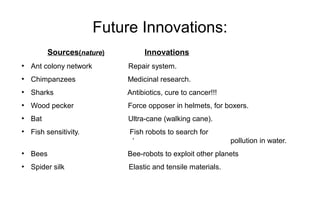
Biomimicry is an innovation method that seeks solutions from nature by emulating biological strategies and patterns. It involves studying challenges like increasing resource efficiency and moving from linear to closed-loop systems, then applying principles from examples like solar cells inspired by leaves and termite mounds providing natural cooling. Biomimicry offers advantages like creating sustainable products and processes while reducing costs and waste. Promoting biomimicry involves research, education, and encouraging its application to solve human problems in fields like transportation, energy, and materials.