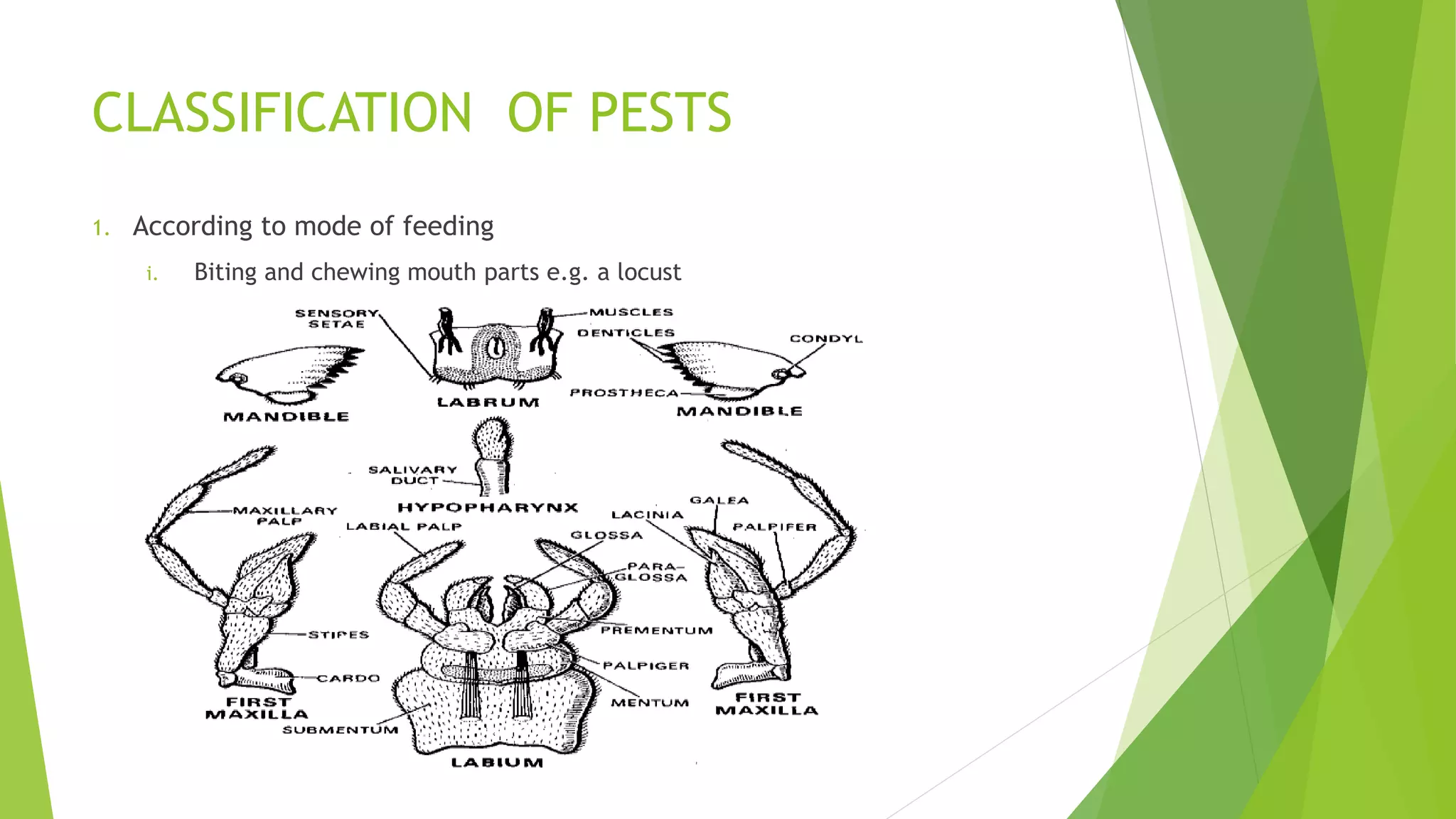
This document discusses crop pests and diseases. It introduces how pests and diseases lower crop yields and quality, raising production costs for farmers. To effectively manage these issues, it is important to understand pest life cycles, damages, and natural enemies as well as disease causes and effects. The document defines crop pests as living organisms that directly or indirectly destroy crops through physical damage or disease transmission. Examples of pests include insects, nematodes, birds, rodents, and mites. Pests negatively impact crops by damaging seeds, roots, leaves, fruits and flowers which can lead to reduced growth, yields and germination. Pests are classified based on feeding method, targeted crops, life stage, crop growth stage attacked, and