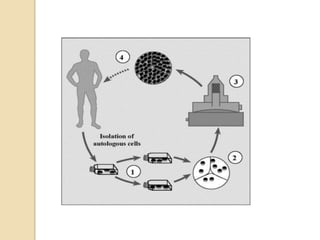
Biomimetics involves imitating nature to address human needs. It deals with developing innovations by studying natural structures, functions, processes and systems. Nature acts as a model. Some key points of biomimetics include mimicking nature through natural or synthetic substitutes, and studying nature's solutions to problems like the lotus plant's water resistance. Biomimetics has applications in areas like energy efficient buildings, bionic vehicles, tissue engineering and more. It is a growing field with potential for developing new materials, technologies and applications.