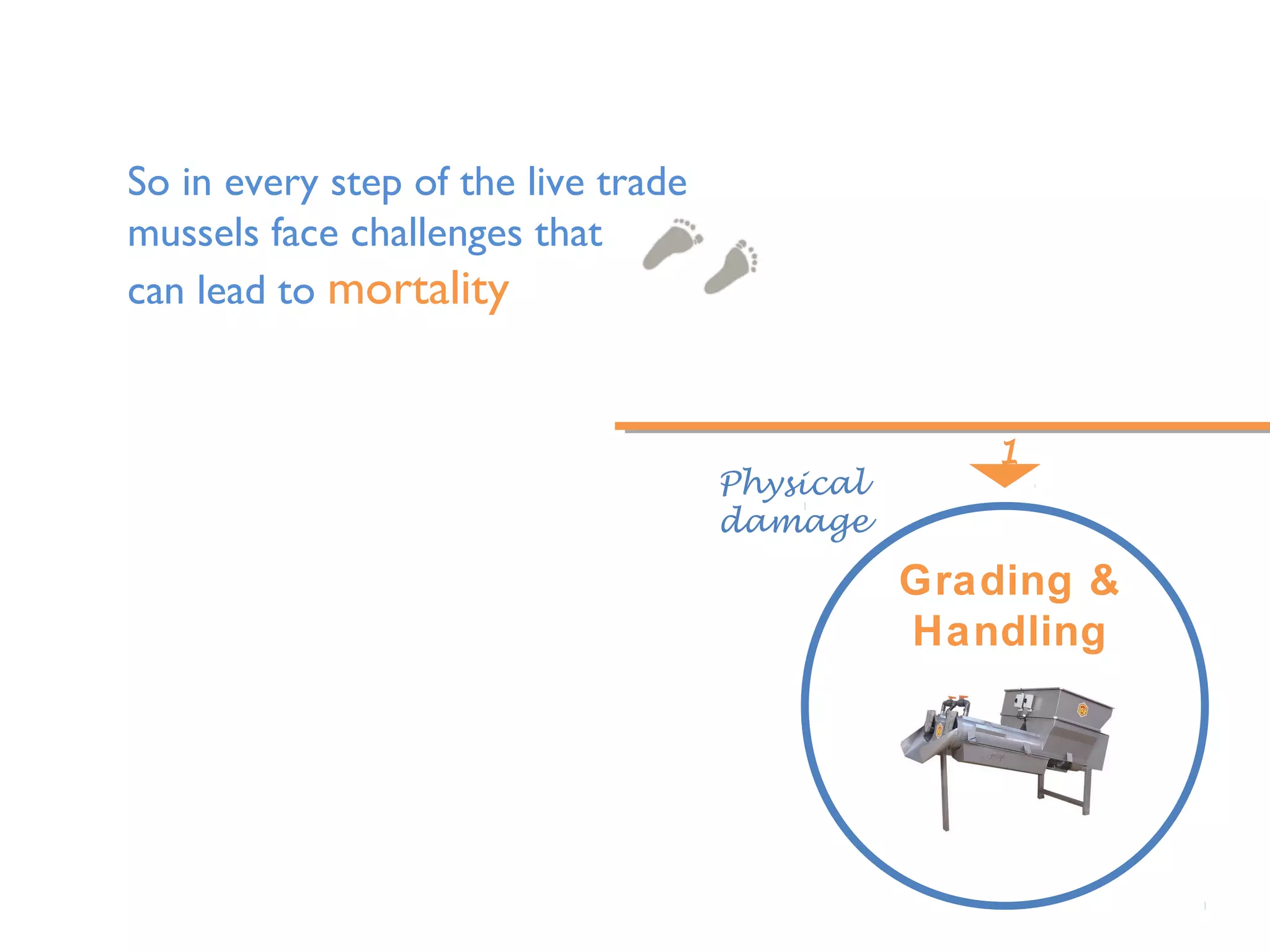
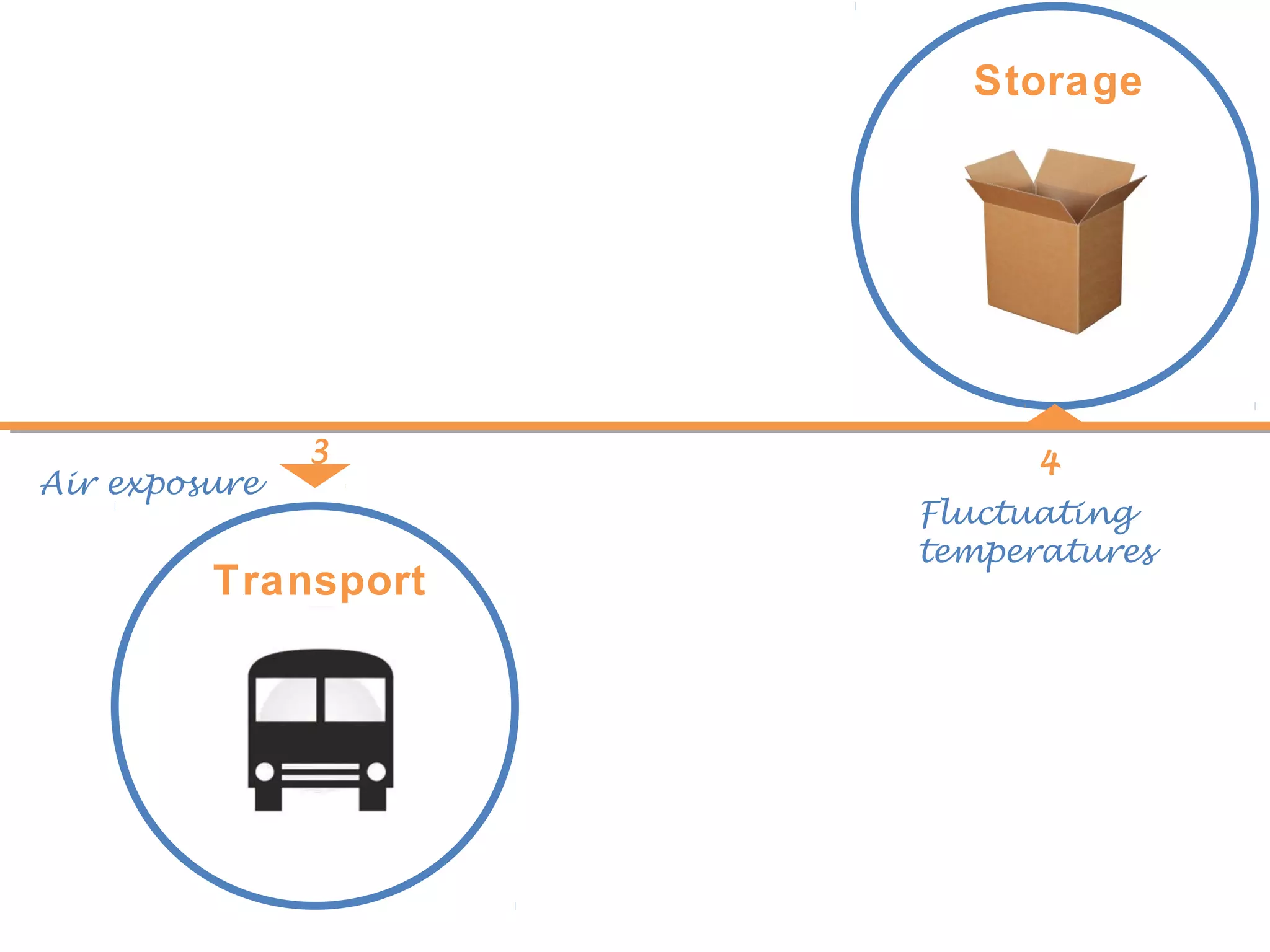
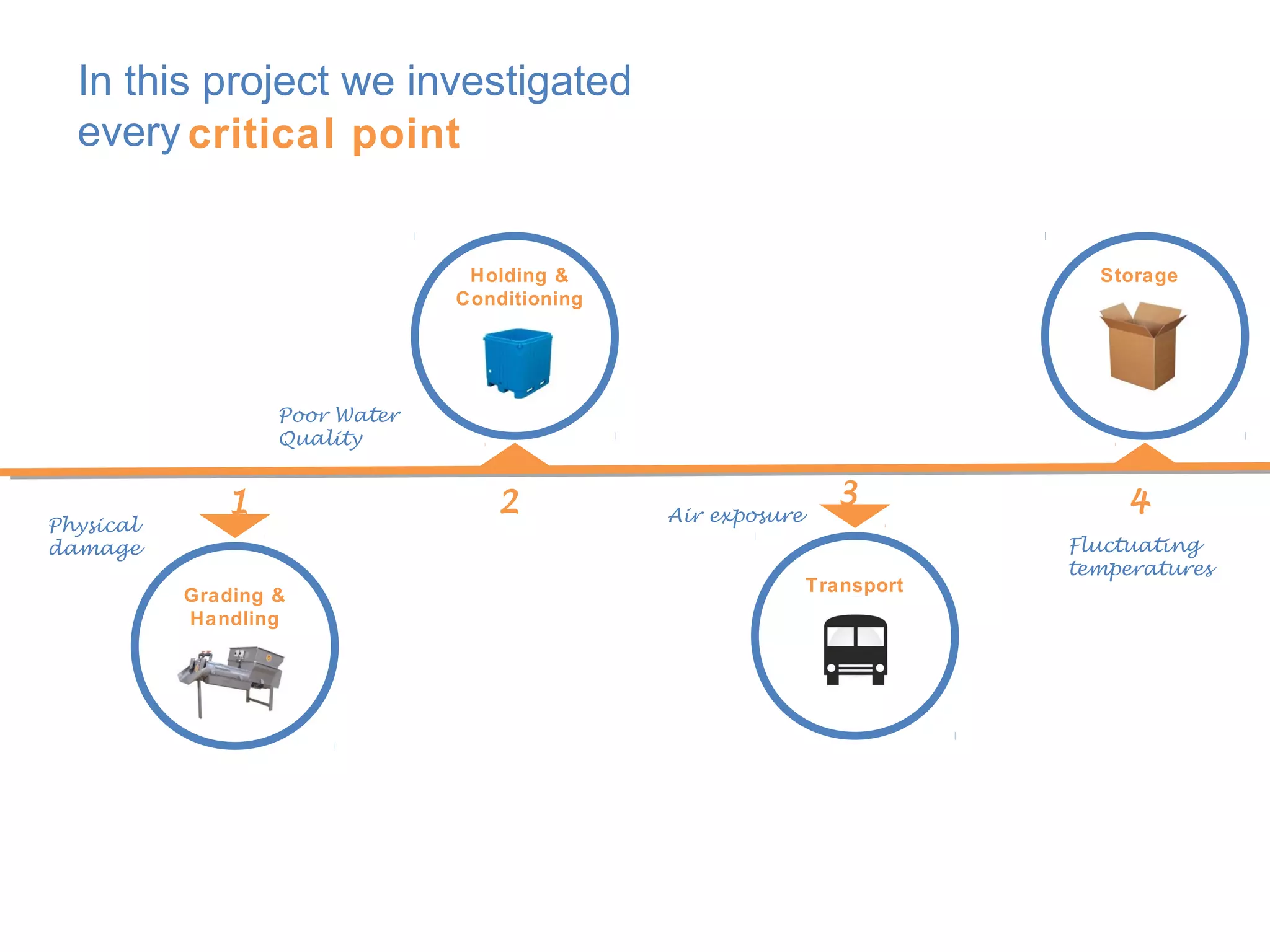
The document discusses the development of best practices and new technologies for grading, handling, transportation, conditioning, and storage of mussels in the European industry. It highlights the challenges faced by mussels during live trade, including physical damage, poor water quality, and temperature fluctuations, which can lead to mortality. The information is part of a collaborative research project supported by the European Commission, aimed at improving the live mussel supply chain.