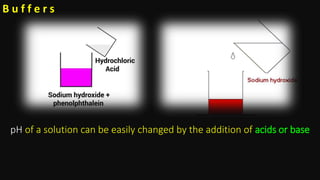
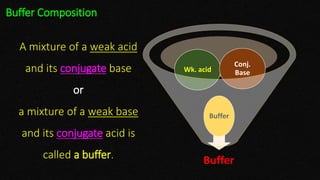
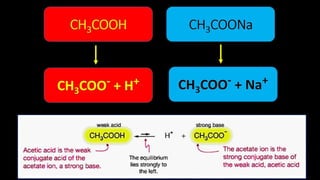
This document discusses biophysical properties related to buffers. It defines buffers as solutions that resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added. Buffers are composed of either a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Acidic buffers contain a weak acid and its salt with a strong base, while basic buffers contain a weak base and its salt with a strong acid. The document also defines conjugate acids and bases, and explains the mechanism of buffer action including buffer capacity, which is a quantitative measure of a buffer's ability to resist pH changes when ions are added.