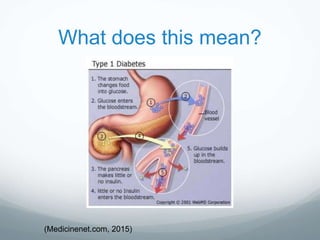
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This results in insulin deficiency and the need for external insulin administration. It accounts for approximately 5% of diabetes cases and usually develops in childhood or early adulthood. Long-term effects of uncontrolled type 1 diabetes can include damage to organs like the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. Proper management is needed to minimize health risks and maximize quality of life.

![What is type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disorder where the
beta cells in the pancreas are destroyed or unable to
make enough insulin to support the body (American
Diabetes Association [ADA], 2015).
In type 1 DM, the person become insulin dependent
and requires close monitoring.
Diagnosis usually occurs in a person’s juvenile years,
but can happen at any time.
Type 1 DM accounts for approximately 5% of diabetes
cases (ADA, 2015).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blueteam-150826221616-lva1-app6891/85/Blue-team-2-320.jpg)