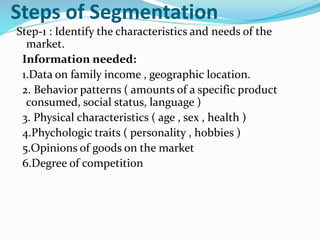
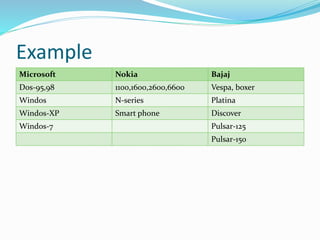
The document discusses the concepts of marketing and market segmentation, defining marketing as a series of activities aimed at fulfilling consumer needs and building strong customer relationships. It outlines the marketing process, including identifying target markets, analyzing needs, and creating products to meet those needs, as well as the importance of segmentation based on demographics, geography, psychographics, and benefits. Additionally, it details the marketing mix, including product, price, promotion, and place strategies while emphasizing the product life cycle and new product development.