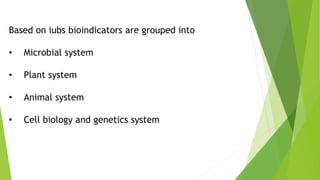
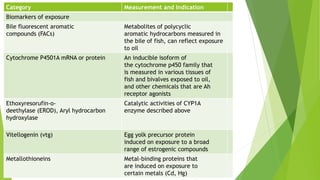
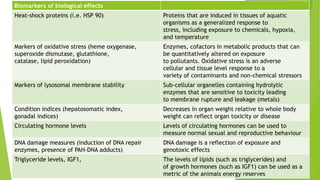
Bioindicators and biomarkers are tools used to monitor environmental contamination. Bioindicators are living organisms that respond to changes in the environment, while biomarkers are measurable substances that indicate exposure to pollutants or disease. Examples of bioindicators include microbes, plants, animals, and cellular/genetic systems. Biomarkers of exposure measure chemicals or metabolites in organisms to determine contamination levels, while biomarkers of effect quantify physiological changes in organisms resulting from exposure. Together, bioindicators and biomarkers can provide early warnings of pollution impacts and be used to assess ecosystem health.