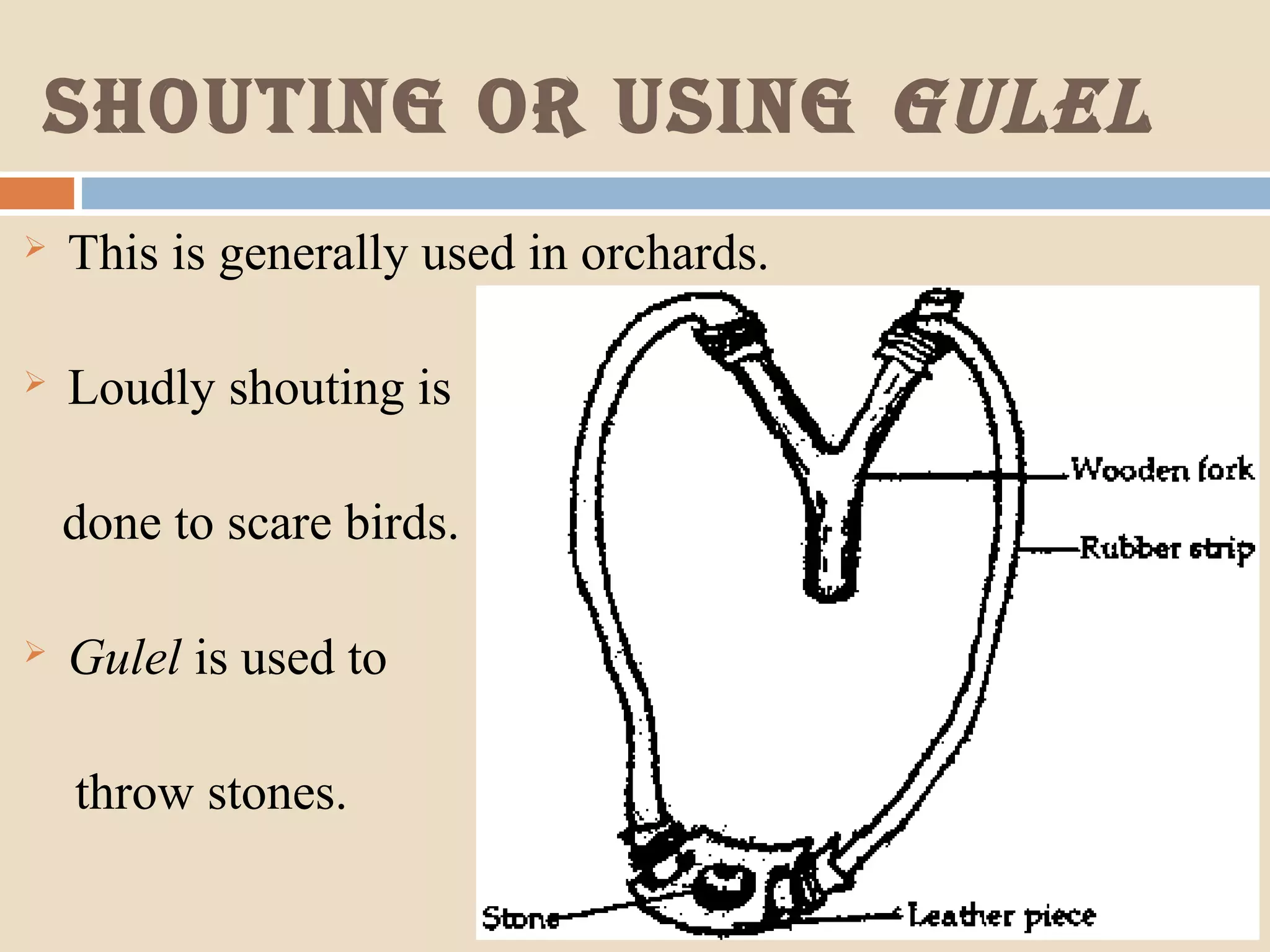
This document discusses bird control techniques used in India. It describes the general characteristics of birds and lists some bird species that are considered agricultural pests. These include house crows, common mynas, and rose-ringed parakeets. The document outlines different control methods like man-operated traps that use nets or baskets, automatic traps like potter traps and house traps, and scaring techniques including scarecrows, drums, balloons and fireworks. It also discusses chemical controls using poisoned bait and notes other deterrents like spikes and nets.