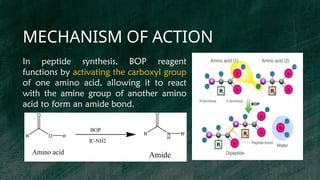
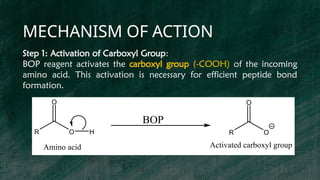
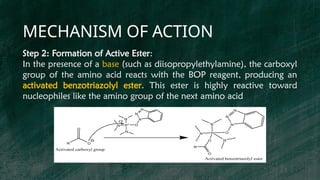
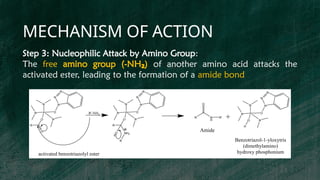
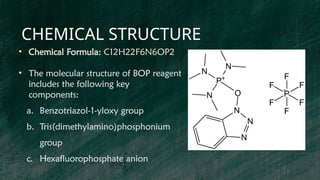
BOP reagent (benzotriazol-1-yloxytris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate) is a synthetic coupling agent used in peptide synthesis for forming amide bonds during amino acid coupling. Its synthesis involves multiple steps, including the formation of a tris(dimethylamino)phosphine intermediate and reaction with 1-hydroxybenzotriazole, resulting in the final BOP compound. The reagent is favored for its low racemization, versatility, and compatibility in solid-phase peptide synthesis, although it has drawbacks such as potential toxicity and cost.


![SYNTHESIS OF BOP REAGENT
P
N N
N
N
N
N
OH
P+
N
N
N
O
N
N
N
Cl-
1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-ol
tris(dimethylamino)phosphine
intermediate.
((1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-
yl)oxy)tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium chloride
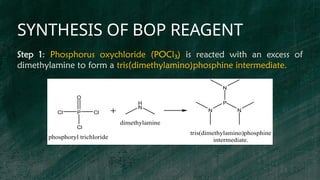
Step 2: This intermediate is then reacted with 1-Hydroxybenzotriazole
(HOBt) to produce Benzotriazol-1-yloxytris(dimethylamino)phosphonium
chloride.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bopreagent-240929030844-bfaf0816/85/BOP-REAGENT-SYNTHETIC-COUPLING-REAGENT-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![SYNTHESIS OF BOP REAGENT
P+
N
N
N
O
N
N
N
Cl-
P+
N
N
N
O
N
N
N
P-
F
F
F
F
F
F
((1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-
yl)oxy)tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium chloride
NH4PF6
((1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-
yl)oxy)tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate
Step 3: The final step involves exchanging the chloride ion with
hexafluorophosphate (PF )
₆⁻ by treating the phosphonium chloride with a
hexafluorophosphate salt to form the BOP (Benzotriazol-1-
yloxytris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate) reagent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bopreagent-240929030844-bfaf0816/85/BOP-REAGENT-SYNTHETIC-COUPLING-REAGENT-pptx-6-320.jpg)