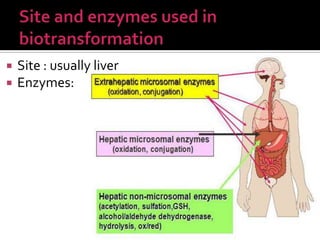
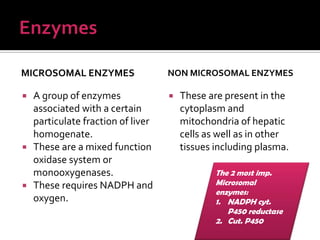
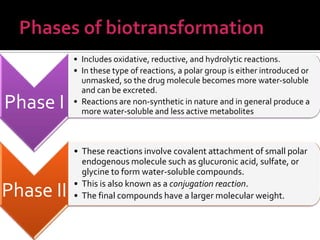
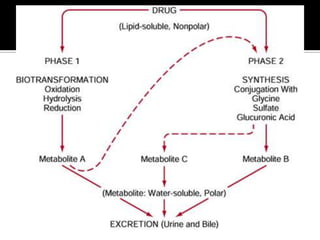
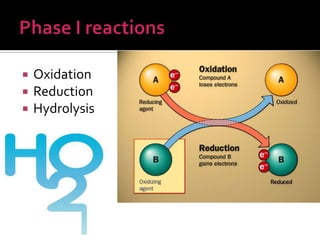
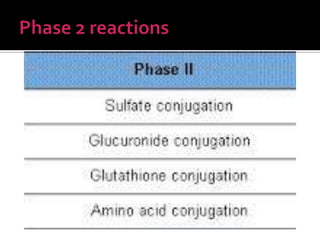
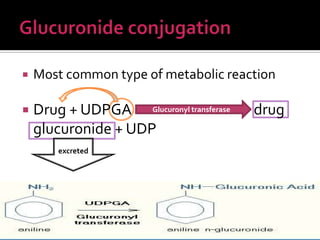
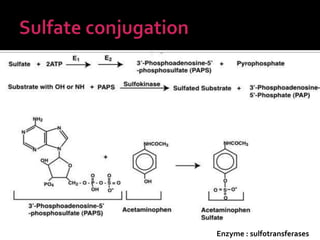
The document discusses drug metabolism and biotransformation in the liver. It notes that the liver uses metabolic enzymes to make nonpolar compounds more water soluble through oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis reactions so they can be excreted in urine. These phase I reactions introduce or expose polar groups. Phase II then involves conjugating the metabolite to glucuronic acid, sulfate, or glycine for excretion. The major sites of these reactions are the microsomal and cytoplasmic enzymes in hepatic cells.