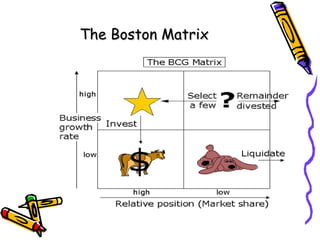
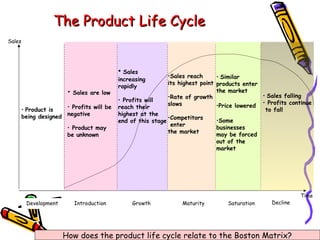
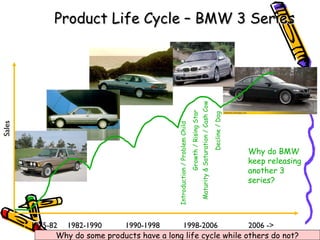
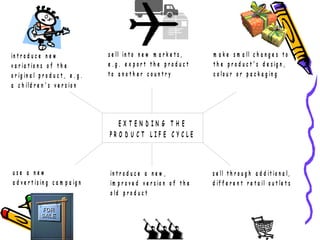
Product portfolio analysis involves identifying the position of each product in a company's portfolio based on its market share and the market's growth. The Boston Matrix is a common method used, classifying products as stars, cash cows, question marks or dogs. Stars have high market share in growing markets while cash cows have high share in stagnant markets. Question marks have low share but are in growing markets, while dogs have low share in declining markets. Extending a product's lifecycle can involve introducing variations, exporting to new markets, minor redesigns, new advertising, or improved versions. The next class will cover the price aspect of the marketing mix.