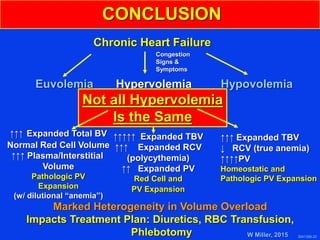
This document discusses the assessment of blood volume in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF), focusing on the measurement of total blood volume (TBV) to guide treatment and management. It highlights the heterogeneity in TBV among patients with volume overload, noting the presence of different red blood cell profiles such as true anemia and dilution-related pseudo-anemia. The findings suggest that quantifying TBV can significantly improve understanding and management strategies for volume overload in CHF.




![3041388-5
Measurement of Total Blood Volume
• Total Blood Volume = Red Cell Mass + Plasma
Volume can be quantitated using a standardized
semi-automated computer-based clinically
available laboratory test.
• Mayo Clinical Nuclear Medicine Lab uses BVA-100
Blood Volume Analyzer (Daxor Corp., NY)
[FDA approved 1998].
Technique: Indicator dilution principle
(concept introduced 1915)
Intravenous administration of low dose (5-30 µCi)
iodinated-131 labeled albumin (10mg).
W Miller, 2015](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1066-160211113658/85/Blood-Volume-Measurement-5-320.jpg)




![3041388-10
Blood Volume Measurement
Values are reported as:
1) Absolute measured volumes in mLs,
(TBV, RBC Mass, and PV)
2) Expected normal reference volumes
(TBV, RBC Mass, and PV)
3) Percent deviation from normal expected
volumes [% excess (+) or deficit (-) from
normal]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1066-160211113658/85/Blood-Volume-Measurement-10-320.jpg)


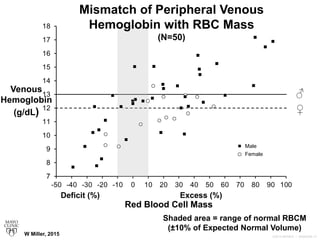
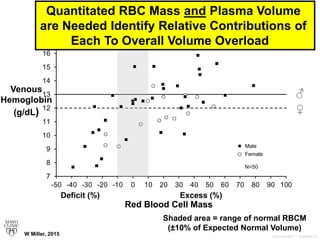
![3047010-16
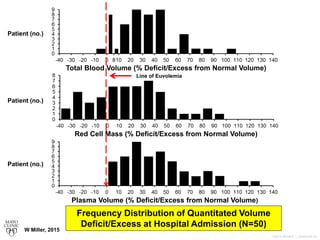
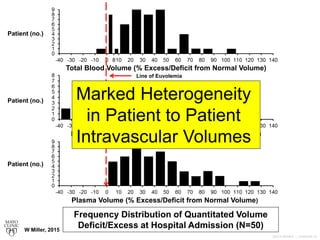
Multiple RBC Profiles Identified
1) True anemia [low RBC mass and low
peripheral venous hemoglobin (Hb) values]
2) Dilution-related pseudo-anemia
secondary to PV expansion (normal RBC
mass but low Hb)
3) RBC polycythemia (excess RBC mass
with low/normal range Hb – pathologic PV
expansion). W Miller, 2015](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1066-160211113658/85/Blood-Volume-Measurement-16-320.jpg)