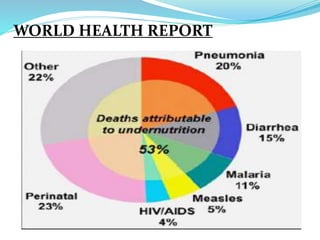
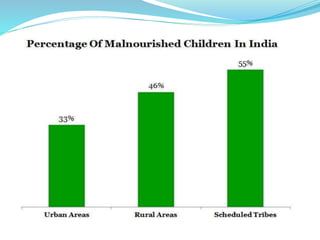
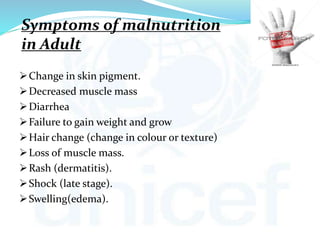
This document discusses malnutrition, including its definition, types, causes, symptoms, and treatment. Malnutrition is defined as a cellular imbalance between the supply of nutrients and energy and the body's demand. There are four main types: undernutrition, overnutrition, imbalance, and specific deficiency. Causes can be related to food, such as lack of a nutritious diet, or general factors like disease, poor environment, and lack of exercise. Symptoms vary depending on if the malnutrition is in adults or children but can include hair/skin changes, edema, fatigue, and failure to grow. Treatment involves resolving life-threatening conditions, restoring nutritional status through dietary management, and rehabilitation through nutritional education.