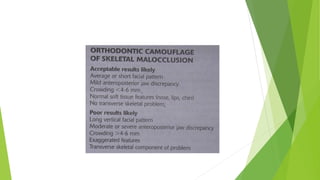
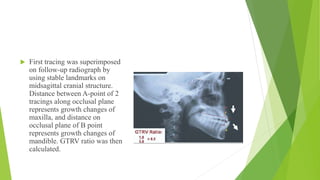
This document discusses factors to consider when evaluating borderline cases in orthodontics that are between requiring extraction versus non-extraction treatment. It outlines various clinical examinations, cephalometric evaluations, and indices used to assess tooth-size arch length deficiency, lip prominence, curve of spee, and skeletal and dental variables to determine whether extraction is necessary to achieve functional occlusion or if non-extraction can be used. Borderline cases are defined as those with permanent dentition, healthy periodontium, normal anteroposterior maxilla-mandible relationship, and where extraction may be needed to obtain stable occlusion but could impact facial aesthetics.