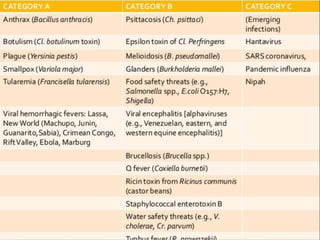
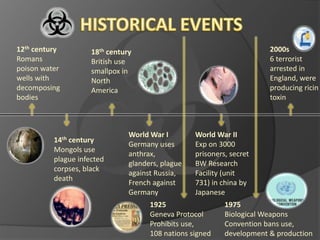
Biological weapons are living organisms or toxins that can be used as weapons to kill or incapacitate humans, animals, or plants. They include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other pathogens. Biological weapons are categorized based on their priority and how easily they can spread. Some historical uses of biological weapons include using plague-infected corpses in the 14th century and smallpox against Native Americans in the 18th century. Modern concerns include the growing availability of gene editing technology that could be misused to create new biological weapons. Defenses against biological weapons focus on detection, protective equipment, vaccines, and rapid medical response.