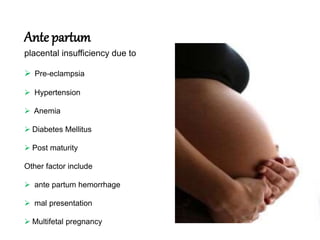
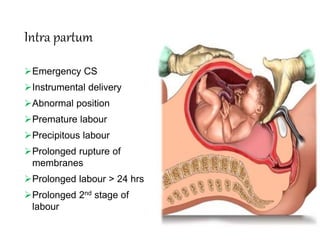
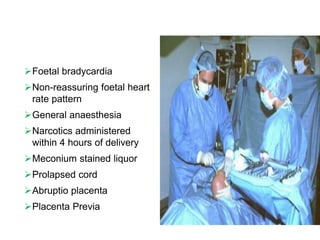
Birth asphyxia is the inability of an infant to establish regular respiration following birth, which can lead to hypoxia, hypoventilation, hypercapnia, and metabolic acidosis. Approximately 90% of cases are caused by placental insufficiency due to factors before or during delivery like pre-eclampsia, prolonged labor, or meconium aspiration. This can result in complications for the newborn like hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, intracranial hemorrhage, or multi-organ dysfunction. Proper antenatal care, monitoring for fetal distress, and resuscitation at birth can help prevent birth asphyxia and its consequences.