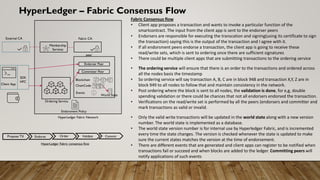
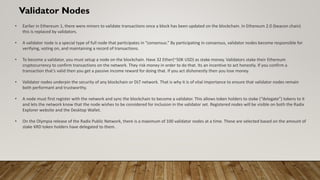
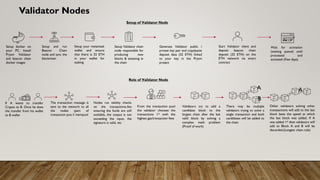
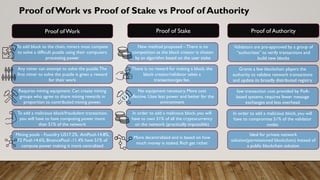
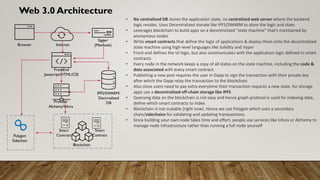
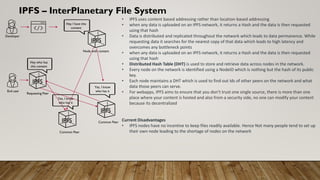
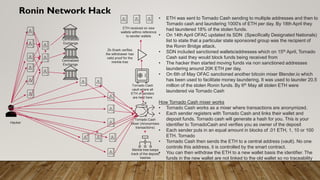
The document provides a comprehensive overview of blockchain technology, discussing its key elements, benefits, mining processes, and various types of blockchains including permissioned and permissionless models. It introduces Hyperledger, a collaborative effort to advance blockchain for businesses, and details the structure and functioning of Hyperledger Fabric, including transaction consensus and smart contracts. Furthermore, it explains layer 2 scaling solutions, sidechains, and the roles of validator nodes in maintaining blockchain security.