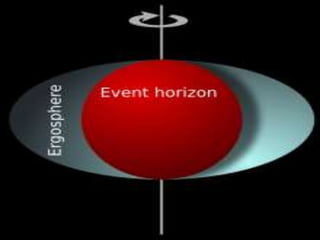
The document discusses black holes and their properties. It describes how John Archibald Wheeler coined the term "black hole" and how Pierre Simon Laplace first proposed the concept in 1795, calculating that an object compressed into a small enough radius would have an escape velocity greater than the speed of light. It provides details on escape velocity and the event horizon of a black hole, beyond which nothing, not even light, can escape. The document classifies different types of black holes by mass and size.