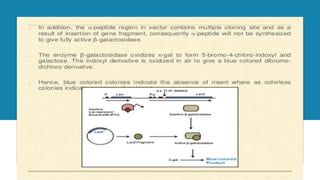
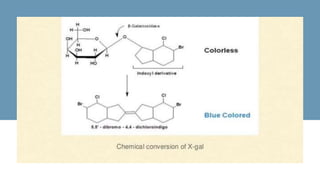
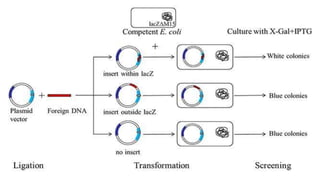
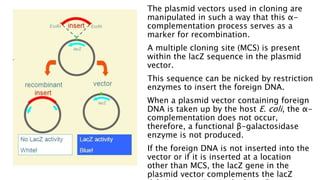
The document details the blue-white screening technique for identifying recombinant bacteria, utilizing the enzyme β-galactosidase in E. coli. It explains how the α-complementation of the lacZ gene works, whereby a functional β-galactosidase enzyme is produced in the presence of a functional lacZ gene, leading to blue colonies, while non-recombinant bacteria form white colonies. This method leverages specific plasmid vectors and the manipulation of the lacZ gene to facilitate the insertion of foreign DNA.