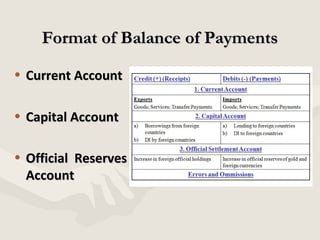
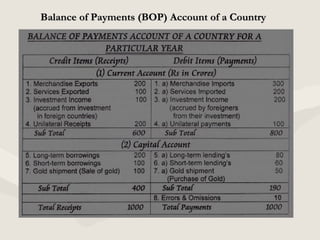
This document provides an overview of balance of payments (BOP). It defines BOP as a systematic record of all economic transactions between residents of a country and foreign countries. It notes that BOP has two sides, includes both visible and invisible items, and is prepared for a certain period of time. The main components of BOP are the current account, capital account, and official reserves account. The current account covers trade in goods and services and transfers, while the capital account covers financial assets. A BOP surplus occurs when payments received exceed payments made, while a deficit is when payments made exceed receipts. For accounting purposes, the BOP of a country must always balance as every debit has an offsetting credit.