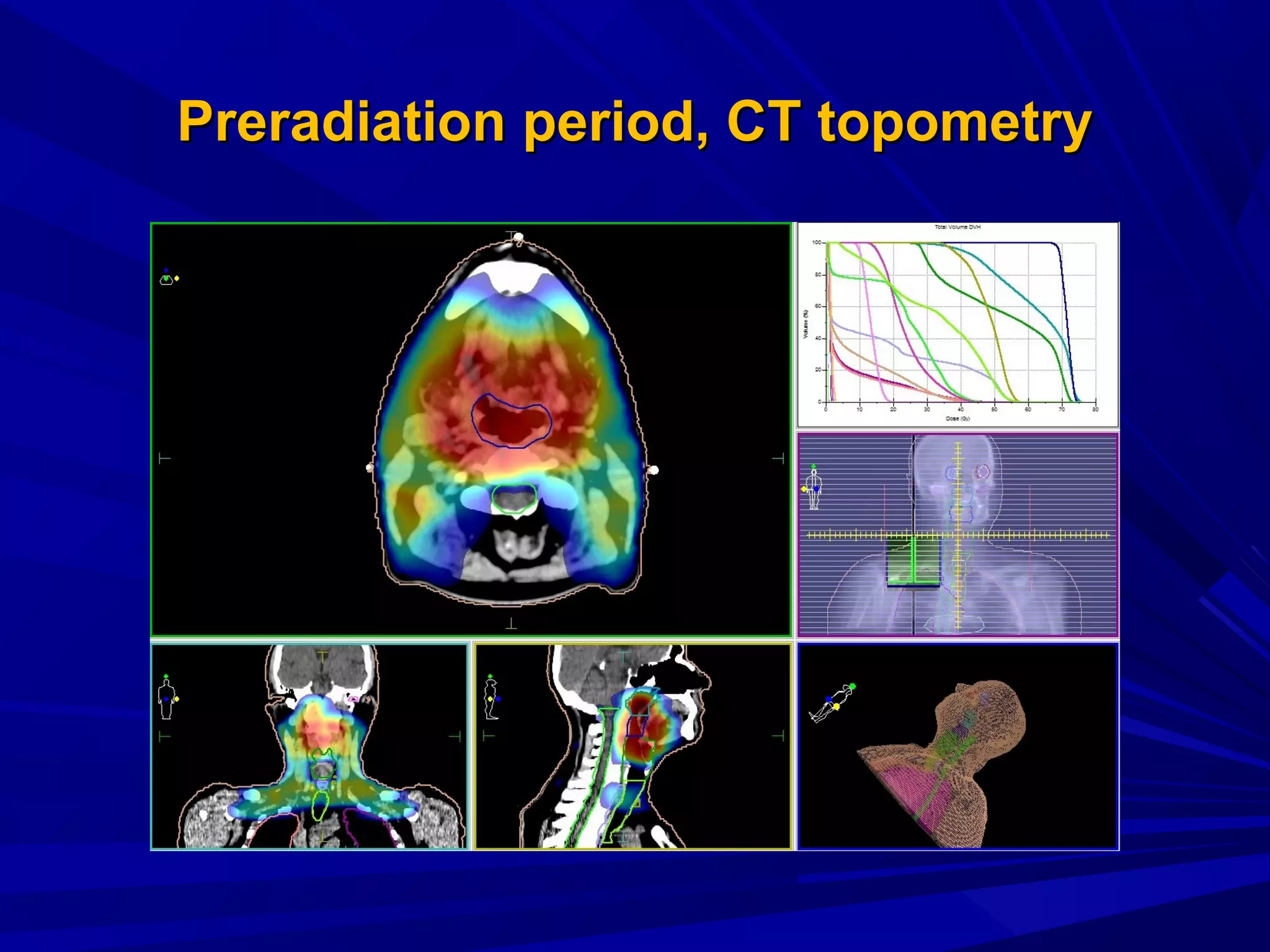
Radiation therapy involves using ionizing radiation to treat diseases. It is one method of medical radiology and examines using radiation to treat human diseases. The document discusses principles of radiation therapy including determining the optimal radiation dose with minimal damage to normal tissues. It describes external radiation methods, classification by radiation source placement, and goals of determining optimal dose while minimizing side effects. Radiation therapy consists of pre-radiation preparation and examination, the radiation period consisting of planned treatment sessions over weeks, and post-radiation evaluation and follow-up.