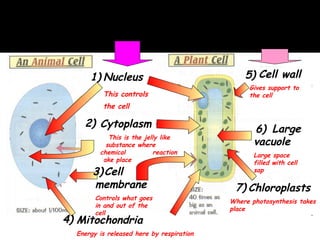
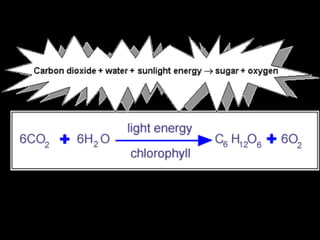
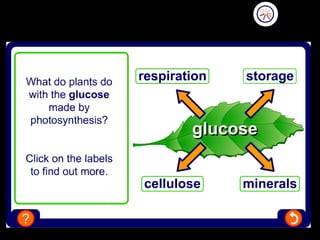
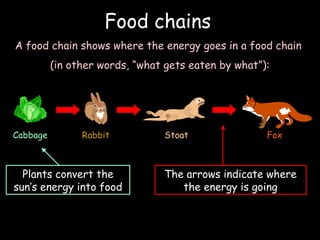
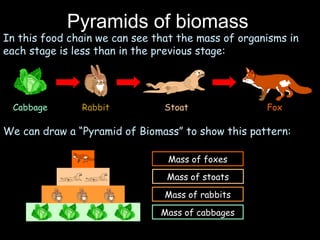
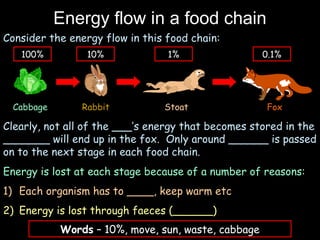
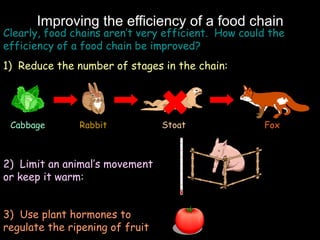
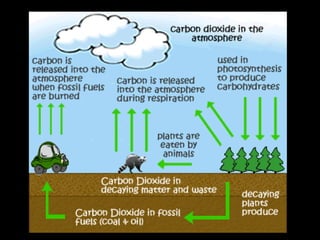
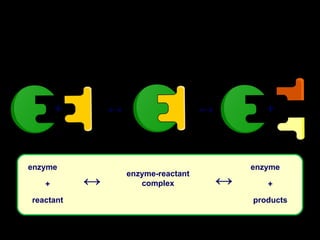
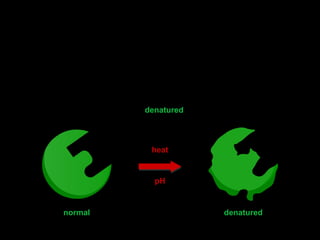
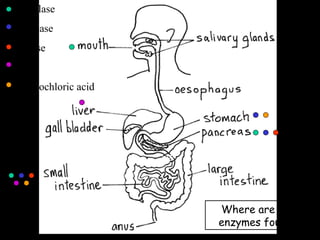
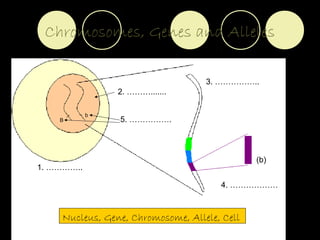
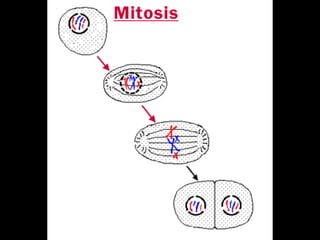
The document outlines key biological concepts such as the differences between plant and animal cells, the processes of diffusion and osmosis, and the role of photosynthesis in energy transfer within food chains. It discusses the efficiency of food production, the carbon cycle, enzyme functionality, and homeostasis. Additionally, it touches on genetics, including inheritance patterns of diseases like Huntington's and cystic fibrosis.